ET710 What are Hyperlinks?
advertisement

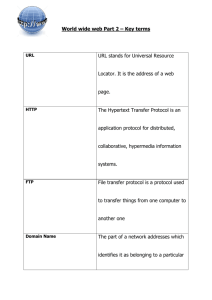
ET710 What are Hyperlinks? A hyperlink, or hot link, is a selectable element in an electronic document that serves as an access point to other electronic resources (the targets). Typically, you click the hyperlink to access the linked resource. Familiar hyperlinks include buttons, icons, image maps, and clickable text links. Material containing hyperlinks is often called hypertext (although not all hypertext contains hyperlinks). Hypertext systems can be very simple, such as a text document with internal references, or very large and complex, such as the World Wide Web. The web is built around hypertext and hypermedia. A hypertext document has certain keywords or phrases linked to other online documents. A person reading a hypertext document about dogs, for example, might be able to select the highlighted word "beagle" and call up another document for more information about that particular breed. With documents intertwined by links into a web of information, you can select paths to browse online resources, a process often referred to as surfing. Hypermedia extends the concept of hypertext to other forms of information, including images, sounds, and even video clips. A person reading a hypermedia document about dogs, for example, might select a picture of a beagle and hear the sound of a dog barking. ET710 What is a URL? • URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator, and is used to specify addresses on the World Wide Web. A URL is the fundamental network identification for any resource connected to the web (e.g., hypertext pages, images, and sound files). • URLs have the following format: • protocol://hostname/other_information For example, the URL for Indiana University's home page is: • http://www.indiana.edu/ The protocol specifies how information from the link is transferred. The protocol used for web resources is Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). Other protocols compatible with most web browsers include FTP, telnet, newsgroups, and Gopher. The protocol is followed by a colon, two slashes, and then the domain name. The domain name is the computer on which the resource is located. Links to particular files or subdirectories may be further specified after the domain name. The directory names are separated by single forward slashes. • In the URL http://newmedia.qcc.cuny.edu/sp08/et_710_m1/ Newmedia is a subnetwork of the qcc network which is a subnetwork of the cuny network. sp08 is a folder name on the newmedia subnetwork. Et_710_m1 is a subfolder of sp08 The root of your personal website is a subfolder of et_710_mi