What are autotrophs?
advertisement

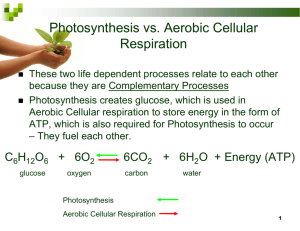
What are autotrophs? Organisms that make their own food (like plants) What do autotrophs need to make their own food? Sunlight photosynthesis What are the products of photosynthesis? Glucose and oxygen How do all organisms obtain energy? by absorbing nutrients from food we eat (not by digesting it) What are the reactants of photosynthesis? Carbon dioxide and water (combined with sunlight and chlorophyll) What are heterotrophs? Organisms that cannot make their own food (like animals)s Heterotrophs are consumers - they must obtain their food by consuming producers or other consumers What is the formula for photosynthesis? (with sunlight and chlorophyll) What are the 2 basic forms of energy? Kinetic – movement Potential energy – based on position Give an example of when you would have high kinetic energy + high potential energy. Going up stairs or roller coaster (the potential energy increases as you go up) What is cellular respiration? Harvesting energy (ATP) stored in food – occurs in both plants and animals What are the reactants and products in cellular respiration? Opposite to photosynthesis: Glucose and oxygen Carbon dioxide, water and ATP What is the formula for cellular respiration? What is chemical energy? The potential energy of organic compounds – related to the arrangement of the atoms within a molecule. (see peanut diagram) What is a calorie? A unit of energy – the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius What is deceptive about the number of calories on a food label? 1 kilocalorie=1000 calories called “big C” The calories shown on a food label is are kilocalories What is thermal energy? energy transferred from a warmer object to a cooler object – heat that cannot be saved or collected Give an example of thermal energy 1- About 75% of all the available energy in gasoline is lost as heat. 2-60% of heat is lost from the human body – this is why we get hot in a small crowded room. What is the structure of Chloroplasts? Where photosynthesis takes place in plants Where do Oxygen, CO2 (gases) and water leave the leaves from in plant leaves? Stomata – like a door on the underside of a leaf What is the liquid inside a chloroplast called? stroma Coin-like structures that are found in the stroma Thylakoid In a leaf, where are the greatest number of chloroplasts found? Facing the sun (on top) The chlorophyll uses “this” along with carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions to produce sugar molecules Energetic electrons What are the 2 stages of photosynthesis Light and dark reactions (dark reactions are also called the Calvin Cycle) What does ATP stand for? adenosine triphosphate What are the three types of work cells perform? Mechanical(physical movement), chemical (dehydration synthesis or building amino acids) and transport (movement od molecules across a membrane) An important fact about ATP It is recyclable (ADP + phosphate) ATP is produced at the rate of 10 million ATP molecules per cell per second What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic? With oxygen vs. w/o oxygen How does the heart help the body get oxygenated blood? -heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs where the blood exchanges carbon dioxide w/oxygen. -The oxygen in the blood returns to the heart so that oxygenated blood can be pumped to the rest of the body. -The carbon dioxide to released to exit the body through breathing. What do all living things need as fuel for cellular respiration? Where does it occur? What does it produce? -Glucose -in the mitochondria -ATP (38) Does glucose burn quickly or slowly? It gets burned slowly. It provides you w/energy so that you can use it throughout the day (slow and steady). True or false: you use the same amount of energy when you are sleeping compared to when you are awake True! What unique structure permits a great deal of energy production in the mitochondria? The folded inner membrane that has a a surface area What are the 3 stages of respiration and which stage produces the most ATP? 1- Glycolysis - nonaerobic (2 ATPs) 2- Krebs Cycle – aerobic (2 ATPs) 3- Electron Transport Chain – aerobic (32-34 ATPs)