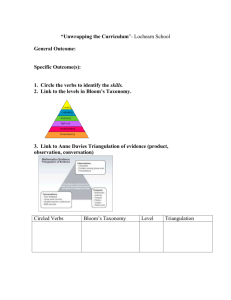
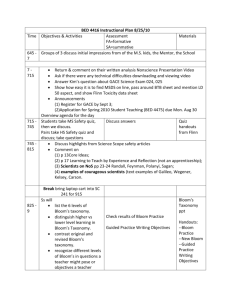
workshop 3 new adition
advertisement

ENTRY LEVEL CURRICULUM PROGRAM 1 2nd .–7th. October 2011 1 Welcome ENTRY LEVELCURRICULUM PROGRAM 1 Week2 (10 Min.) 2 AGENDA 10:00–10:10 AM Welcome 10:10–10:30 AM Starter: Real Science “Full to Overflowing “ 10:30–11:45 Bloom’s Taxonomy AM 11:45-12:00 PM 12:00-12:15 PM 12:15-1:15 PM 1: 15-1:25 PM 1:25-1:30 3 PM Activity 2 Prayer Break Unpacking the Curriculum Standards Summary Survey Full to Over Flowing: (20 Min.) How do you make sure your eye drops are the same size? Demonstration on eye drops 4 Predict: How many drops of water can you place on a coin? How many mL of water can you place on the coin? 5 Was your prediction correct? What standard(s) does this activity address? 6 CS: G12, G7 (1.3 & 1.4) 7 Bloom’s Taxonomy 8 Benjamin Bloom )1999-1913( •Educational Professor at Chicago University •Classified educational learning •There are increasingly subtle and complex educational levels to master as we develop cognitively 9 Bloom’s Taxonomy- Overview: • Taxonomy for categorizing level of learning. •There are six levels of knowledge according to Benjamin Bloom et al. •The levels are thought to build on one another. •The higher levels of learning have to do with brilliance and getting well educated. 10 11 Bloom’s Taxonomy- Knowledge • Observation and recall of information • Knowledge of dates, events, places • Knowledge of major ideas • Mastery of subject matter • Question Cues when evaluating: list, define, tell, describe, identify, show, label, collect, examine, tabulate, quote, name, who, when, where, etc. 12 Bloom’s Taxonomy- Understanding • Understanding information • Grasp meaning • Translate knowledge into new context • Interpret facts, compare, contrast • Order, group, infer causes • Predict consequences • Question Cues when evaluating: summarize, describe, interpret, contrast, predict, associate, distinguish, estimate, differentiate, discuss, extend 13 Bloom’s Taxonomy- Application • Use information • Use methods, concepts, theories in new situations • Solve problems using required skills or knowledge • Question Cues when evaluating: apply, demonstrate, calculate, complete, illustrate, show, solve, examine, modify, relate, change, classify, experiment, discover 14 Bloom’s Taxonomy- Analysis • Seeing patterns • Organization of parts • Recognition of hidden meanings • Identification of components • Question Cues when evaluating: analyze, separate, order, explain, connect, classify, arrange, divide, compare, select, explain, infer 15 Bloom’s Taxonomy- Synthesis • Use old ideas to create new ones • Generalize from given facts • Relate knowledge from several areas • Predict, draw conclusions • Question Cues when evaluating: combine, integrate, modify, rearrange, substitute, plan, create, design, invent, what if, compose, formulate, prepare, generalize, rewrite 16 Bloom’s Taxonomy- Evaluation • Compare and discriminate between ideas • Assess value of theories, presentations • Make choices based on reasoned argument • Verify value of evidence • Recognize subjectivity • Question Cues when evaluating: assess, decide, rank, grade, test, measure, recommend, convince, select, judge, explain, discriminate, support, conclude, compare, summarize 17 Activity -118 Activity -2Design Bloom’s taxonomy tree 19 Unpacking the Curriculum Standards According Bloom Taxonomy 20 Analyzing Standards Standards can be classified as Knowledge standards Application standards Product standards Standards can be deconstructed into parts. Standards should be interpreted in terms of what students do. 21 Activity: (5 Min.) Know the properties of metals and explain how these properties make them useful. How many parts? (properties) (uses) Know the properties of metals and explain how these properties make them useful. Knowledge Application Product How do students demonstrate understanding? Answer a direct question. Fill out a chart. Identify uses. Produce a report. 22 Activity -3Analyzing these Standards? 23 Biology standards 11A .9.5 -Describe the similarities and differences between nervous and hormonal control systems in mammals. 11A.10.2 -Differentiate between tidal volume and vital capacity of the lungs. 12A.7.2-Know the composition of the blood and explain the roles of red cells, plasma, haemoglobin and carbonic anhydrase in the transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide. 12A.9.2 Using water potential terminology, explain the functioning of the kidney in osmoregulation and in controlling metabolic wastes. 24 Chemistry standards 10A .22.1 Understand how carbon and nitrogen are recycled in nature and recognise that many of our activities interfere with these processes. 11A.27.5. Define power as the rate of doing work or converting energy and solve problems using P = W/ t. 12A 21.6.Calculate the standard entropy change for a reaction using absolute entropy values and recognise and explain the impact of changes of state on this value. 25 Physics' standards 10A.26.2 Derive, from the definitions of velocity and acceleration, equations that represent uniformly accelerated motion in a straight line and use them to solve problems relating to the motion of objects under uniform acceleration 11A.30.1 Demonstrate an understanding of the construction of capacitors and their use in electrical circuits. 12A26.5.Apply the kinetic particle model to an ideal gas and explain, in terms of molecular size and intermolecular forces, how the behaviour of real gases deviates from the ideal model at high pressures and low temperatures. 26 Write journal Full the Evaluation sheet 27 See you next Monday 28 29