File
advertisement

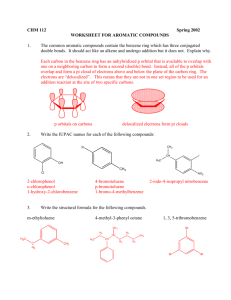
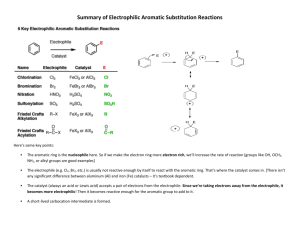
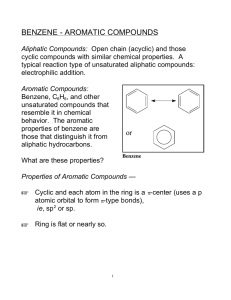
Aromatic compounds Aromatic compounds Aromatic compounds are compounds which contain a benzene ring in their molecules Aromatic hydrocarbons Benzene C6H6 Methylbenzene C7H8 Ethylbenzene C8H10 Benzene Benzene molecule The six carbon-carbon bonds in benzene are identical, intermediate in length between double and single bonds Sigma bonding in benzene Six carbon atoms joined to form a hexagonal planar ring. Each carbon has four valence electrons One of these is used to form a bond with a hydrogen atom. Two other electrons are used to form sigma bonds with the carbon atoms on either side. What the circle means The 6 valence electrons not involved in sigma bonding are shared between the six carbon atoms in the molecule not localised into 3 double bonds For convenience the C and H atoms are not shown Ring in centre indicates a delocalised pi bond Methylbenzene Ethylbenzene Physical properties Physical state: Benzene. methylbenzene and ethylbenzene are liquids Insoluble in water Soluble in non-polar solvents such as cyclohexane Uses Methylbenzene is used as an industrial solvent Range and scope of aromatic chemistry Pharmaceutical compounds, e.g. Morphine Herbicides, e.g. Diuron Detergents, e.g. Sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate Dyes, e.g. Martius Yellow Aromatic acid-base indicators The acid-base indicators phenolphthalein and methyl orange are also aromatic compounds Phenolphthalein Methyl orange Aromatic compounds and cancer Some aromatic compounds are carcinogenic, e.g. Benzene However, not all aromatic compounds are carcinogenic; aspirin is an example