Defining Acids and Bases Arrhenius Definition: acid – any
Defining Acids and Bases
Arrhenius Definition: acid – any substance that can produce __________ ions in aqueous solution base – any substance that can produce __________ ions in aqueous solution
Bronsted-Lowry Definition: acid – a substance that _________________ a proton, or hydrogen ion, to another substance.
What is formed from the acid is called the conjugate base.
base – a substance that __________ a proton, or hydrogen ion, from another substance.
What is formed from the base is called the conjugate acid
For the following reactions, circle the proton that is being transferred and draw an arrow to show its transfer. Underline the final location of that proton on the product side. Then identify the acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base.
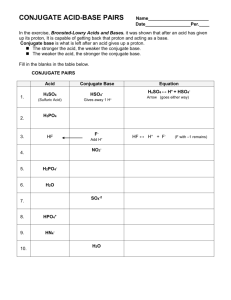
1.
HC
2
H
3
O
2
+ H
2
O ⇔ H
3
O + + C
2
H
3
O
2
-
2.
SO
3
2-
3.
NH
3
4.
NH
4
+
5.
SO
4
-2
+
+
+
+
HCl
HNO
2
CO
3
2-
HClO
⇔
⇔
⇔
⇔
HSO
3
-
NH
4
+
NH
3
HSO
4
-
+
+
+
+
Cl -
NO
2
-
HCO
3
-
ClO -
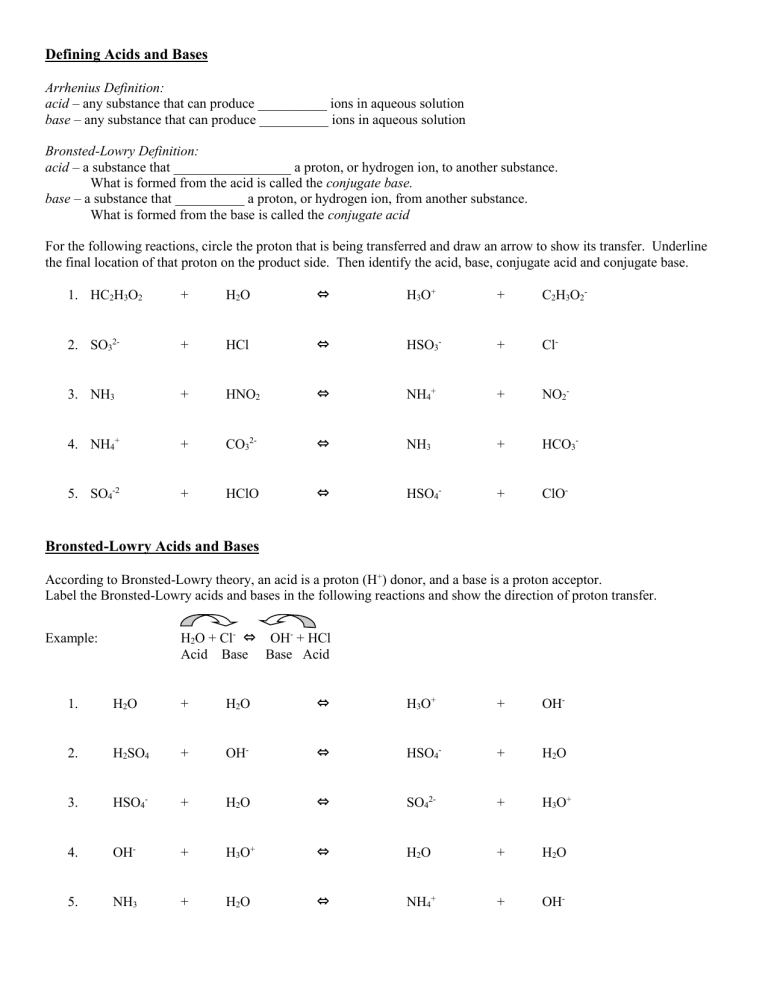
Bronsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
According to Bronsted-Lowry theory, an acid is a proton (H + ) donor, and a base is a proton acceptor.
Label the Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases in the following reactions and show the direction of proton transfer.
Example:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
H
2
O
OH -
NH
3
H
2
O + Cl ⇔ OH + HCl
Acid Base Base Acid
+
H
2
SO
4
+
HSO
4
+
+
+
H
2
O
OH -
H
2
O
H
3
O +
H
2
O
⇔
⇔
⇔
⇔
⇔
H
3
O +
HSO
4
-
SO
4
2-
H
2
O
NH
4
+
+
+
+
+
+
OH -
H
2
O
H
3
O +
H
2
O
OH -