File
advertisement

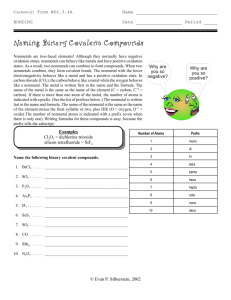
Naming and Writing Formulas Binary – Ionic or covalent Binary compounds (Compounds with just two elements) ALL Binary compounds have a suffix “IDE” on the second element name (hydride, oxide, sulfide nitride…….) REMEMBER…… Ionic – metal and nonmetal Covalent – nonmetal and nonmetal Naming Binary Covalent compounds Numerical prefixes are used to name covalent compounds of two elements First element can have any prefix EXCEPT mono Second element will always have both a prefix and a suffix Number of atoms 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Prefix Mono DiTriTetraPentaHexaHeptaOctaNonaDeca- Binary Covalent Binary compounds (Compounds with just two elements) H2S 1. Name the first element adding the correct prefix (IF NEEDED)– di Hydrogen 2. Name the root of the second element, adding the correct prefix – mono “Sulf” 3. Add the ending “IDE” to the root dihydrogen monosulfide What about covalent compounds? Many covalent compounds are named with prefixes. Examples: CO2 SO2 H 2O 5 Many covalent compounds are hydrocarbons with special names Examples: CH4 C 2H 6 C 2H 4 C 2H 2 Naming Ionic Compounds Binary compounds (Compounds with just two elements) Na2S 1. Name the first element - Sodium 2. Name the root of the second element – “Sulf” 3. Add the ending “ide” to the root Sodium Sulfide ALL binary compounds will end with “ide”. *There is an exception – compounds with ammonium can also end in “ide”….. Ammonium Bromide Naming ionic compounds The first name is the name of the cation Example: CaCl2 has first name calcium The last name has the name of the anion. (Anion names always end in “ide” unless they are from your polyatomic ion chart.) Example: CaCl2 has last name chloride, so CaCl2 is calcium chloride Name these ionic compounds 1. BaF2 2. K2Se 3. CaS 4. AlF3 5. LiH Atoms and Charges Barium Flouride BaF2 Barium 1 atom, +2 1 x (+2) = +2 Flourine 2 atoms, -1 Calcium Phosphide Ca3P2 Calcium 3 atoms, +2 3 x (+2) = +6 Phosphorous 2 atoms -3 2 x (-1) = -2 (+2) + (-2) = 0 Charges balance ! (+6) + (-6) = 0 Charges balance ! 2 x (-3) = - 6 Ionic Compounds Some common Cations Name and Symbol Ion charge Cesium ion, Cs +1 Lithium ion, Li +1 Potassium ion, K +1 Rubidium ion, Rb +1 Sodium ion, Na +1 Barium ion, Ba +2 Beryllium ion, Be +2 Calcium ion, Ca +2 Magnesium ion, Mg +2 Strontium ion, Sr +2 Aluminum ion, Al +3 Some common Anions Name and Symbol Ion charge Fluorine, F FluorIDE - 1 Chlorine, Cl ChlorIDE - 1 Bromine, Br BromIDE - 1 Iodine, I IodIDE -1 Oxygen, O OxIDE - 2 Sulfur, S SulfIDE -2 Nitrogen, N NitrIDE -3 Some cation names must show their charge Transition metals may form several different cations each with a different charge because they have more than one oxidation number These cations must have a Roman Numeral in their name. The Roman Numeral shows the cation’s charge. Naming Binary Ionic Using Transition metals 1. Identify the cation (IF it is a transition look at second element) 2. Identify the oxidation of the second element. 3. Multiply oxidation # (of 2nd element) by # of atoms (for total charges) 4. Use this total to identify oxidation of transition metal. Formulas with transition metals……….. Fe2O3 - Fe Yikes a transition! Look at the element combined with Fe. Oxygen forms a -2 ion , if there are 3 atoms each with a -2 charge there is a total charge of -6 ……. So if Iron has 2 atoms, the total charge must equal +6. Then this iron must be have a +3 oxidation # (+3 X 2 = +6), so it is named Iron (III) Oxide; Some Transition Metal Cations Ion name Copper (I) Copper (II) Iron (II) Iron (III) Nickel (II) Nickel (III) Lead (II) Lead (IV) Mercury (I) Mercury (II) Gold ((I) Gold (III) Symbol Cu +1 Cu +2 Fe +2 Fe +3 Ni +2 Ni +3 Pb +2 Pb +4 Hg +1 Hg +2 Au +1 Au +3 Ion name Symbol Chromium (II) Cr +2 Chromium (III) Cr +3 Tin (II) Sn +2 Tin (IV) Sn +4 Titanium (II) Ti +2 Titanium (III) Ti +3 Titanium (IV) Ti +4 Manganese (II) Mn +2 Manganese (III) Mn +3 Manganese (IV) Mn +4 Manganese (VI) Mn + 6 Manganese (VII) Mn + 7 Ternary compounds contain 3 elements Compounds containing polyatomic ions have charges listed on your polyatomic ion chart. Naming non-binary compounds (polyatomics) NaNO3 1.Use the first element name Na - Sodium 2. Add the polyatomic name CHECK YOUR LIST NO3 - Nitrate NaNO3 - Polyatomic Ion Names Most “normal” polyatomic ion names will have a suffix of ATE ATE suffix indicates Oxygen in formula ITE suffix – has one less Oxygen atom than the “normal” Add a prefix of HYPO - has two less Oxygen atoms than “normal” Prefix of PER with “normal” – ADD 1 oxygen atom Example of Polyatomics – ate – ite –hypo - per Note: Oxidation DOES NOT change “Regular” Chlorate - ClO3 One less Oxygen Chlorite - ClO2 Two less Oxygen Hypochlorite – ClO One more Oxygen Perchlorate - ClO4 With transition elements You will have to look at oxidation number of the polyatomic Follow “rules” for using transition elements Name these….. Mg(NO3)2 Pb(OH)2 CuCO3 K3PO4 NH4Cl Check your understanding ASSIGNMENTS Naming of Non-Binary Compounds Naming Compounds (Mixed): Use flow chart Binary Covalent – prefixes, & IDE suffix Binary Ionic – NO prefixes, & IDE suffix Ionic with transitions – Roman Numerals and IDE suffix Non-Binary – use polyatomic list Names of Acids 1. H in binary (an “ide”) compound = acid name with prefix “Hydro” HCl – (Hydrogen chloride) aka Hydrochloric Acid 2. H with “ate” polyatomic, use suffix “ic” HNO3 is nitric acid 3. H with “ite” polyatomic, use suffix “ous” H2SO3 is sulfurous acid Writing Formulas Binary Covalent Binary Ionic Binary Ionic (metals with various oxidation numbers) Ternary (with polyatomics) Writing Formulas General rules to remember…… 1. Ide suffix means only 2 elements 2. Use prefixes for covalent (di, tri,…) 3. Roman numeral IS the oxidation # 4. Ate, ite suffix or Hypo, per prefix : use the polyatomic list. 5. REMEMBER – cation always goes first 6. Reduce when possible Quick try…. Write formulas for binary compounds when given the oxidation number Na +1 , NaCl Ba +2 , +2 X3, & Ba3N2 Cl -1 N -3 -3 x2 so………………. With Polyatomics REMEMBER – a polyatomic is treated as one substance with its own charge……. Formula for Lithium phosphate Lithium +1 Phosphate -3 Li +1 (PO4) -3 Least common multiple is 3…… Li +1 x 3 = +3 (PO4) -3 x1 = -3 Final formula Li3PO4 Writing Formulas: Binary Covalent Look at prefixes to determine number of atoms (subscripts) Dinitrogen octofluoride Di means two nitrogen N2 Octo means eight fluorine F8 Formula N2F8 Practice writing covalent formulas 1. Dinitrogen monoxide N2O 2. Carbon tetraphosphide CP4 3. Sulfur difluoride SF2 Ionic Compounds from name only 1. 2. 3. 4. What is the chemical formula for aluminum fluoride? List symbols & oxidation for each ion Al +3 F -1 Identify # of atoms to “balance” the formula need total of 3 negative charges to balance with Al’s 3 positive charges. Write chemical formula, using subscripts for # of atoms for a neutral compound…… AlF3 Reduce if possible and leave the charges off Practice makes perfect only if you practice perfect! Write formulas for: Calcium sulfide Ca2+ S2 CaS Potassium oxide K+1 O2 K2O For Transition metals REMEMBER – the roman numeral tells you the charge (oxidation #) Follow previous steps for writing ionic formulas Iron (III) oxide This iron has +3 oxidation Oxygen has -2 Formula: Fe2O3 Practice makes perfect only if you practice perfect! Write formulas for: Iron (III) sulfide Fe3+ S2 Fe2S3 Lead (II) phosphide Pb+2 P3 Pb3P2 More practice 1. oxalate combined with potassium K1+ C2O42 K2C2O4 2. barium bromate Ba2+ BrO31 Ba(BrO3)2 Check your understanding ASSIGNMENTS Writing formulas: Binary with charges given Polyatomic with charges given Mixed with names only “Math Skills” workbook # 9 Chemistry workbook mixed Or - the easy way….. Use the “criss-cross” method…… aluminum fluoride Aluminum has a +3 charge Fluorine has a -1 charge Cross the two… +3 -1 Al F 1 atom 3 atoms Formula for aluminum fluoride is AlF3 For Polyatomic ions….. Use the “criss-cross” method……. Calcium nitrate Calcium has a +2 charge Nitrate has a -1 charge Cross the two… +2 Ca 1 atom -1 (NO3) 2 atoms Formula for calcium nitrate is Ca (NO3)2