7 LE osteology ligaments and gluteal muscles
advertisement

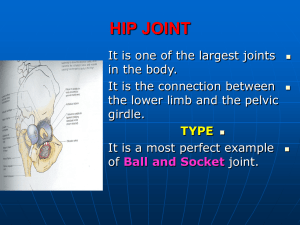
Lower Extremity OSTEOLOGY, LIGAMENTS, GLUTEAL MUSCULATURE Which of the following is most likely pertaining to the two pelves depicted? 95% ro m a yo un ge a sf ro m Th e r ig ht i sf ft i le Th e rp er s.. ti le f th e nd ea sm al yo un ge rp er so ... s.. . .. is. r ig ht th e ht i The right is from a younger person than the left an d D. r ig The left is from a younger person than the right Th e C. 0% 5% 0% sm al e The right is male and the left is female ft i B. le The left is male and the right is female Th e A. LE Unit Overview Superficial fascia, veins, lymph Skeletal structures / joint surfaces Ligamentous support Musculature / vasculature Nerves Forces and injuries Objectives Describe the gross anatomy for each system (circulatory, muscular, nervous, and skeletal) in the lower extremity. Integrate the systems to discuss the lower extremity stability and mobility functions. Analyze common injuries in the lower extremities. For each muscle, describe how the attachment sites result in an action around a joint. For each muscle, identify the innervation (peripheral nerve and nerve roots). LE Overview Coxae (Pelvis) Obturator Membrane Anatomical Position Sacroiliac Joint - Ligaments Primary: Anterior Sacroiliac Interosseus Short and long posterior sacroiliac Secondary: Sacrotuberous Sacrospinous Sacroiliac Joint Motions Anterior Tilt and Posterior Tilt Nutation (sacral flexion) and Counternutation (sacral extension) Stability vs. Mobility http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=elo2_sWBXaM Your patient has significant posterior tilt in his pelvis but when palpating, you notice his sacrum is nutated. What ligament would be most stretched? 18% of th es e w ou ld be os pi n Sa cr No ne s.. . ou s 8% c None of these would be stretched lia D. 23% ro i Sacrospinous ac C. ac Anterior Sacroiliac ro ili B. 51% An te r io rS Posterior Sacroiliac Po st er io rS ac A. Your female patient has anterior pelvic tilt due to excessive lumbar lordosis. Which of the following is TRUE? Sh e is be in co un te at rn ris ut k at fo io rp n os te rio rd isc h. .. No ne of th es e nu ta tio n in be m us t D. 0% Sh e C. 15% 15% m us t B. She must be in nutation She must be in counternutation She is at risk for posterior disc herniation None of these Sh e A. 69% Femur: Torsion Angle Averages: 7 degrees in males 12 degrees in females Discussion question: What effect does this difference have? Femur: Angle of Inclination D. E. 0% 0% 0% ha ft. m ed ia th lc e on in te dy rt le ro . ch an te ric lin e. C. al on g B. mid-shaft. medial condyle. along the intertrochanteric line. neck. intercondylar area. m id -s A. 100% 0% ne in ck te . rc on dy la ra re a. The part of the femur that is most susceptible to fracture in conjunction with osteoporosis is: In the following radiograph of the hip, the arrow points to the: 95% or al ne ck . 0% fe m pi ne . femoral neck. 0% isc hi al s D. 5% nt er . ischial spine. tro ch a C. er lesser trochanter. r. B. le ss greater trochanter. gr ea te rt ro ch an te A. Coxa vara refers to: an abnormal decrease in the angle between the shaft of the femur and the tibia. B. an abnormal decrease in the angle between the head and neck of the femur and its shaft (angle of inclination). C. an abnormally short distance between the anterior superior iliac spine and the center of the acetabulum. D. an abnormally short distance between the iliac crest and the greater trochanter. E. an abnormally short femur. A. 79% 18% an ab no rm al de an cr ab ea no se rm in al th de e an an cr e ... ab as e no in rm th al e ly an an sh g. ab or . no td rm i st an al ly ce sh ... or an td i st ab an no ce rm ... al ly sh or tf em ur . 0% 3% 0% Hip musculature Gluteal region Anterior hip Gluteus maximus Iliopsoas Gluteus medius Pectineus Gluteus minimus Sartorius TFL Rectus femoris Piriformis Obturator internus Gemelli Obturator externus Quadratus femoris Bursa Ischial Obturator internus Trochanteric Gluteofemoral The iliotibial tract is the conjoint distal aponeurotic attachment of which of the following pairs of muscles? 100% gluteus medius and minimus B. gluteus medius and maximus C. gluteus maximus and the tensor of the fascia lata D. the tensor of the fascia lata and rectus femoris E. rectus and biceps femoris A. 0% 0% gl ut eu sm ed iu gl sa ut nd eu sm m gl in ed ut im eu iu us s sm an ax d m im th ax us e im te a nd us ns or th e of te th ns e or fa sc .. ia re la ct ta us an an d d ... bi ce ps fe m or is 0% 0% Which of the following is incorrect pertaining to the great saphenous vein? E. 0% 5% 3% 0% po st It er pa io rt ss es o th po e st m er ed io ia r It ... to dr th ai e ns m in It ed to ha ia th sa l.. . e ne fe m ar ly or It al un tra ve ifo ve in rm rs . es di am th e et sa er ph ... en ou so pe n. .. D. es C. pa ss B. 92% It passes posterior to the medial malleolus. It passes posterior to the medial condyle of the femur. It drains into the femoral vein. It has a nearly uniform diameter because blood is shunted to deeper veins. It traverses the saphenous opening in the fascia lata. It A. For Monday Readings in Moore Study for lab quiz