Genetics Notes
advertisement
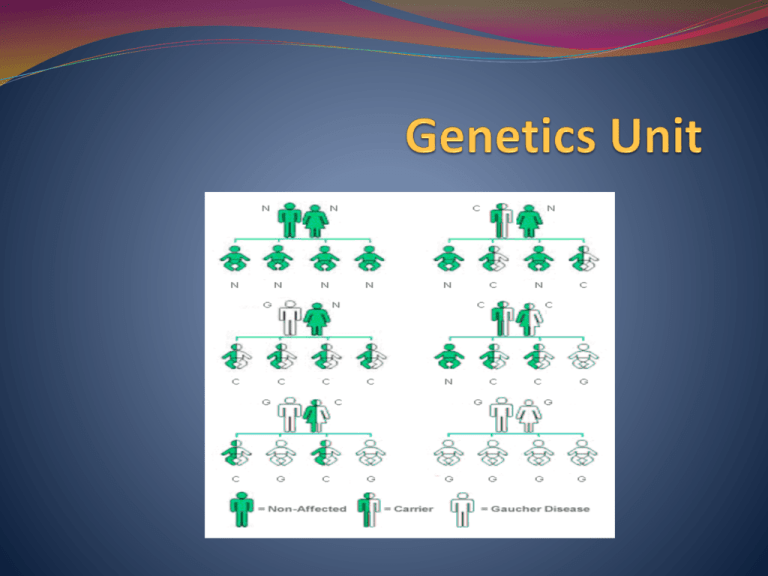
Introduction to Genetics -Genetics is the study of heredity. -Heredity is how different genes are passed down from parents to children. PHENOTYPE A phenotype is the expression of an observable physical trait or characteristic of an organism, such as stature or blood type, based on genetic and environmental influences. Examples vs Non-examples Hair PHENOTYPE Twins born with blonde and red hair Hair-do: not a phenotype A weird girl who fros-out her hair Phenotypes Can you think of some examples of phenotypes? Write down at least 2 examples of phenotypes (traits) in your notes How good are you at judging chimpanzee phenotype? Which chimps are related? Phenotypes? Yes or no? Polydactyl Phenotypes? Yes or no? NO! Flamingos get their pink color from the food they eat, not their genes! HOMOZYGOUS organism with two identical alleles for the same trait **root word “homo” = same HETEROZYGOUS organism with two different alleles for the same trait **root word “hetero” = different Homozygous vs. Heterozygous Two alleles for the “height gene” might be TALL (T) and SHORT (t) A homozygous individual would be TT or tt –two of the same alleles A heterozygous individual would be Tt – two DIFFERENT alleles DOMINANT allele that is expressed when at least one allele is present (TT or Tt = tall) “cover up” RECESSIVE allele that is expressed only when homozygous (no dominant allele) (tt = short) Recessive aa Dominant AA or Aa Dominant WW or Ww Recessive ww Dimples (D) No dimples (d) dd What could AC Slater’s genotype be? Zach’s? DD or Dd SNOWFLAKE –rare albino gorilla Albinism •combination of recessive alleles passed from both parents of an individual •prevents the body from My PHENOTYPE is making the usual(or amounts of the pigment Albino no color). melanin NN = Normal pigmentation (dominant) My GENOTYPE is nn. Nn = Normal pigmentation nn = Albinism About 1 in 17,000 people have some type of albinism, although up to 1 in 75 are carriers. TRAIT a characteristic Examples: Plant size, seed color, pod shape GENE (a segment of DNA that controls traits) Above you see chromosomes. The circled area is a gene on chromosome #22. The absence of this gene causes velocardio-facial syndrome (VCFS) which may cause ADD and mental illness Breast Cancer and Genes ALLELES Each gene comes in different forms called alleles, so the gene that controls flower color may come in two alleles: purple and white. ALLELES different forms of a gene Genotype The combination of the two alleles for a given gene MENDEL’S EXPERIMENTS GREGOR MENDEL The “father” of Genetics Lived from 1822-1884 Austrian Monk Published his work in 1866, but no one took him seriously until 1900. Studied Pea Plants! Mendel experimented with 7 different characteristics GENES Each feature of the pea plants is controlled by a gene. It may have a gene that controls its color, another size for and another for shape. Monohybrid cross. First, Mendel kept all the traits the same except for _one___. This is a called a __monohybrid___cross___ ________ One trait disappeared in the _F1_______ It reappear in the F2 in a ratio of 3:1_____ Dihybrid Cross Next, Mendel controlled all traits except for __2__. He called this a _dihybrid cross_____ Again, two traits disappeared in the F1 They reappeared in the F2 in a ratio of 9:3:3:1 Mendel’s Principles of Inheritance Inherited traits are transmitted by genes which occur in alternate forms called alleles Principle of Dominance - when 2 forms of the same gene are present the dominant allele is expressed Principle of Segregation - in meiosis two alleles separate so that each gamete receives only one form of the gene Principle of Independent Assortment - each trait is inherited independent of other traits (chance) If we saw an organism that had round seeds (round is dominant), how could we figure out what its genotype is? Test Cross A cross between an unknown and a homozygous recessive Example of a Test Cross Unknow n Incomplete Dominance When a combination of the dominant and recessive creates a new phenotype. RR = red, rr = white, and Rr = pink Incomplete Dominance RR Rr rr Co-dominance When both traits are expressed equally. Example: AB blood type Sex Linked Trait a trait that is found on either the X or Y chromosome Hemophilia is an example of a sex linked trait. Hemophilia a disease where your blood doesn’t clot. Hemophilia only occurs when all of the X chromosomes have a copy of the recessive gene. SICKLE CELL ANEMIA PEDIGREE chart that shows the relationships within a family Pedigree Basics Males are squares, females are circles, and unborn babies are triangles or octagons Shaded figures represent individuals with the trait, a carrier could be 1/2 shaded Generations are numbered with roman numerals (I, II, II, IV) from top to bottom People within generations are numbered (1,2,3) from left to right ANTIBODY a protein produced by white blood cells in the body in response to the presence of an antigen, for example, a bacterium or virus ANTIGEN a substance, usually a protein, on the surface of a cell or bacterium that stimulates the production of an antibody Blood Groups Blood group A You have A antigens on the surface of your red blood cells and B antibodies in your blood plasma. Blood group B You have B antigens on the surface of your red blood cells and A antibodies in your blood plasma. Blood Groups Blood group AB You have both A and B antigens on the surface of your red blood cells and no A or B antibodies at all in your blood plasma. Blood group 0 You have neither A or B antigens on the surface of your red blood cells but you have both A and B antibodies in your blood plasma. AMNIOCENTESIS A technique used to determine the genetic traits of a baby before it is born Klinefelter Syndrome Have male genitalia and internal ducts, but underdeveloped testes Do not produce sperm Slight enlargement of the breasts 47,XXY 1 out of every 500 male births Turner Syndrome Has female external genitalia Underdeveloped ovaries Short (under 5 feet) Webbed Neck Broad, Shield-like chest 45,X 1 out of every 3000 female births Cri-du-Chat Syndrome Partial monosomy (part of 1 chromosome is lost) Loss of about 1/3 of the short arm of chromosome 5 Anatomical malfomrations (gastrointestinal and cardiac complications) Mentally retarded Abnormal development of the larynx which makes the baby’s cry sound like a cat’s cry 1 in 50,000 live births Down Syndrome BKA trisomy 21 (47, 21+); 3 copies of the 21st chromosome Short Small round heads Protruding, furrowed tongues which cause mouth to remain partially open Mentally challenged (IQ below 70) Shortened life expectancy (<50) Prone to reparatory disease and heart malformations Have 15x higher chance of getting leukemia Chance of having a baby with Down syndrome goes up as the mother gets older








