BIOMOLECULES
advertisement

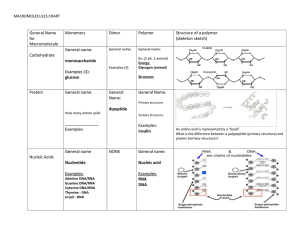
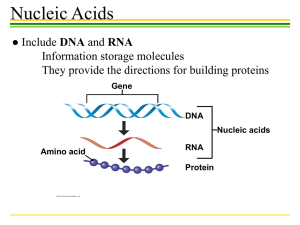
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY All living things contain the element Carbon (C). Carbon is unique because …………… 1. it has 4 valence electrons 2. it can form single, double & triple covalent bonds with other elements 3. it can form chains or rings Macromolecules are “giant molecules” formed by many smaller molecules. Small molecules that join to make larger molecules are called “monomers.” Monomers join together to form “polymers.” This process is called “Polymerization.” There are 4 major macromolecule groups found in living things: * Carbohydrates * Lipids * Proteins * Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates: Used as the main source of energy by all living things. -Contain the elements C, H and O in a 1:2:1 ratio (CHO) _ Broken down as sugar for cells to carry out cellular activities (i.e. cellular respiration, photosynthesis) _ Monomers or building blocks are called monosaccharides (simple sugars). Glucose, galactose and fructose are all examples of a monosaccharide. When 3 or more monosaccharides combine, they form what is known as a Polysaccharide (complex sugars). “Poly” means many. Examples of polysaccharides: bread, rice, pasta, potatoes. Most animals store excess sugar as glycogen to be used when needed by muscles (contraction) or low blood sugar. Plants store excess sugar as starch. Cellulose is another important polysaccharide found in plants which gives plants rigidity and flexibility. Lipids (fats, waxes, oils, steroids): Used to store energy -Also contain elements C, H & O but not in a 1:2:1 ratio. (CHO) -Insoluble as they do not dissolve in water. - Building blocks are a glycerol molecule combined with fatty acid tails making long chains. 2 types of lipids: Saturated & Unsaturated Carbon to carbon double bond Some lipids are important parts of biological membranes (phospholipids contain hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails) and waterproof coverings such as the plasma membrane of the cell and the cuticle of plants. Proteins: Used to form bones and muscles, transport substances into or out of cells, help fight diseases, control rate of chemical reactions and regulate cell processes. -Contain elements C, H, O & Nitrogen (CHON) -Monomers or building blocks are called amino acids. The general structure of an amino acid is an amino group (-NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (-COOH) on the other end. The portion of each amino acid that is different is the side chain called The R Group. Different Types of Amino Acids: Food Examples of Proteins: Nucleic Acids: transmit or store genetic or hereditary information. -Contain elements, C, H, O, N and Phosphorus (CHONP) 2 types: DNA and RNA Monomers or building blocks are called Nucleotides. A Nucleotide contains a 5 carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogen base. 2 Types of Nucleic Acid: DNA or RNA Double stranded Genetic code Single stranded Copies genetic code