NOTES Acids, Bases, pH, and Neutralization
advertisement

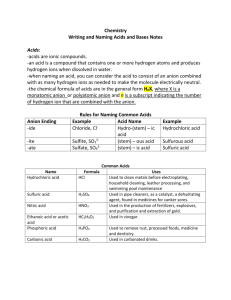
CAPT STRAND II: Chemical Structures and Properties D 12. Explain the chemical composition of acids and bases, and explain the change in pH in neutralization reactions. Definitions: 1. acid: an acid is any compound that produces hydrogen ions (H+1) when the compound is dissolved in water. The (aq) after the compound formula means that the compound is dissolved in water or is in aqueous solution. Examples: hydrogen chloride (HCl) dissolves in water to become hydrochloric acid: HCl(aq); hydrogen nitrate dissolves in water to become nitric acid: HNO3(aq). Other common acids include sulfuric acid: H2SO4(aq); carbonic acid: H2CO3(aq); acetic acid: HC2H3O2(aq); and phosphoric acid: H3PO4(aq). In water, each of the acids forms H+1(aq) and the anion (the negative ion) in aqueous solution: Example: HCl(aq) → H+1(aq) + Cl-1(aq) 2. base: a base is any compound that produces hydroxide ions (OH-1) when the compound is dissolved in water. Most compounds that are bases contain hydroxide ions: sodium hydroxide, NaOH; potassium hydroxide, KOH. Ammonia gas, NH3(g), does not contain hydroxide ions in its chemical formula but produces hydroxide ions when ammonia gas is bubbled into water: NH3(g) + H2O(l) → NH4+1(aq) + OH-1(aq) Ammonia gas doesn’t dissolve in water but rather REACTS with water to form the ammonium ion (NH4+1) and the hydroxide ion (OH-1). Because hydroxide ions are formed in aqueous solution, ammonia gas is a base. 3. pH: a number used to indicate the hydrogen ion concentration, or acidity, of an aqueous solution; the pH value is the negative exponent of the hydrogen ion concentration written in scientific notation: a solution having a hydrogen ion concentration of 1 x 10-4 would have a pH of 4. A pH of 7 is considered to be neutral: the number of H+1 equals the number of OH-1 in solution. If the number of H+1 is greater than the number of OH-1 in solution, the pH of the solution will be less than 7 and the solution is said to be acidic. If the number of H+1 is less than the number of OH-1 in solution, the pH of the solution will be greater than 7 and the solution is said to be basic (or alkaline). 4. neutralization: a chemical reaction in which an acid reacts with a base to produce a salt (contains the positive ion of the base and the negative ion of the acid) dissolved in water; HCl(aq) + KOH(aq) → KCl(aq) + H2O(l) (acid) (salt) (base) (water)