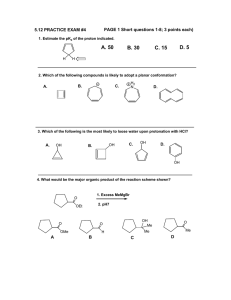
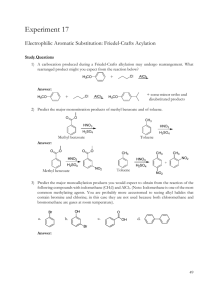
Organic Chemistry II Sample Problems and Solutions: Chap 16. (1
advertisement
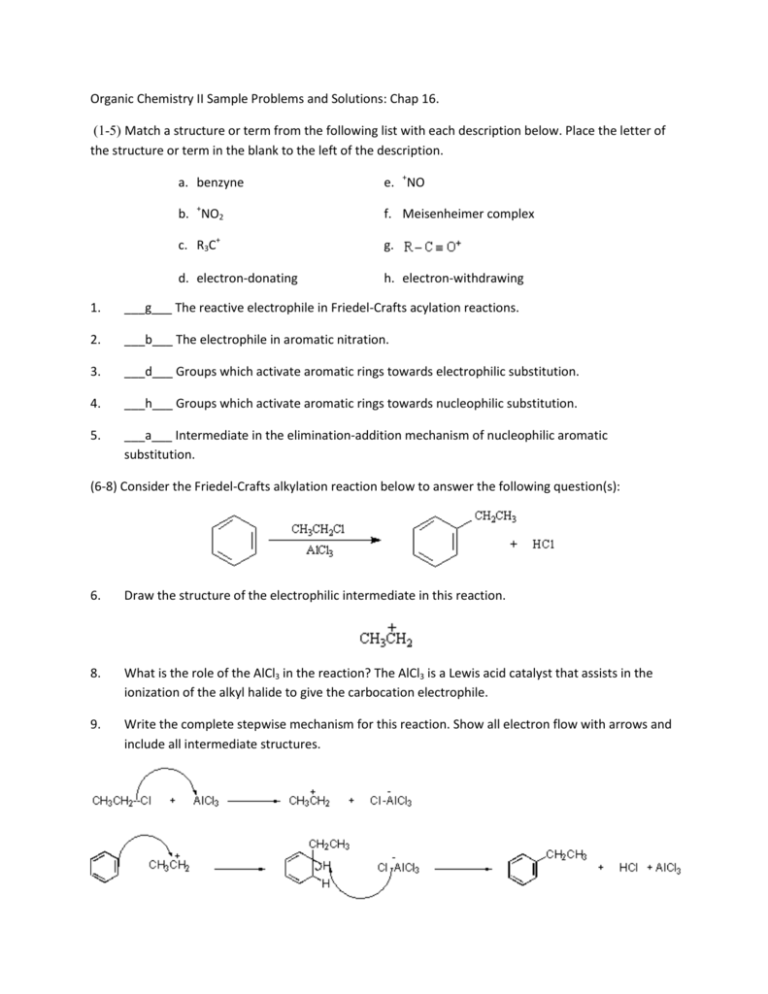
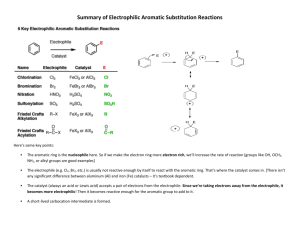
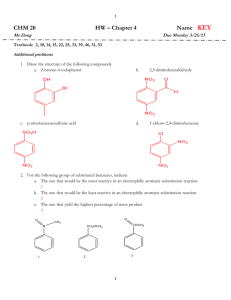
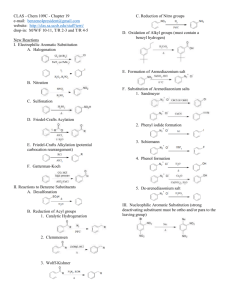
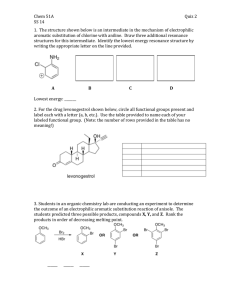
Organic Chemistry II Sample Problems and Solutions: Chap 16. (1-5) Match a structure or term from the following list with each description below. Place the letter of the structure or term in the blank to the left of the description. a. benzyne e. +NO b. +NO2 f. Meisenheimer complex c. R3C+ g. d. electron-donating h. electron-withdrawing 1. ___g___ The reactive electrophile in Friedel-Crafts acylation reactions. 2. ___b___ The electrophile in aromatic nitration. 3. ___d___ Groups which activate aromatic rings towards electrophilic substitution. 4. ___h___ Groups which activate aromatic rings towards nucleophilic substitution. 5. ___a___ Intermediate in the elimination-addition mechanism of nucleophilic aromatic substitution. (6-8) Consider the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction below to answer the following question(s): 6. Draw the structure of the electrophilic intermediate in this reaction. 8. What is the role of the AlCl3 in the reaction? The AlCl3 is a Lewis acid catalyst that assists in the ionization of the alkyl halide to give the carbocation electrophile. 9. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for this reaction. Show all electron flow with arrows and include all intermediate structures. (10-11) Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). 10. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for the formation of the ortho product. Show all intermediate structures and show all electron flow with arrows. 11. Draw resonance structures for the intermediate carbocation that explain the directing effect of the Br. (12-13) Rank the compounds in each group below according to their reactivity toward electrophilic aromatic substitution (most reactive = 1; least reactive = 3). Place the number corresponding to the compounds' relative reactivity in the blank below the compound. 12. 13. 14. At what position, and on what ring, is bromination of phenyl benzoate expected to occur? Explain your answer. Phenylbenzoate: Attack occurs in the activated ring and yields ortho and para bromination. (15-20) Give the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions. If none is predicted, write "N.R." 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. How would you prepare diphenylmethane, (Ph)2CH2, from benzene and an acid chloride? 22. Predict the major product(s) of nitration of the following substrances. Which react faster than benzene, and which slower? (a) Bromobenzene (b)Benzonitrile (c) Benzoic Acid (d) Nitrobenzene (e) Benzenesulfonic acid (f) Methoxybenzene Only methoxybenzene reacts faster than benzene (Please refer to Figure 16.11) 23. What product(s) would you expect to obtain from the following reactions? 24. How would you synthesize thefollowing substraces starting from benzene or phenol? Assume that ortho- and para-substitution products can be separated. (a) o-Bromobenzoic acid (b) p-Methoxytoluene (c) 2,4,6-Trinitrobenzoic acid (d) m-Bromoaniline