LITERARY PERIODS OF WESTERN CIVILIZATION filled
advertisement

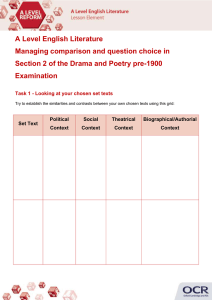
Page 1 LITERARY PERIODS OF WESTERN CIVILIZATION Time frame? Region of origin? What did the period emphasize? Classical Period: Greece 2000 BC – 146 BC Classical Period: Rome 753 BC to 476 AD Greece Rome early forms of democracy (Athens) individual freedoms power of rational thought ideals of beauty and justice development of alphabet drama festivals/competition s athletic competitions (Olympics) trade by sea citizenship and its rights, protection and duties support of sculptors, architects, and potters (statues, great buildings and Military strength and use of the army for building and expansion projects Absolute rule by the paterfamilias who decided all for the family Middle class developed made up of plebians who were civil servants and merchants, tradesmen, etc. Joining the army for 25 years was a way to escape poverty Women could own property, appear in public, and control their own money Invented concrete and perfected the arch Construction of roads all over the empire Public entertainment in Medieval Period Page 2 Major historical and/or social influences? vases) Support of writers (supported by the 9 Muses – goddesses of arts and sciences) Trojan War Independent city states such as Athens, Sparta (major military state), Thebes and Corinth Persian Wars (city states vs. Persians) Pericles rules Athens during Golden Age (461 429 BC) Peloponnesian War (between Sparta and Athens who lost in 404 BC) Alexander the Great defeated Greek city states (334 -323 BC) Romans take over Greek lands (146 – 30 BC) the Circus Maximus and the Colosseum Largest empire of Western Civilization Longest period of peace (Pax Romana) Influence of Latin in the development of Italian, French, and Spanish Spread of Christianity (official religion in 391 AD) Roman law – right to equal treatment under the law, innocent until proven guilty, burden of proof rests with accuser Punic Wars – gained control of the Mediterranean Sea Conquests and rule (46 44 BC) by Julius Caesar Caesar Augustus (Octavius) first emperor who ushered in a golden Page 3 Major writers? Characteristics of the literature? Homer (Iliad and Odyssey) Aesop (fables) Philosophers (Socrates, Plato and Aristotle) Aeschylus (The Persians) Sophocles (Oedipus) Euripides (The Trojan Women) Aristophanes (The Frogs) mythology (stories of gods/goddesses) poetry – epic (Homer) and lyric (Sappho) drama (tragedy and comedy) age of art, architecture, and literature Art forms (frescoes, basrelief and mosaic) Fall of Rome mainly from being overrun by Germanic tribes from the north Virgil (Aeneid) Ovid (Metamorphoses) Plautus (playwright) Terence (playwright) Horace (poet – odes) Cicero (philosophy) Livy (history) Tacitus (history) Imitated the Greek format of epic poetry, lyric poetry, tragedies and comedies Emphasized what it meant to be Roman: duty, discipline, integrity, and dignity. Page 4 Renaissance (Neoclassical) Enlightenment (Age of Reason) Romanticism Time frame? 1800-1840 Region of origin? What did the period emphasize? Europe Major historical and/or social influences? Rejected science and reason and emphasized nature in an idealized form, emotion, and individual experience Political and social change Spread of nationalism – devotion to one’s nation rather than to a ruler Rise and fall of Napoleon Boneparte Successful revolutions leading to the independence of Greece and Belgium Artists focused on the dramatic and imaginative as well as individual feelings and beliefs as subject matter Beethoven – used classical Page 5 forms but to express Romantic ideals such as passion and the dramatic Arthur Schopenhauer – philosopher who believed the world is understood as people perceive it through their senses. William Wordsworth and Samuel Coleridge – Lyrical Ballads Johann Wolfgang von Goethe – Faust Heinrich Heine – The Lorelei Characteristics of all forms: emphasis on emotion, imagination, the individual, and nature. Major writers? Characteristics of the literature? Realism Time frame? 1840-1900 Region of origin? Europe Modernism Contemporary (Post-Modernism) Page 6 What did the period emphasize? Major historical and/or social influences? Scientific discoveries and inventions (light bulb, photography, Darwin’s theory of evolution) Imperialism of major European nations (colonization) Mass production Industrial Revolution Growth of factories and poor working class/child labor Expansion of railroads Attempts at reform: suffrage, freedom of slaves in English and French lands and serfs in Russia Unification of Germany and Italy Free public education (by end of Page 7 Major writers? Characteristics of the literature? period) Discovery by Louis Pasteur that bacteria caused disease. Guy de Maupassant (“Old Milon”) Anton Chekhov (“A Problem”) Charles Dickens (A Tale of Two Cities, Oliver Twist) Leo Tolstoy (Anna Karenina) Henrik Ibsen (A Doll’s House) Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels (The Communist Manifesto) Charles Darwin (The Origin of the Species) Examined real life as it is (rejection of Romanticism and its idealism) Addressed social Page 8 and political issues Emphasis on development of the novel Drama that was realistic in content, staging and language