Notes 1 - Tenafly Public Schools

It’s All Gr k to Me
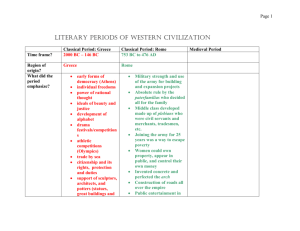
700 B.C. to 145 B.C.
Section 1: City-States
• Polis – “city-state”
– Geographic & political center of Greek Life
– City was in the inner & farms on the outer
Acropolis
– Built on an Acropolis: fortified(military) limestone hill
Agora
• Bottom of hill was the agora: open marketplace
– Political & legal center, shops, water for the women
Running the City-States
• Own government & laws
• Contained 5,000 to 10,000 citizens
• Only males from Greece could vote
– Citzens could vote, own property, and hold gov. positions
• Polis gave them sense of belonging and civic & personal honor
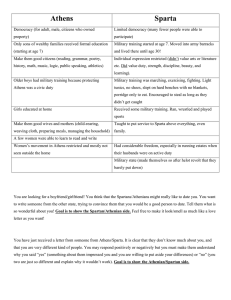
Section 2: Sparta
• Aristocrats (nobles) took over gov.
– Led by 2 Kings who lead the army and conducted religious services
• Aristocrats = only Spartan citizens
Assembly: passed laws & made decisions about war
Ephors: Public affairs and education of the young
Council of Elders: suggested laws & was high court
Helots and Perioeci
• Spartans believed in totalitarianism
– Gov. that uses force & power to rule
• Helots: enslaved people who farmed the land
• Perioeci: merchants and artisans who lived in villages
– Neither enslaved ppl nor citizens
• Helots & Perioeci outnumber aristocrats
• Aristocrats trained for army & war
Spartan Way of Life
• Goal: to be militarily strong
– Did not believe in change b/c it would weaken way of life
• Newborns check to see if they were healthy
• Men
– At 7, sent to military camps to be educated & to train for fighting
• Strict Rules: silence, 1 piece of clothing, slept outdoors, measured weight
– Expected to marry at 20 & Became hoplites
– Left army at 60
• Women
– Had more freedom then other women in Greece
– Had public schooling – read & write
– Owned land
– Loved sports such as wrestling & racing
– Told men to come home w/ their shields or on them
Section 3: Athens
• 750 BC – Set up an oligarchy
• 594 – Solon made plans to change gov.
– Made constitution: set of principles & rules for ruling
• Broke power of rich, established an assembly, offered citizenship, and trade
• 508 – Spartans overthrown by Cleisthenes
– Created 1 st democratic society
Democratic Constitution
• Freedom of speech
• Opened assembly
• Council of Five Hundred
– Handled daily business
– Chosen by lot
• Required to educate sons
• At 18, took an oath of citizenship
Daily Life in Athens
• Young children would read Aesop’s fables
• Youth were to develop artistic and intellectual talents
• Men
– Boys from wealthy families would go to school
– Age 12: Phys. Ed. was most important
– 18 to 20: went to military training school
– Clothing: wool tunics or himation
– Hair: Short (young) & Long (old)
– Did the shopping
• Women
– Only did physical activities at festivals
– No schooling
– Clothing: long wool or linen tunics
– Hair: Long but pulled up in bun or pony tail
– Marriages were arranged
– Confined to certain part of the house
– Jobs: cook, weave, raise children
– No social life w/ husband
• Homes
– Large, airy luxurious buildings made of mud brick
Persian Wars
• 545 B.C. – Persia conquered Ionia
• Ionians w/help from mainland Greece revolted against the
Persians
– Persians won
• Darius (Persian King) wanted to continue to punish the Greeks
Battle of Marathon
• 490 – Darius & Persians sailed to Marathon
– They then decided to sail to Athens
• Athenians decided to surprise attack the Persians
– Ran down the hills of Marathon
– Athenians defeated the Persians
• Afraid that the Persians would still come to Athens after, Athenians sent Pheidippides to tell them: “Nike”
Battle of Thermopylae
• Athenians triremes built
– Made strong navy
• Xerxes (New King of Persia) brings his large army back to Northern Greece
• Sparta & Athens teamed together
• Met the Persians at the narrow pass
• For the first few days, the Greeks esp. the
Spartans held off the Persians
– While doing so, people of Athens were told to flee
• A Greek traitor helped the Persians through the mountain pass
– Persian were able to surround the Greeks
– 300 Spartans and 700 Greeks stayed to fight to the bitter end
• 1 Spartan survived the war
• Athens burned
Battle of Salamis
• Persians moved toward Athens
• Greek army went to Salamis & waited for
Persians
– Themistocles tricked the Persians
• Caused Persians to come through narrow pass
– Difficult: Too many ships & large ships
• Greeks destroyed Persians
Battle of Plataea
• Xerxes went back to Persia
• ½ his army stayed in N. Greece
– They decided to go South
• Greeks crushed the Persians
Delian League & Athenian Empire
•Delian League: protective group head-quarted on the island of Delos
• Most city-states joined – Sparta did not
Effects of the
Delian League in Athens
• Controlled ships
• Led gov.’s of other city-states
• Gained more power over others
• Rebuilt palaces & temples
in other city-states
• Had a common navy
• Had to use Athenian money
• Controlled by Athens
• Disliked the Athenian power
Peloponnesian War
• 433 BC – Athens aligned themselves with Corinth a
Sparta ally
– Sparta accused Athens of aggression & threatened war
• 431 – War starts when Sparta allies attack Athens’ ally
• 1 st Phase – 10 years of fighting
• 2 nd Phase – Nicias – a truce of 6 years
• 3 rd Phase – Athens lost attack on Sicily
• Ended with a crushing defeat of Athens by Sparta
• Sparta set up a King in Athens
– Athens was never again as strong even though they would revolt and set up a democracy once again
Decline of City-States
1. Lost sense of community
2. Money issues
3. Harsh rule by the Spartans and then
Thebes