Combining Sentences and Clauses Coordinating Conjunctions
advertisement
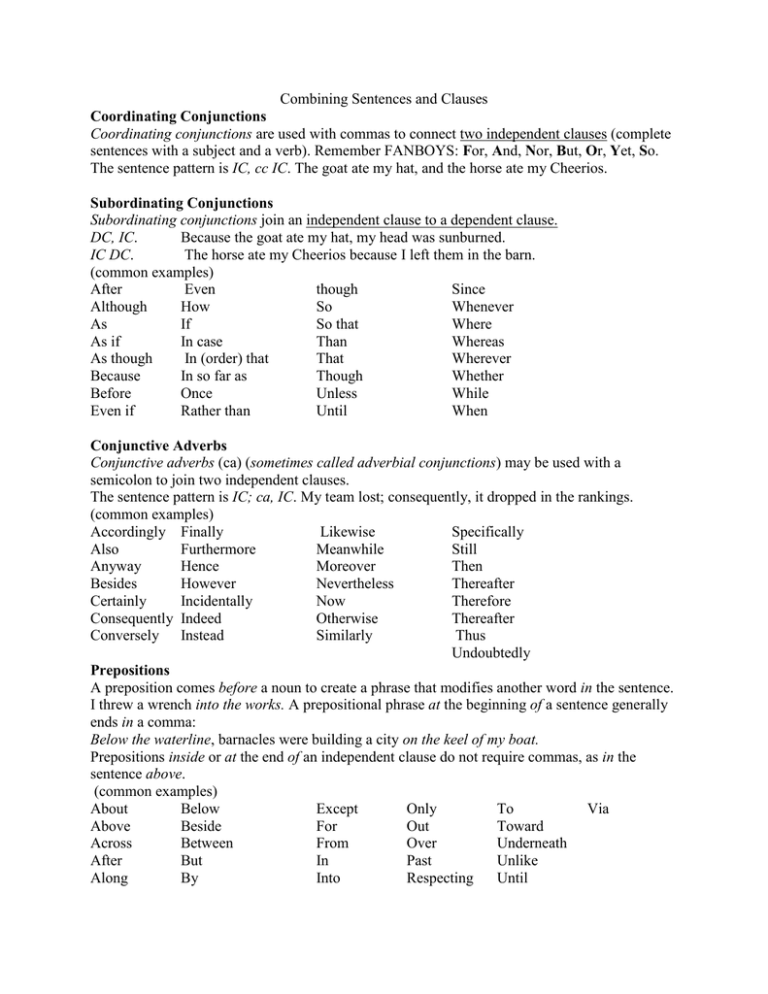
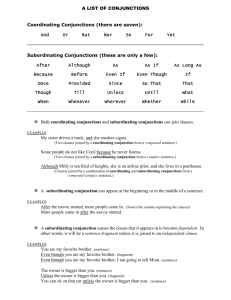
Combining Sentences and Clauses Coordinating Conjunctions Coordinating conjunctions are used with commas to connect two independent clauses (complete sentences with a subject and a verb). Remember FANBOYS: For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, So. The sentence pattern is IC, cc IC. The goat ate my hat, and the horse ate my Cheerios. Subordinating Conjunctions Subordinating conjunctions join an independent clause to a dependent clause. DC, IC. Because the goat ate my hat, my head was sunburned. IC DC. The horse ate my Cheerios because I left them in the barn. (common examples) After Even though Since Although How So Whenever As If So that Where As if In case Than Whereas As though In (order) that That Wherever Because In so far as Though Whether Before Once Unless While Even if Rather than Until When Conjunctive Adverbs Conjunctive adverbs (ca) (sometimes called adverbial conjunctions) may be used with a semicolon to join two independent clauses. The sentence pattern is IC; ca, IC. My team lost; consequently, it dropped in the rankings. (common examples) Accordingly Finally Likewise Specifically Also Furthermore Meanwhile Still Anyway Hence Moreover Then Besides However Nevertheless Thereafter Certainly Incidentally Now Therefore Consequently Indeed Otherwise Thereafter Conversely Instead Similarly Thus Undoubtedly Prepositions A preposition comes before a noun to create a phrase that modifies another word in the sentence. I threw a wrench into the works. A prepositional phrase at the beginning of a sentence generally ends in a comma: Below the waterline, barnacles were building a city on the keel of my boat. Prepositions inside or at the end of an independent clause do not require commas, as in the sentence above. (common examples) About Below Except Only To Via Above Beside For Out Toward Across Between From Over Underneath After But In Past Unlike Along By Into Respecting Until Among Around As Before Behind Concerning Considering Despite Down During Like Near Next Of On Round Since Than Through Till Up Upon With Within Without Indefinite Pronouns Indefinite pronouns refer to nonspecific persons or things. Someone took all the Hershey's kisses. Everybody in the class is in deep trouble. All Any Anybody Anything Anyone Both Each Either Everybody Everyone Everything Few Many Neither No one Nobody Nothing Several Some Somebody Someone Something