Chapter 3: Cells

CELLS
Structure and Functions of Human Cells
Human cells
Basic unit of structure & function
200 different cell types
3 main parts:
1.
Plasma membrane
2.
3.
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Cell diversity
Cell Structure
Cytoplasm
Between plasma membrane & nucleus
Three elements:
Cytosol : fluid
Eg. water, proteins, salts, sugars
Organelles : specific functions
Inclusions : chemical substances that vary depending on cell type
Eg. glycogen (liver), lipid droplets (fat cells), melanin
(skin & hair)
Organelles
“ little organs ”
Specialized compartments specific functions
Membranous = membrane-bound
Mitochondria, peroxisomes, lysosomes, ER, Golgi apparatus
Nonmembranous = no membrane
cytoskeleton, centrioles, ribosomes
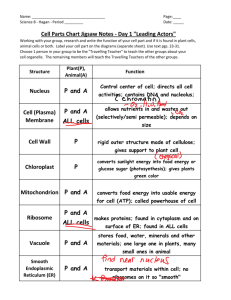
Cell Organelles
Ribosomes: Make proteins.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER): Make proteins.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER): Make lipids.
Golgi Apparatus: Molecules are packaged and transported.
Mitochondria: Power center. (ATP)
Lysosomes: Contain digestive enzymes.
Microfilaments and microtubules: cell structure and transport (cytoskeleton)
Cilia and flagella: Increase surface to volume ratio for absorption and helps with locomotion.
Plasma membrane
Function: enclose cell contents, control exchange of substances with environment, cell communication
Made of:
Lipid bilayer-Phospholipids
Cholesterol
Glycolipids
Proteins
Fluid mosaic model
Proteins float in fluid lipid bilayer
Membrane lipids:
1.
Phospholipid:
Polar/ hydrophilic (water-loving) “head”
Nonpolar/ hydrophobic (water-fearing) “tail”
Lipid bilayer
Semipermeable Membrane
Very small molecules (like water) can flow freely through the membrane.
Large molecules can only get in or out by using a protein “door”.
Very small molecules that are polar must also use a protein.
2 Types of Transport
Passive Transport: No energy required. With the concentration gradient.
Active Transport: Energy being used to move something into the cell.
Against the gradient.
Passive Transport
Diffusion: Molecules moving from an area of high concentration to low concentration .
Osmosis: The diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane.
Osmosis can damage cells…
Hypertonic
(Water leaves cell.)
Isotonic
(Balanced.)
Hypotonic
(Water enters cell.)
Very Hypotonic
(Water enters, cell bursts.)
Diffusion
Solutes moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Diffusion
Solutes moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Diffusion
Solutes moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Diffusion
Solutes moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Diffusion
Solutes moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Diffusion, cont.
Small molecules diffuse faster than large molecules.
Increasing the temperature causes diffusion to occur more quickly.
Facilitated Diffusion
Molecules moving across the membrane with the assistance of a carrier protein but requiring no energy.
This is passive transport because it requires no energy!
2 Types of Transport
Passive Transport: No energy required. With the concentration gradient.
Active Transport: Energy being used to move something into the cell. Against the gradient.
Active Transport
Moving solutes against a concentration gradient.
Active Transport, cont.
Carrier Proteins: Proteins in the membrane of the cell that bring out or take out large molecules.
Bulk Movement: Transporting large molecules (such as polysaccharides or proteins) across the cell membrane.
Bulk Movement
Exocytosis: Transporting out of the cell.
Endocytosis: Transporting into the cell.
Pinocytosis: Cell drinking.
Phagocytosis: Cell eating.
Endomembrane system
System of organelles that work to
1.
2.
Produce, store, export biological molecules
Degrade harmful substances
Nuclear envelope, rough ER, smooth ER, Golgi apparatus, secretory vesicles, lysosomes
Endomembrane system
Nucleus
Nucleus
Control center contains DNA
Most cells have only 1 nucleus
Multinucleate : many nuclei (muscle, some liver cells)
Anucleate : no nucleus (mature RBC)
Three main structures:
1.
2.
3.
Nuclear envelope
Nucleoli
Chromatin
Multinucleated Muscle Cells
Multinucleated Liver Cells
Anucleated Red Blood
Cells
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane barrier surrounds nucleus
Outer part continuous with Rough ER
Nuclear pores : control entry/exit of molecules
Nucleolus (nucleoli)
Dark-staining bodies in nucleus
1-2 per cell
Site where ribosomes are made
chromatin
Chromatin = DNA + Proteins
Nucleosome = DNA wrapped around 8 histone proteins
Histones allow for compact and orderly packing of long
DNA molecules
During cell division, chromatin condenses to form chromosomes .
replication
Make identical copies of DNA before a cell divides
Mitosis
Part of cell division
Replicated DNA divided into 2 daughter cells
Usually lasts about an hour
Interphase prophase metaphase anaphase telophase & cytokinesis
DNA = blueprint for protein synthesis
Gene : segment of DNA that codes for 1 polypeptide
Exon : part of DNA that codes for polypeptides
Intron : part of DNA that is noncoding (not “junk”!)
Information Flow: DNA RNA proteins
Protein synthesis
Transcription : RNA formed from DNA
Occurs in nucleus
Types: mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
Translation : protein synthesis
polypeptide formed from mRNA
Occurs in cytoplasm
By ribosomes