Name Date ______ Pd ______ Mapping in the Cosmos Purpose
Name ________________
Date ________ Pd ______
Mapping in the Cosmos
Purpose:
The purpose of this exercise is to become familiar with the sky in general, and several classes of objects in particular.
Definitions and Fun Facts:
M (as in M31) stands for Messier, an early comet hunter, who was annoyed by the fuzzy, stationary objects in the sky which he might easily confuse with comets. So he made a list of stationary fuzzy objects. The Messier objects are the brightest extended objects in the northern sky other than planets.
NGC stands for New General Catalogue - now 100 years old - of extended objects.
Right Ascension and Declination are the coordinates of the sky, much like longitude and latitude on Earth
Apparent Magnitude is an indication of how bright an object appears to be. Apparent Magnitude runs backwards so that low numbers are brighter objects (the Sun has apparent magnitude = -26) and high numbers are fainter objects.
One degree is 60 arcminutes (60'). The Sun and the moon are 30' in angular size.
1 pc = one parsec = 3.26 light years = 2X10
13
miles. The nearest star is 1.3 pc away.
Procedure:
1.
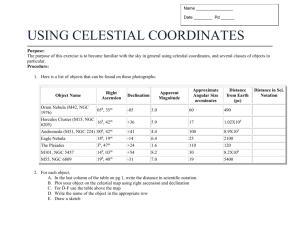
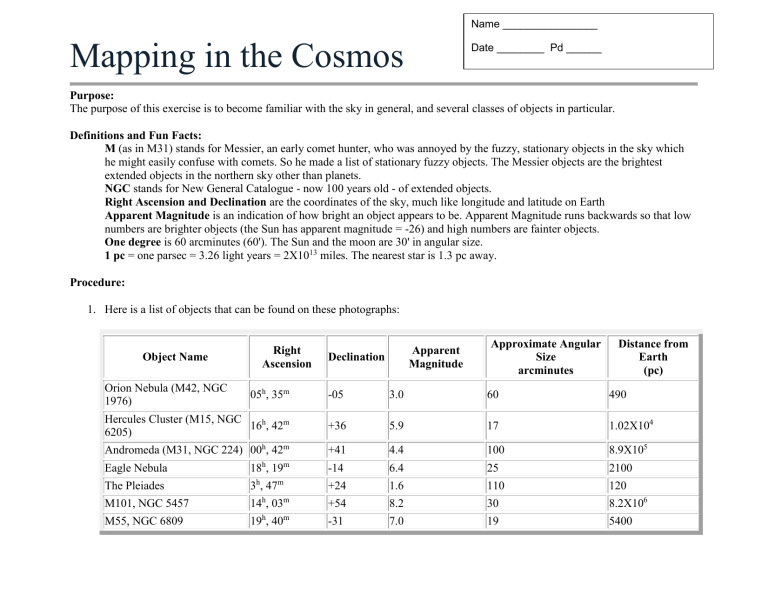
Here is a list of objects that can be found on these photographs:
Object Name
Right
Ascension
Declination
Orion Nebula (M42, NGC
1976)
05 h , 35 m
Hercules Cluster (M15, NGC
6205)
16 h
, 42 m
Andromeda (M31, NGC 224) 00 h , 42 m
Eagle Nebula 18 h
, 19 m
The Pleiades
M101, NGC 5457
M55, NGC 6809
3 h , 47 m
14 h
, 03 m
19 h
, 40 m
-05
+36
+41
-14
+24
+54
-31
3.0
5.9
4.4
6.4
1.6
8.2
7.0
Apparent
Magnitude
Approximate Angular
Size arcminutes
60
Distance from
490
Earth
(pc)
17
100
25
110
30
19
1.02X10
8.9X10
5
2100
120
8.2X10
6
5400
4
2.
For each object in the table above, do the following to the table and map below,
A.
Map using Right Ascension and Declination coordinates
B.
Write the name of the object in the appropriate row in table, closest to where it is on map
C.
Draw a sketch
D.
Identify the type of object from the following list
Bright Nebula: looks like a cloud (because it is a cloud in space). Stars are born in nebulae.
Globular Cluster: spherical group of about 1 million (10 6 ) stars. Distinct from stars because rather than having
fuzzy edges, it has edges made of lots of dots.
Open Cluster: loose cluster of a few hundred-few thousand nearby stars.
Spiral Galaxy: In 3-D, a spiral galaxy looks much like a frisbee, but depending on which way you look at it, it might be a circle, an ellipse, or a relatively thin line.
Questions:
1.
Describe each of the object types as far, farther, or farthest away. Change distance from Earth to all scientific notation or all standard form. o Bright nebula: o Globular cluster: o o
Open cluster:
Spiral galaxy:
2.
Do you think that the types of objects you described as only 'far' exist at the 'farthest' distances as well? If so, why can't we see them?