Chapter 7 - Business Level Strategy
advertisement

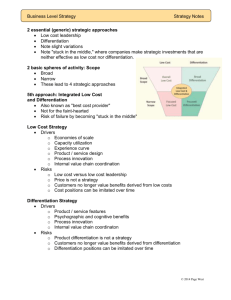
Business-Level Strategy Chapter 7 Strategic Management:Value Creation, Sustainability, and Performance, 3e, 2014 Learning Objectives 1. Compare business-level strategies. 2. Describe how each type of business-level strategy creates competitive advantage. 3. Examine the underlying drivers for each type of business-level strategy. 4. Analyze when outsourcing makes sense. Two Important Dimensions Strategic Approach Low Cost Leadership – lower costs while providing competitive level of benefits Differentiation – increasing benefits while providing competitive level of cost / price Scope Broad – multiple segments or geographies Narrow – tailored to specific segments or areas Five Business-Level Strategies Connecting Strategy to Superior Performance (Above Average Profits) Caveats for Business Strategy Parity on other conditions valued by the market Low cost – cost is not the only factor Differentiation – price / value relationship Evolution of customer expectations Evolution of competition Low Cost Leadership - Drivers Economies of scale Capacity utilization Experience curve Product / service design Process innovation (value chain design) Internal value chain coordination Low Cost Leadership - Risks Not owning low cost leadership position Price is not a strategy Price is tactical & immediate; low cost requires strategic investments over the long run Customers no longer value benefits derived from low costs Cost position can be imitated over time Differentiation – Drivers Product and service features Respond to customer needs Integrity of product / service Use of quality inputs Psychographic and cognitive benefits Marketing and advertising Perceived responsiveness to customers Corporate reputation Process innovation (value chain design) Internal value chain coordination Differentiation – Risks Product differentiation is not strategy (Value Chain differentiation is) Customers no longer value benefits derived from differentiation Differentiation positions can be imitated over time Variations on Business Strategy Focus Subset of industry's products / services Segmenting customers or customer needs Targeting narrow geography or customer access Integrated Low Cost / Differentiation Strategy Seeking to address both dimensions Runs risk of becoming "stuck in the middle" Strategy and Outsourcing Enhance position in the market Joint ventures for R&D Offloading non-essential activities No particular internal competence Does not contribute to strategic position Outsourcing Risks Loss of control over costs or differentiation values Disruption of coordination and linkages across internal value chain "Hollowing out the core" Possible cumulative effect of sets of activities that are outsourced Competitive learning Competitors can more easily observe "what remains" after the outsourcing