Industry Value and Profit Patterns
advertisement

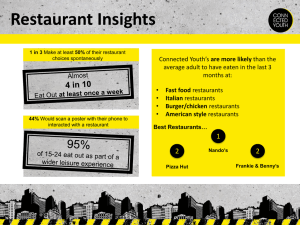
Since Ray Kroc’s first franchised McDonald’s in 1955, fast food restaurants have been popping up all over the United States and beyond. With no signs of stopping anytime soon, the fast food, or quick service restaurant, industry has grown in spite of the recent economic troubles into a worldwide multibillion-dollar industry. Industry Value and Profit Patterns According to the National Restaurant Association, the overall restaurant industry will have an estimated $580 billion in worldwide sales for 2010 with almost one million locations. For the last five years, sales in the United States’ Quick Service Restaurants have grown to an estimated $173.013 billion dollars for 2010 (Mintel, 2010). The restaurant industry is projected to grow at 3-5 percent annually after 2011 per Mintel, which is congruent with Datamonitor’s estimated 3.7 percent compound annual growth rate. The United States fast food restaurant industry is large and split into multiple categories: Quick Service Restaurants, Takeaways, Mobile and Street Vendors, and Leisure Locations (Datamonitor, 2007). These categories are defined per Datamonitor as follows: Quick Service Restaurants (QSR’s): Restaurants where full meals are served without wait staff. Fast food restaurants such as McDonald’s, Burger King, Taco Bell, Wendy’s, and Arby’s are included in this category. Takeaways: Establishments providing freshly prepared food for immediate consumption. Approximately 80 percent of customers take food off premises to consume. An in-supermarket prepared foods counter is an example of a takeaway establishment. Mobile and Street Vendors: Mobile and Street Vendors are mobile trailer-style entities offering a limited range of freshly prepared foods and beverages. These entities are also known as “food carts”. Leisure Locations: Locations serving food and beverage for immediate consumption on-site. This category includes movie theater and stadium concessions. Aggressive pricing, such as the “Dollar Menu” or “Value Menu,” in a highly competitive landscape have helped Quick Service Restaurants increase sales with an especially high rate of unemployment and underemployment in the country. Value pricing has been an attractive option for the public in tough economic times as citizens continue to save more and spend less. As the economy slowly turns around, fast food chains are looking to continue to grow revenue through “higher priced menu items as affordable luxuries.” Luckily for Quick Service Restaurants, government mandates in the last few years requiring nutritional labeling have not shown an impact, either good nor bad, on sales in the industry thus far (Mintel, 2010). Many restaurants have taken advantage of increased attention to nutrition and have added healthier items to menu options. According to the chart above, restaurant sales have slowed down after the recession started in 2008 but are projected to increase after 2011. Current and Future Products & Growth The majority of growth in the QSR industry is due to the ease and low-risk investment in which franchisees can open a branded fast food location (Eating Places, 2009). Franchised restaurants make up a large percentage of fast food revenues. For example, McDonald’s Corporation saw approximately 32 percent of its 2009 revenues from franchised locations (About McDonald’s, 2010). The market has had many identifiable trends in the last few years. As chains compete agressively for greater market share, locations have popped up in other stores and chains, such as McDonald’s restaurants inside of Wal-mart stores, or Little Caesar’s restaurants inside of K-Mart stores. The concept of “multi-branding” has also become more popular as chains share a location (Restaurant Report, 2010). Yum! Brands, the conglomerate including Taco Bell and KFC, has utilized this approach with its Taco Bell/Pizza Hut locations (Datamonitor, 2007). Another way the industry has grown is through acquisitions of other brands, such as Long John Silver’s and A&W by Yum! Brands (Eating Places, 2009). Breakfast menu items have been popping up all over fast food advertisements. From 2004 to 2009, industry breakfast sales have increased 16 percent. The speed and price point of quick service restaurants’ breakfast items have fueled this growth, as in other areas. Almost all fast food chains, from McDonald’s to Subway, have rolled out breakfast menu items. Subway reported that “the daypart has increased sales systemwide and exceeded expectations” (Mintel, 2010). With heightened attention to increasing obesity rates and nutrition labeling requirements in the United States, healthier food options have become more and more popular with fast food chains (Mintel, 2010). McDonald’s has added milk and “Apple Dippers” options to its Happy Meal menu. Burger King now offers the BK VEGGIE® Burger and Wendy’s promotes its “Garden Sensations®” salads. According to Interbrand, McDonald’s is the top Quick Service Restaurant brand and the number sixranked brand in the world due to multiple factors: “The market leader in its category, McDonald’s remains globally versatile, approachable, value-driven and reliable in a year when Burger King fell off the table. Already a strong brand with deep roots, the recession reminded people once again of its great value. McDonald’s seized the opportunity to capture a new audience and drive sales even further by upgrading its coffee to make it more premium and introducing healthier menu options – a move that should help it in the long-term. This, along with constant rollouts of new café concepts and contemporized environments, put McDonald’s in more consideration sets for more occasions. The brand wins A’s all around for its corporate citizenship efforts, as well as its social media endeavors (particularly “Voice of McDonald’s”).” –Interbrand 2010 KFC also earned a spot on the Interbrand chart due to its introduction of healthier items onto its menu, and “huge blog and social media buzz” from its KFC Double Down option. Interbrand also adds the restaurant chain’s ability to reach untapped markets such as Nepal and areas of China and India as criteria for making the list. Marketing Trends In 2009, the quick service industry spent $4.069 billion in advertising, a number that continues to grow. As the recession advanced, chains within the industry turned to advertising to communicate value offerings across demographics, successfully increasing revenues in hard economic times (Mintel, 2010). Traditional advertising such as TV ads remains an integral part of Quick Service Restaurants’ marketing activities along with new tools such as social media and interactive websites (Mintel, 2010). In August 2010, McDonald’s led the way in radio airplay with 37.5 percent of the fast food radio advertising market share. Subway came in second at 14.3 percent and Wendy’s came in third at 11.9 percent (Marketing Charts, 2010). McDonald’s uses a blog and Twitter handle to establish a “voice” by posting photos, information on promotions, and conversing with followers. The company also has a corporate site with public relations activities such as press releases, responses to negative press, and company information. Recently, Smart Cars wrapped with McDonald’s logos have been spotted in various places as well. The BK Subservient Chicken was an early example of a popular viral marketing campaign. A promotion for Burger King’s line of chicken sandwiches, the Subservient Chicken will do whatever it’s told by typing instructions into a box. Since the chicken’s inception in 2004, the site has had more than 450 million hits (CP+B, 2010). Category Structure As a mature and saturated industry, there is tough competition among fast food chains. With the introduction of quick service sandwich, pizza and ethnic food restaurants, the competition is growing. Additional competitors now includes an array of frozen foods, deli selections, and prepared foods from supermarkets, not to mention mobile vendors and leisure locations (Eating Places, 2009). There is no doubt that McDonald’s is the industry leader within the industry. Industry sales rankings are as follows: McDonald’s Corporation, $22.745 billion in 2009 world sales, about 13.5 percent market share (About McDonald’s, 2010) Yum! Brands, $10.836 billion in sales 2009, about 6.42 percent market share (Yum! Earnings Release, 2010) Wendy’s/Arby’s Group Inc., $3.58 billion in sales in 2009, about 2.1 percent market share (Wendy’s/Arby’s Group, 2010) Burger King, $2.537 billion in sales in 2009, about 1.5 percent market share (Burger King, 2010) Conclusion As the world continues to crawl out of a major recession, the fast food industry, especially QSR’s, should continue to grow as consumers search for affordable and quick eating options. With more and more alternatives, there is an option for everyone—from the traditional burger and fries to a healthy salad. With heightened competition among brands and industry categories, fast food chains will have to differentiate themselves and constantly adapt to industry trends and new marketing approaches. References "Best Global Brands Ranking for 2010." Interbrand | Global Branding Consultancy. Interbrand, Web. 4 Oct. 2010. "Burger King Subservient Chicken." CP+B | Advertising & Design Factory. Web. 1 Oct. 2010. “Company Overview." Burger King - Investor Relations - Company Overview. Burger King, Web. 30 Sept. 2010. Datamonitor. "United States-Fast Food." DataMonitor 1 (2007): 1. Business & Company Resource Center. Web. 26 Sept. 2010. "Eating Places." Encyclopedia of American Industries. Online Edition. Gale, 2009. Reproduced in Business and Company Resource Center. Farmington Hills, Mich.:Gale Group. 2010. "Financial Reports." Wendy’s/Arby’s Group, Inc. Investor Relations. Wendy's Arby's Group, Inc., Web. 30 Sept. 2010. Gorodesky, Ron, and Ed McCarron. "Restaurant Report - Trends in the Quick-Service Restaurant Industry." Restaurant Management - Restaurant Marketing - Restaurant Business. Restaurant Report, Web. 26 Sept. 2010. “Investors - About McDonald's ." About McDonald's. Web. 26 Sept. 2010. "Quick Service Restaurants - US - August 2010." Mintel 1 (2010): n. pag. Mintel. Web. 26 Sept. 2010. "Research & Insights: Facts" Home Page | National Restaurant Association | National Restaurant Association . National Restaurant Association, 2010. Web. 26 Sept. 2010. "Top Radio Advertisers Quick Service Restaurant - August 2010." MarketingCharts: charts and data for marketers in web and Excel format. Marketing Charts, Web. 4 Oct. 2010. "Yum! Earnings Release." Yum! Brands - Investors - Stock-Performance Charts. Yum! Brands, Web. 30 Sept. 2010.