Invertebrates - Baldwin Schools Teachers
advertisement

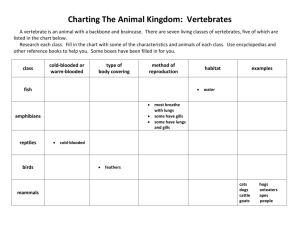
The Kingdom Animalia Compare and contrast the parts of animals. Observe and describe developmental patterns in selected animals. Vocabulary • Cold-blooded: Body temperature changes with the environment • Heterotroph: Can not make its own food, must eat • Invertebrate: Does not have a backbone • Metamorphosis: Change in appearance during development • Regeneration: The ability to regrow missing body parts • Vetertebrate: Has a backbone • Warm-blooded: Body temperature stays the same despite the environment Characteristics • Multicellular • Heterotrophs or __________________________ Consumers Cells and Tissues • Specialized___________________ Invertebrates backbone Animals without a _____________ Types: • Porifera: Pores •Covered in _______________ •Filter Feeders: Water filters through pores and extract food----wastes go out Simplest animal---least complex •Examples: Sponges Invertebrates Types: or Coelenterate • Cnidarians ______________ tentacles • Have ____________________ to capture prey • Nematocysts Stinging cells---paralyze or kill prey • Examples: Hydra & Jellyfish Invertebrates Types: • Worms: •Some can regenerate: Rebuild missing body parts _____________________________ •Some are parasites •Examples: Earthworm & Tapeworm Invertebrates Types: • Mollusks: Shell •Soft body with a ___________ •Example: Slugs, Snails, Clams, Octopus Invertebrates Types: Echinoderm • _________ Spiny •___________skin Radial •Five part _________symmetry •Water vascular system: Water filled transport tubes •Tube feet •Examples: Starfish, SandDollar Types: Invertebrates • Arthropods: •Exoskeleton Jointed •_______________appendages Segmented •_______________ body •Molt: Shed skin after they grow •Metamorphosis: Series of developmental changes of an organism •Crustaceans, Arachnids, Insects Metamorphosis • Change in appearance due to development • Complete metamorphosis; Includes Egg ______, Larva _______, Pupa four stages (____, Adult ______) • Example:Butterfly Metamorphosis • Incomplete metamorphosis: includes Egg Nymph Adult three stages (_____, ______, ______) • Example:Grasshopper • What is the similarity between complete and incomplete metamorphosis? Both have an egg and adult stage • What is the difference between complete and incomplete metamorphosis? Complete metamorphosis has a larva and pupa stage and incomplete has a nymph stage Vertebrates (Endoskeleton) Backbone • Animals with a ____________ Chordata • Belong to the phylum__________ • Two types: 1.Cold-blooded- Ectotherm 2.Warm-blooded- Endotherm Cold-blooded Vertebrates Changes • Body temperature __________ with the environment • Types: • Fish: Cold-Blooded, gills, scales, external fertilization, lay eggs in water • Examples: Trout, Flounder, Sharks Cold-blooded Vertebrates • Types: • Amphibians: “Double Life” Cold-Blooded, gill lungs, lay eggs in water, smooth skin, external fertilization • Examples: Frogs, Newts, Salamanders Cold-blooded Vertebrates • Amphibian Metamorphosis: Cold-blooded Vertebrates • Types: • Reptiles: Cold-Blooded, dry scaly skin, lay eggs on the land with leathery shells, lungs, internal fertilization • Examples: Lizards, Snakes, Turtles, Alligators Warm-blooded Vertebrates • Body temperature Stays the same ____________________________ despite the environment (homeostasis) • Types: • Birds • Mammals Warm-blooded Vertebrates Birds Feathers Lay eggs Feed young regurgitated food Both Warmblooded, care for young, Internal fertilization Mammals Hair or Fur Internal gestation Feed young milk that was produce in mammary glands Review - Energy • Mechanical energy is composed of two types of energy: potential energy and kinetic energy • Potential Energy is stored energy • The greater the mass and the higher the object, the more potential energy • Kinetic Energy is energy associated with motion • The greater the mass and the faster the object moves, the greater the kinetic energy • Potential energy gets transformed to kinetic energy and vice versa (energy isn’t created or destroyed)