File
advertisement

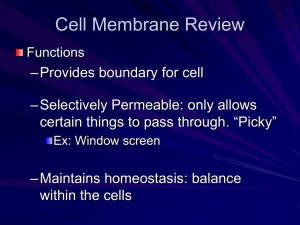
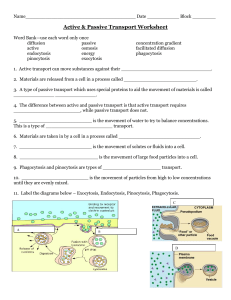
December th 10 , 2014 Complete problems 12 and 13 on your ALA sheet. You have 7 minutes to complete both problems. (3.5 mins/question) Agenda Catalyst (8 minutes) Tables and Figures Guided Practice (15 minutes) Interpreting Tables and Figures Independently (15 minutes) Exit Ticket (Remaining) Homework: Finish wksht if you do not in class Study for a quiz/test on passive vs. active transport—There will also be solution bonus questions!!! Announcements Mastery packets due December 15th, 2014 Unit 4.2: Guiding Questions How do cells take in the nutrients they need and release the substances they do not? Today’s SPI & Objectives SPI 3210.1.8 Compare and contrast active and passive transport. SWBAT compare and contrast passive and active transport in terms of molecule movement and energy usage SWBAT interpret a diagram or table to determine whether it is depicting passive or active transport Review: Passive Transport Passive transport: Molecules move from high low concentration With the concentration gradient No energy is needed Review: Active Transport Active transport: Molecules move from low high concentration Against the concentration gradient Energy and transport proteins are needed Endocytosis/Exocyto sis • Endocytosis: cells absorb molecules by engulfing them • Exocytosis: cell releases waste material using secretory vesicles Interpreting a Figure: Follow along on the practice worksheet!!! Question 1: Figure Where is there a higher concentration? Outside of the cell Do molecules move from high low or low high concentration High low concentration Interpreting a Figure Question 1: Figure What type of transport is this? Passive transport Is it diffusion or facilitated diffusion? Facilitated diffusion (transport proteins used) Interpreting a Table Millimoles (mM) are units that measure concentration Question 2: Interpreting a table a. Is the concentration of oxygen higher inside or outside of the cell at 0 seconds? • Outside of the cell b. Is oxygen moving into or out of the cell during the 90 seconds? • Into the cell c. Is oxygen moving from high low concentration or from low high concentration? • High low concentration Interpreting a Table Question 2: Interpreting a table d. Is this an example of passive or active transport? • Passive transport e. Does it require energy to move the oxygen molecules across the cell membrane? No. Energy is not required Passive vs. Active Transport WS Complete Independent Practice questions on the Passive vs. Active Transport Worksheet If you complete Ms. M check If you do not complete homework Exit Ticket 1. Large molecules are ejected from the cell using what process? 2. Draw a diagram that represents active transport. 3. Draw a diagram that represents passive transport. Catalyst #5: December 11th, 2014 Agenda Catalyst: 5 minutes Unit 4.2 Review Game: 15 minutes Unit 4.2 mini-assessment: Remainder Homework: Semester 1 Study Guide Announcements Mastery packets due December 15th Question 1 Does water move from high solvent to low solvent concentration OR from low solvent to high solvent concentration during osmosis? Answer: From high solvent (higher % of water) to low solvent (lower % of water) concentration. #1 on the Unit 3 Practice Test Question 2 What happens to a cell when it is placed in an isotonic solution? Answer: The cell remains the same size in an isotonic solution because the same amount of water moves into and out of the cell #2 & 3 on the Unit 3 Practice Test Question 3 Where does more water move when a solution has a higher solute concentration than the inside of the cell? Answer: More water moves out of the cell until the solute concentration is the same inside and outside of the cell # 4 on the Unit 3 Practice Test Question 4 What type of solution causes the cell to swell Answer: Hypotonic ; because more water moves into the cell Question 5 What type of solution has the effect shown by the cells below? Answer: A hypertonic solution– causes the cell to shrink as more water moves out of the cell #5-7 on the Unit 3 Practice Test Question 6 In what direction do molecules move during passive transport? Answer: From high to low concentration (with the concentration gradient) #8-9 on the Unit 3 Practice Test Question 7 What type of cellular transport requires energy? Answer: Active transport requires energy; passive transport does not use energy #10 on the Unit 3 Practice Test Question 8 Oxygen enters the cell without the use of energy and without the help of transport proteins. Does oxygen move through diffusion, facilitated diffusion, or active transport? Answer: Diffusion #11 - #12 on the Unit 3 Practice Test Question 9 What type of cellular transport is shown in the figure to the right? Answer: Passive transport (high low concentration) # 13 on Unit 3 Practice Test Question 10 Are molecules moving by passive or active transport? Answer: Passive transport (high low concentration) # 14 on the Unit 3 Practice Test Time Concentration Inside Concentration Outside 0 seconds 150 mM 750 mM 30 seconds 300 mM 600 mM 60 seconds 450 mM 450 mM Unit 4.2 Mini-Assessment Independently. By yourself. In your seat. On a sheet of paper. We will be trading and grading.