WP3-ROMA
advertisement

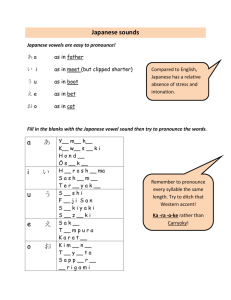
KPIs for WP3 Outlook to Year 4 Final Thematic Workshops: Disseminate SIG outcomes Validate recommendations Feedback from domain experts Consolidation: Finalization of ongoing user studies Evaluate SGs for the VRE Transition to the SGS Scientific dissemination Validation and update of contributions to the GALA roadmap Related to the final thematic workshops #participants New relations established, new involved partners … Related to publications, special issues, invitations Related to the upcoming evaluation methodology??? Comprehensive SG evaluation framework in WP3 Used for the user studies in year 3 A comprehensive model devised considering the outcomes emerged from the reports and according to the analysis performed in the previous years about the strategies implemented and the data collected. a long-term assessment is included by means of post game interviews and post game learning communities. Granularity: e.g. specific levels in Bloom taxonomy – not only Cognitive domain For each game a subset of the evaluation steps has been used. Learning Impact Evaluation Educational Content What to measure? (domain-specific) To verify the achievement of the expected outcomes (domain-specific) Educational objectives ? Learning outcomes Educational Goal How to measure? (new skills / new knowledge/ competence acquisition/ behavioural change / raise awareness … In order to verify if the new skills/ knowledge/ have been acquired, the behavioural change took place, etc… Evaluation steps 1. Learning Evaluation as an Impact project: preliminary work about serious game fitness in the educational program in cooperation with educators, facilitators and relevant stakeholders (e.g. HRs and CLOs in organisations) 2. learning goals: raising awareness, training skills, supporting motivation, experience of collaborative learning, … 3. Identification of domain-specific expected learning outcomes according to the SG Description Template (refers to Bloom’s revised taxonomy) 4. Identification of the kind of data that can be collected, based on game deployment, on privacy and ethical settings and requirements, and on available data analysis tools / instruments 5. Identification of the learning metrics, based on matching the learning goals with the variety of data available 6. Set-up of the Post Game Learning Community by populating it with preliminary material for raising awareness or providing insights about the subject matter Evaluation steps 7. Training the trainers 8. Pre-game test (questionnaires / interviews) (perceived&objective) 9. (If Facilitated workshop) Briefing 10. Game session 11. Direct observation 12. (If Facilitated workshop) De-briefing 13. Post-game test (questionnaire / interviews ) (objective) 14. Just after the game session: (perceived) Enjoyment of the game (Kirkpatrick’s Level 1) What you learnt & to which extent, performance perception (Kirkpatrick’s Level 2) 15. Time (e.g. up to one year) after the game session (Kirkpatrick’s Level 2) Technology Acceptance Model (Davis, 1986)) Testing “on the job” / Direct Observations) (Kirkpatrick’s Level 3) 16. Post Game Learning Community (Kirkpatrick’s Level 3) User Studies Eagle Racing, WhatADay Shortfall, Seconds GBVR Motor Skill Learning, Knowledge of Results Boarders Ahoy!, Afghanistan pre-deployment Playing History – The Plague, Icura Stop Disaster!, My Dream Theatre Example – the Icura user study Evaluation steps 1. Learning Evaluation as an Impact project: preliminary work about serious game fitness in the educational program in cooperation with educators, facilitators and relevant stakeholders (e.g. HRs and CLOs in organisations) No – INFORMAL SETTING 2. learning goals: raising awareness, training skills, supporting motivation, experience of collaborative learning, … RAISING AWARENESS, NEW KNOWLEDGE 3. Identification of relevant domain-specific expected outcomes according to the SG Description Template (refers to Bloom’s revised taxonomy) COGNITIVE: remembering the Japanese words for hello, goodbye, … applying the correct salutation…AFFECTIVE: valuing the principles of Japanese culture, … 4. Identification of the kind of data that can be collected, based on game deployment, on privacy and ethical settings and requirements, and on available data analysis tools / instruments. Various Users; no in-game tools; user data = demographics, game competence, Japanese familiarity; game data= time, achievements, exploration; data about gaming experience: perceived usability, engagement, … data about the learning exp: perceived effectiveness, feedback, motivation, … (SG description Template) 5. Identification of the learning metrics, based on matching the learning goals with the variety of data available see Table Learning goal Type of learning Cognitive (Remembering) Cognitive (Understanding) Learn about the Japanese culture and etiquette Raise awareness about the Japanese culture Expected learning outcome The learner remembers the Japanese word for “gift-wrapping” The learner remembers the Japanese word for say “hello” The learner recalls the most popular religions in Japan The learner understands that saying “no” is impolite The learner understands that keep off shoes is a sign of respect How to assess Multiple-choice (MC) Question: Who or what is „Tsutsumi“? MC Question: How do you say „Hello“ in Japanese? MC Question: Which religions are prevalent in Japan? MC Question: What do you have to keep in mind when talking to a Japanese man or woman? MC Question: When you are invited as a guest in Japan, what do you have to keep in mind? Cognitive (Applying) The learner is able to use the correct salutation Accomplishment of the game task and MC Question: You are going to talk to a senior person named Shotaro and you want to show high respect for him. Which salutation is best to choose in this situation? Cognitive (Analyzing) The learner is able to identify the main characteristics of the Japanese culture Open Answer(OA) Question: How would you describe in 3 adjectives the Japanese culture? Cognitive (Synthesizing) The learner is able to generalize and deduce new facts about the Japanese culture OA Question: What can you deduce from the facts you learnt in the game about the Japanese culture? Cognitive (Evaluating) The learner is able to compare the Japanese culture against his own OA Question: How would you compare the Japanese culture to the Western? Affective (Responding to phenomena) The learner shows new interest towards the principles of the Japanese culture and behavior, he is willing to respond and take the questionnaire, and even to find out more by himself Observation during the experience; Likert question: The game is able to motivate the user on the learning topic; OA Question: Did the game increase your interest towards Japan/ Japanese culture? Would you read more about Japan? Would you visit it? OA Questions (if the respondent spontaneously assign positive The learner identifies positive (or /negative connotation): How would you describe in 3 adjectives the negative) aspects in the Japanese culture Affective (Valuing) Japanese culture? What can you deduce from the facts you learnt and behavior (with respect to our own in the game about the Japanese culture? How would you compare culture) the Japanese culture to the Western? Affective He changes his mind about japan, and maybe now he wants to apply some OA Question in the long-term post-test: Did you take any concrete Evaluation steps 6. Set-up of the Post Game Learning Community by populating it with preliminary material for raising awareness or providing insights about the subject matter 7. Training the trainers – just game play 8. Pre-game questionnaires / interviews 9. Facilitated workshop 10. Briefing – just introduction 11. Game session 12. Direct observation 13. De-briefing 14. Post-game questionnaire / interviews – taking care to avoid selective attention bias 15. Just after the game session: Enjoyment of the game (Kirkpatrick’s Level 1) What you learnt & to which extent, performance perception (Kirkpatrick’s Level 2) 16. Time (e.g. up to one year) after the game session (Kirkpatrick’s Level 2) Technology Acceptance Model (Davis, 1986)) Testing “on the job” / Direct Observations) (Kirkpatrick’s Level 3) – repetition of post-test 17. Post Game Learning Community (Kirkpatrick’s Level 3) VRGB training for rehabilitation Evaluation steps 1. Learning Evaluation as an Impact project: preliminary work about serious game fitness in the educational program in cooperation with educators, facilitators and relevant stakeholders (e.g. HRs and CLOs in organisations) 2. Beyond domain-specific learning objectives: raising awareness, training skills, supporting motivation, experience of collaborative learning, … TRAINING MOTOR SKILLS, DEVELOP SELFCONFIDENCE 3. Identification of relevant learning goals / outcomes according to the SG Description Template (refers to Bloom’s revised taxonomy) 4. Identification of the kind of data that can be collected, based on game deployment, on privacy and ethical settings and requirements, and on available data analysis tools / instruments Users=students; nintendo wii controller; dominant hand performance as own control condition; # strokes on target 5. Identification of the learning metrics, based on matching the learning goals with the variety of data available #strokes on target, perceived skill and self-efficacy improvement 6. Set-up of the Post Game Learning Community by populating it with preliminary material for raising awareness or providing insights about the subject matter Evaluation steps 7. Training the trainers 8. Pre-game questionnaires / interviews self-efficacy rating questionnaire; Edinburgh Handedness Inventory; baseline assessment in RW: forearm and backhand shoots with dominant and nondominant hand 9. Facilitated workshop 10. Briefing introductory video; Familiarization session: target shooting on game console 11. Game session 3 sessions of 30 mins each; with both hands; fixed and moving target 12. Direct observation 13. De-briefing 14. Post-game questionnaire / interviews repeated assessment in RW and self-efficacy questionnaire 15. Just after the game session: Enjoyment of the game (Kirkpatrick’s Level 1) What you learnt & to which extent, performance perception (Kirkpatrick’s Level 2) 16. Time (e.g. up to one year) after the game session (Kirkpatrick’s Level 2) Technology Acceptance Model (Davis, 1986)) Testing “on the job” / Direct Observations) (Kirkpatrick’s Level 3) 17. Post Game Learning Community (Kirkpatrick’s Level 3) Reviewers’ comment With regard to WP3, the priority should be on analysing what has been learned to date. A framework for evaluating SGs would be an important contribution. It might be worthwhile to apply that framework to SGs evaluated by others to see how the outcomes of the GaLA evaluation framework compare with what has already been reported in the literature. Conducting such an analysis would help to frame how the GaLA evaluation framework is different from what is being done by others, and what the GaLA evaluation framework contributes to the larger community. Framework for designing the evaluation experiment for a SG (aim: evaluating its learning impact) A tool helping developers to set up the user study to evaluate their game. Learning Impact Evaluation Educational Content What to measure? (domain-specific) To verify the achievement of the expected outcomes (domain-specific) Educational objectives ? Learning outcomes Educational Goal How to measure? (new skills / new knowledge/ competence acquisition/ behavioural change / raise awareness … In order to verify if the new skills/ knowledge/ have been acquired, the behavioural change took place, etc… Reference Models Educational Content (domain-specific) Educational Goal (new skills / new knowledge/ competence acquisition/ behavioural change / raise awareness … A specific model of the domain (e.g. a taxonomy) A validated model of learning outcomes (e.g. Bloom Taxonomy, Kirkpatrick model,…) A validated list of the possible educational goals of a SG ???? Validated “rules” to match expected outcomes to the right way to measure them ??? e.g. Kirkpatrick’s examples What to measure? To verify the achievement of the expected outcomes (domain-specific) How to measure? In order to verify if the new skills/ knowledge/ have been acquired, the behavioural change took place, etc… Kirkpatrick’s model Bloom’s taxonomy Kirkpatrick’s Four Levels of Learning Evaluation Model Suggestion Try to macth our steps & Igor’s framework into an abstract, comprehensive flow For each step/phase in the flow, provide a set of validated models and suggestions for use Need contributions!!! WP3 activities in Y4 Eval methodology Final thematic workshops Input to the roadmap & dissemination SG descriptions Monitoring the field & updating web pages NEED PRIORITIES!!! Best practices in cooperation Best practices in cooperation in WP3 Papers Associate partners (SG descriptions&papers) Liaisons (SIG3.3&games4health, SIG3.6&games4change) Final workshops User studies: CEDEP&ESADE, BIBA&POLIMI, CMRE&MAN, CNR&SERIOUSGAMESINTERACTIVE, CNR&ORT&RWTH, …