Lesson Planning Form
advertisement

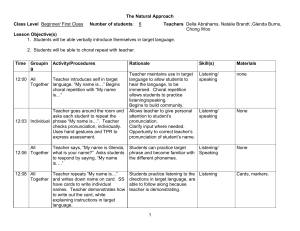
The Natural Approach Class Level Beginner/ First Class Number of students: 6 Teachers Della Abrahams, Natalie Brandt ,Glenda Burns, Chong Woo Lesson Objective(s) 1. Students will be able verbally introduce themselves in target language. 2. Students will be able to choral repeat with teacher. Time 12:00 12:03 12:06 12:08 Grouping Activity/Procedures Rationale Teacher maintains use in target All Teacher introduces self in target language to allow students to hear Together language. “My name is…” Begins choral the language, to be immersed. repetition with “My name is…” Choral repetition allows students to practice listening/speaking. Begins to build community. Teacher goes around the room and asks Allows teacher to give personal each student to repeat the phrase “My attention to student’s pronunciation. Individual name is…”. Teacher checks Clarify input where needed. pronunciation, individually. Uses hand Opportunity to correct teacher’s gestures and TPR to express assessment. pronunciation of student’s name. Skill(s) Listening/ speaking Materials none Listening/ speaking None All Teacher says, “My name is Glenda, what Students can practice target phrase Together is your name?” Asks students to respond and become familiar with the by saying, “My name is….” different phonemes. Listening/ Speaking None All Teacher repeats “My name is…” and Together writes down name on card. SS have cards to write individual names. Teacher demonstrates how to write out the card, while explaining instructions in target language. Students practice listening to the Listening directions in target language, are able to follow along because teacher is demonstrating. 1 Cards, markers. The Natural Approach was designed by Tracy Terrell and Stephen Krashen. It was published in 1977. Krashen and Terrell believed the following about language acquisition: Language: Language is an unconscious process. Use language meaningfully. Learning: The focus is on implicit learning. Grammar rules are not taught, there is no explanation of syntax or structure. The goal is to achieve communicative competence in target language and target culture. Comprehension precedes production; there will be a silent period. Benefits are found by listening to sounds, vocabulary and structures in target language. Students are not expected to immediately produce in target language, assessments can be observed through appropriate actions. Understanding can be found through actions as well as verbal responses. Teaching: A classroom should be safe, not intimidating and have a low anxiety level. As teachers, we have to provide understandable, comprehensible input in a safe and inviting environment. “The goal [of the Natural Approach] is that the members of the group become genuinely interested in each other’s opinions, feelings, and interested and feel comfortable expressing themselves on the topics of discussion in class.” -The Natural Approach to Language Teaching: An Update T.D. Terrell (1982) *Students that are beginners are best served with this method. *This method would not be appropriate in an intermediate setting or for a grammar specific classroom. Rather, this method is appropriate for an entry-level ESL or foreign language classroom so that the students can be exposed to as much target language as possible. References Kumaravadivelu, B. (2003). Beyond methods: Macrostrategies for language teaching. New Haven and London: Yale University Press. Kiymazarslan,V. (1995). The natural approach: what is it? Retrieved from http://naturalway.awardspace.com/articles/article002.htm Romeo, K. (N.D.). Krashen and Terrell’s “natural approach”. Retrieved from http://www.stanford.edu/~kenro/LAU/ICLangLit/NaturalApproach.htm Terrell, T.D. (1977). A natural approach to second language acquisition and learning. The Modern Language Journal, 61(7), 325-337. Terrell, T.D. (1982). The natural approach to language teaching: an update. The Modern Language Journal, 66(2), 121-132 .Ur, P. (1991). A course in language teaching: Practice and theory. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 2