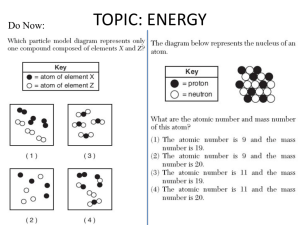
What is energy?

Energy
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat.
The law of conservation of energy states that energy can be created and destroyed.
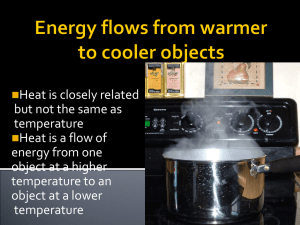
Heat is the flow of energy from a warmer object to a cooler object.
Chemical potential energy is energy stored in a substance because of its composition.
A calorie is the SI unit of heat and energy.
Cooks the food we eat
Propels vehicles that transport us
Allows photosynthesis to occur to start the food chain
Energy from burning fuels heats or cools the classroom
Allows you to think and write
Cells are factories that run on energy derived from the food we eat
The ability to do work or produce heat
Potential energy vs. kinetic energy – 2 basic forms
Potential energy – energy of position
Kinetic energy – energy of motion
Ex. Roller coaster
Contain both kinetic and potential energy
Kinetic energy – directly related to constant random motion of particles – prop. To temp.
Potential energy depends on composition – chemical bonds, arrangement of atoms, etc.
Energy can be neither created nor destroyed, it can only be converted from one form to another.
1 st Law of thermo.
q
Energy flowing from a warmer object to a
cooler object.
As energy flows, change in temperature
Calorie – energy needed to raise one gram of water one º C.
When your body breaks down sugars and fats to form carbon dioxide and water, these reactions generate heat energy that can be measured in calories.
SI unit is the joule which equals 0.2390 calories.
1J= 0.2390 calories
1cal=4.184 Joules.
kcal=Calories (bigC)= 1 nutritional calorie
Pg. 492 practice problems
The specific heat of any substance is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of that substance by one degree Celsius.
So, for water, that’s 4.184J/g
·
º C
Cp = q .
m x ∆T
Cp = specific heat q = heat absorbed or released by substance m= mass
∆T = change in temperature
Pg. 495 #’s 4-6
The relationship between heat and specific heat… q=c ·m·ΔT q total
=q water
+ q material or c water
·m water
·ΔT water
Table pg. 492
= c material
·m material
·ΔT material
(Sounds like…?)
Is an insulated device to measure the change in heat during a chemical reaction.