File
advertisement

CS428 Web Engineering
Lecture 23
MySQL Basics
(PHP - VI)
1
INTRODUCTION
• In order to have really full featured
application. We are going to need to
incorporate a database.
• We can store lots of information in
database, search through it. Added it,
updated. Keep it there for long period of
time. There are so many benefits of using
database.
CRUD
• CRUD is acronym and it stands for…
CRUD
Create, Read, Update, Delete
• These are the basic operations perform on
the data base.
• We create records in the database.
• We read records back in the database.
• We update records in the database.
• We completely delete records in the
database.
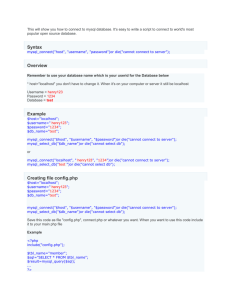
SQL SELECT (Read)
• Format:
• SELECT * FROM table
WHERE column1 = ‘some_text’
ORDER BY column1, column2 ASC;
SQL INSERT (Create)
• Format:
• INSERT INTO table (column1, column2,
column3) VALUES (val1, val2, val3);
SQL UPDATE (Update)
• Format:
• UPDATE table
SET column1 = ‘some_text’
WHERE id = 1;
SQL DELETE (Delete)
• Format:
• DELETE FROM table
WHERE id = 1;
CREATE COMMAND
• CREATE DATABASE widget_corp;
• USE widget_corp;
• CREATE TABLE subjects (
id int(11) NOT NULL auto_increment,
menu_name varchar(30) NOT NULL,
position int(3) NOT NULL,
visible tinyint(1) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
INSERT COMMAND
• INSERT INTO subjects (menu_name,
position, visible) VALUES (‘About Widget
Corp’, 1, 1);
• SELECT * FROM subjects;
• INSERT INTO subjects (menu_name,
position, visible) VALUES (‘Products’, 2, 1);
• INSERT INTO subjects (menu_name,
position, visible) VALUES (‘Services’, 3, 1);
• INSERT INTO subjects (menu_name,
position, visible) VALUES (‘Misc’, 4, 0);
SELECT COMMAND
• SELECT * FROM subjects
WHERE visible = 1
ORDER BY position ASC/DESC;
• SELECT id, menu_name FROM subjects
WHERE visible = 1
ORDER BY position ASC/DESC;
UPDATE COMMAND
• UPDATE subjects
SET visible = 1
WHERE id = 4;
PHPMyAdmin
• www.phpmyadmin.net
• It is already included in WAMP/XAMP one
package.
• http://localhost/phpmyadmin
Using PHPMyAdmin
• It enables you to access your MySQL database
through a GUI. You can easily do the following:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Drop and create databases
Create, edit and delete tables
Create, edit and delete fields
Enter any MySQL statements
View and Print table structure
Generate PHP code
View data in table format
PHP with MySQL
PHP Database Interaction in
FIVE steps
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Create a database connection
Select a database to use
Perform database query
Use returned data (if any)
Close connection
COMMONLY USED FUNCTIONS
• mysql_connect(“hostname”,”user”,”pass”);
Connects to MySQL
server.
• mysql_select_db(“database name”, “handle”);
• mysql_query(“query”);
Selects a database to
use.
Execute database
query
• mysql_num_rows(result variable from query);
Return number of
rows, after execution
of query
• mysql_fetch_array(“result variable from query”);
• mysql_fetch_assoc(“result
Used to return several
rows of the entire
results of a database
queryfrom query”)
variable
Used to return several
rows of the entire
results of a database
query
• mysql_error();
Shows the error
message that has
been returned directly
from MySQL server.
• md5(string);
It uses is to encrypt a
string. It returns 32
characters
hexadecimal number
md5()
• Example:
$str = “Hello”;
echo md5($str);
• Output:
8bla9953c4611296a827abf8c47804d7
date()
• Example:
echo date(“Y”);
// 2015 (year)
echo date(“m”);
// 12 (month)
echo date(“d”);
// 27 (day)
echo date(“Y-m-d”);
// 2015-01-27
echo date(“d/m/y”);
// 28/12/15
echo date(“F d, Y”);
// January 28, 2015
echo date(“F j, Y, h:i:s a”);
// September 28, 2015, 12:12:35 AM
STEP 1
• <?php
// 1. Create a database connection
$connection = mysql_connect(“localhost”, “root”,
“password”);
if (!$connection) {
die(“Database connection failed: ” . mysql_error());
}
?>
<html>
…
</html>
this function returns a value, that will stored in
$connection. That value is called handle.
STEP 2
• <?php
// 1. Create a database connection
$connection = mysql_connect(“localhost”, “root”, “password”);
if(!$connection) {
die(“Database connection failed: ” . mysql_error());
}
// 2. Select a database to use
$db_select = mysql_select_db(“widget_corp”, $connection);
if(!$db_select) {
die(“Database selection failed: ” . mysql_error());
}
?>
<html>
…
</html>
STEP 3
• Step 1 (create a database connection)
• Step 2 (select a database to use)
• <html>
<head></head>
<body>
<?php
// 3. Perform database query
$result = mysql_query(“SELECT * FROM subjects”,
$connection);
if (!result) {
die(“Database query failed: ” . mysql_error());
}
?>
</body>
</html>
STEP 4
• <html>
…
<?php
// 3. Perform database query
$result = mysql_query(“SELECT * FROM subjects”,
$connection);
if (!result) {
die(“Database query failed: ” . mysql_error());
}
// 4. Use returned data
while ($row = mysql_fetch_array($result)) {
echo $row[1] . “ ” . $row[2] . “<br />”;
}
?>
</html>
STEP 5
• Step 1
• Step 2
• <html>
<head></head>
<body>
Step 3
Step 4
</body>
</html>
<?php
// 5. Close connection
mysql_close($connection);
?>
EXAMPLE
• Create a database name school in
MySQL.
• Create a table name result, with following
fields sId, sName and Marks.
• Create a file name connection.php
EXAMPLE: STEP 1
• Create connection
<?php
// 1. create a connection
$connection = mysql_connect(“localhost”,”root”,””);
if(!connection) {
die(“database connection failed” . mysql_error());
}
?>
EXAMPLE: STEP 2
• <?php
// 1. Create a database connection
$connection = mysql_connect(“localhost”, “root”, “password”);
if (!$connection) {
die(“Database connection failed: ” . mysql_error());
}
// 2. Select a database to use
$db_select = mysql_select_db(“school”, $connection);
if(!$db_select) {
die(“Database selection failed: ” . mysql_error());
}
?>
<html>
…
</html>
EXAMPLE: STEP 3
• Step 1 (create a database connection)
• Step 2 (select a database to use)
• <html>
<head></head>
<body>
<?php
// 3. Perform database query
$query = “SELECT * FROM result”;
$result = mysql_query($query, $connection);
if (!$result) {
die(“Database query failed: ” . mysql_error());
}
if(mysql_num_rows($result <= 0)){
die(“No record found”);
}
?>
</body>
</html>
EXAMPLE: STEP 4
• Step 1 (create a database connection)
• Step 2 (select a database to use)
• <html>
…
<?php
Step 3 (perform database query)
// 4. Use returned data
while ($row = mysql_fetch_array($result)) {
echo $row[0] . “<br />”;
echo $row[1] . “<br />”;
echo $row[2] . “<br />”;
}
?>
</html>
EXAMPLE: STEP 5
• Step 1
• Step 2
• <html>
<head></head>
<body>
Step 3
Step 4
</body>
</html>
<?php
// 5. Close connection
mysql_close($connection);
?>