The Human Circulatory System
advertisement

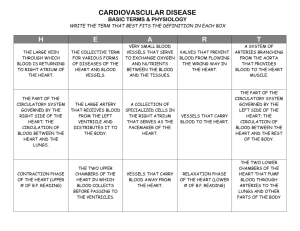
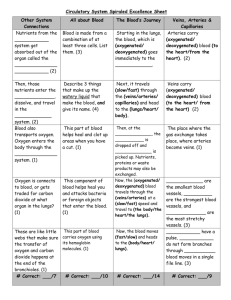
The Human Circulatory System Name:__________________ Date: June 15 – 26, 2015 Class:_________________ Created by Ms. Lucia and Ms. Gayle for Southern Cross School 1 Overview The main purpose of the circulatory system is to exchange wastes for nutrients and oxygen in order to keep the cells working and healthy. The main organs of the human circulatory system are the heart, the blood vessels, and the blood cells. Image taken on June 9, 2015 from http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/t humb/1/19/Circulatory_System_no_tags.svg/400pxCirculatory_System_no_tags.svg.png 2 The heart Image taken on June 9, 2015, from https://www.pinterest.com/pin/186829084517558668/ 3 The heart • Involuntary muscle • Size of a fist • Acts like a pump to circulate, or move, blood around the entire body • Located in the chest between the lungs and inside the ribcage • Separated into 4 parts called chambers • Chambers stop oxygen rich (oxygenated) blood from mixing with oxygen poor (deoxygenated) blood. 4 How blood moves through the heart 6 3 3 right lung 1 4 2 5 The illustration to the right shows the movement of the blood. 1. Deoxygenated blood enters the heart from the body into the right atrium left (RA). lung 2. Deoxygenated blood is pushed to the right ventricle (RV). 3. Deoxygenated blood goes to the lungs to release (get rid of) carbon dioxide and to acquire (get) oxygen. 4. Oxygenated blood comes back into the heart in the left atrium (LA). 5. Oxygenated blood goes into the left ventricle. 6. Oxygenated blood is pumped to the body. 5 How blood moves through the heart 6 Your turn: Color where deoxygenated blood is in blue. Color where oxygenated blood is in red. Then draw arrows to show the movement of the blood through the heart. Label which blood vessels go to the lungs and which go to or come from the body.. 7 Think about it • Why is the left side of the heart bigger than the right side? • Why blood separated in different chambers when it enters the heart? • What might happen if oxygenated and deoxygenated blood mixes? 8 Activity Question: What does your heart do when you exercise? • Find your pulse. Your pulse tells how fast your heart is beating. • Count how many beats you feel in 20 seconds. ________ X 3 = __________ pulse • Run for 1 minute. Count how many beats you feel in 20 seconds. ________ X 3 = __________ pulse • Run for 3 minutes. Count how many beats you feel in 20 seconds. ________ X 3 = __________ pulse • Rest for 2 minutes. Count how many beats you feel in 20 seconds. ________ X 3 = __________ pulse • Rest for 2 MORE minutes. Count how many beats you feel in 20 seconds. ________ X 3 = __________ pulse 9 • Make a graph. Pulse Pulse versus time 130 125 120 115 110 105 100 95 90 85 80 75 70 65 60 55 50 0 1 2 3 4 Minutes 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 Questions 1. What happened to your heart rate do as you exercised more? _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ 2. Why do you think your heart did this? _________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ 11 Blood Vessels: Overview Blood vessels are tubes that connect the heart to all parts of the body, except the hair and nails. There are three types of blood vessels. An artery transports blood away from the heart. A vein transports blood to the heart. A capillary is the smallest type of blood vessel. 12 Types of blood vessels Arteries move blood away from the heart. Veins move blood to the heart. Capillaries (capillary) are very small and have very thin walls. These thin walls allow gases and nutrients or wastes to pass into or out of the blood. Capillaries connect the arteries and the veins. Image taken on June 9, 2015, from http://www.shmoop.com/animalmovement/animal-circulation.html 13 Blood flow simplified upper body lungs heart lower body 14 Activity Question: Why does the body need capillaries? The goal: Keep all cells alive!! 15 Activity Question: Why does the body need capilaries? • Five pairs of students will act like cells and will create carbon dioxide (blue paper). • Ten students will act as red blood cells and will transport the oxygen (red paper) and carbon dioxide. • Four students will be the lungs and exchange carbon dioxide for oxygen. • 6 students will act like blood vessels and direct the blood to the cells. 16 Activity Question: Why does the body need capillaries? In the cell, decide which partner will store wastes and which will transport wastes. The person storing the wastes will hand the transporter a piece of blue paper every 2 seconds. If the transporter has more than 10 pieces of blue paper, the whole cell dies. The blood vessel students will act like arteries and veins (NO CAPILLARIES) and direct the blood cell students to a cell. Each cell may only exchange with one blood cell at a time. When 3 cells die, the game is finished. How long did it take for 3 cells to die? How might this affect the heart and the person´s health? 17 Activity Question: Why does the body need capillaries? cell cell cell cell cell cell 3333333 3333333 3333333 lungs 3333333 3333333 3333333 333 Blood cells move this way. Blood vessels direct cells ONLY to cells to the front line of cells. 18 Activity Question: Why does the body need capillaries? In the cell, decide which partner will store wastes and which will transport wastes. The person storing the wastes will hand the transporter a piece of blue paper every 2 seconds. If the transporter has more than 10 pieces of blue paper, the whole cell dies. The blood vessel students will act like capillaries and allow the blood cell students to surround each cell. When 3 cells die, the game is finished. How long did it take for 3 cells to die? How might this affect the heart and the person´s health? 19 Activity Question: Why does the body need capillaries? cell cell cell cell cell 3333333 3333333 lungs 3333333 33 cell 20 Activity Question: Why does the body need capillaries? _______________________________________ _____________________________________ _____________________________________ _____________________________________ _____________________________________ _____________________________________ _____________________________________ _____________________________________ _____________________________________ 21 Blood: Overview • Blood is a liquid tissue. • Blood is formed by a liquid part called plasma and 3 types of basic cells. – Red blood cells – White blood cells – Platelets 22 Blood: Plasma • Plasma is the liquid that carries the blood cells around the body. • Plasma also carries dissolved substances such as nutrients, wastes, and salts. • About 60% of an organism’s blood volume is plasma. • Plasma is mostly water. Information taken on June 9, 2015 from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2263/ 23 Blood: Red Blood Cells • Red blood cells transport oxygen to the cells. • The scientific word for red blood cells is “erythrocytes.” • Red blood cells are the most numerous in the blood. One cubic MILLIMETER of blood has 46 MILLION red blood cells • Red blood cells have NO nucleus and are round with a concave (spoon-like) shape. Information taken on June 9, 2015 from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2263/ 24 Blood: White Blood Cells • White blood cells make up the immune system of your body. • White blood cells fight germs and infections such as viruses and bacteria. • White blood cells break down and remove dead cells. 25 Blood: Platelets • Platelets are pieces of cells that cause blood to clot. • A clot forms after an organism is cut. This stops the blood from flowing. On humans, if a cut happens on the skin, the blood clots and then dries. This dried clot is called a scab. 26 Blood: Illustration Red Blood Cells White Blood Cells Platelets Image taken on June 9, 2015 from Platelets: http://pvri.info/content/scanning-electron-microscope-images-resting-partially-activated-and-fully-activated-human-0 Red Blood cells http://a2zcancers.blogspot.com/2007/07/blood-cells.html White Blood Cells "SEM Lymphocyte" by Unknown photographer/artist (False color modifications made by myself--DO11.10) - Dr. Triche National Cancer Institute. Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons - http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:SEM_Lymphocyte.jpg#/media/File:SEM_Lymphocyte.jpg 27 Blood: Your turn. Use words and a picture to describe each type of cell that makes up the blood. Write the name of one type of blood cell. Write the name of a different type of blood cell. Write the name of a different type of blood cell. Draw a picture of the blood cell named above. Draw a picture of the blood cell named above. Draw a picture of the blood cell named above. Use words to describe the blood cell named above. Use words to describe the blood cell named above. Use words to describe the blood cell named above. ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ 28 What do you remember? Part Function Picture circulatory system heart 29 What do you remember? Part Function Picture blood vessel artery 30 What do you remember? Part Function Picture vein capillary 31 What do you remember? Part Function Picture red blood cell white blood cell 32 What do you remember? Part Function Picture platelet plasma 33 Why are oxygen, nutrients, and waste transported through the body? How could a person know if his or her circulatory system is not working properly? _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ 34 What can be done to improve the overall health of the circulatory system? _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ 35 How do the structures of the circulatory system work together? (Hint: include all of the cells, tissues, and organs discusses in this unit.) _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ 36