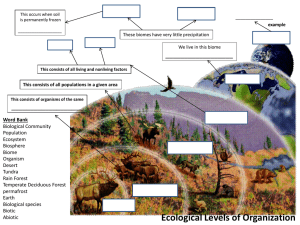
Ecology & Biology Definitions: Organism to Environment
advertisement
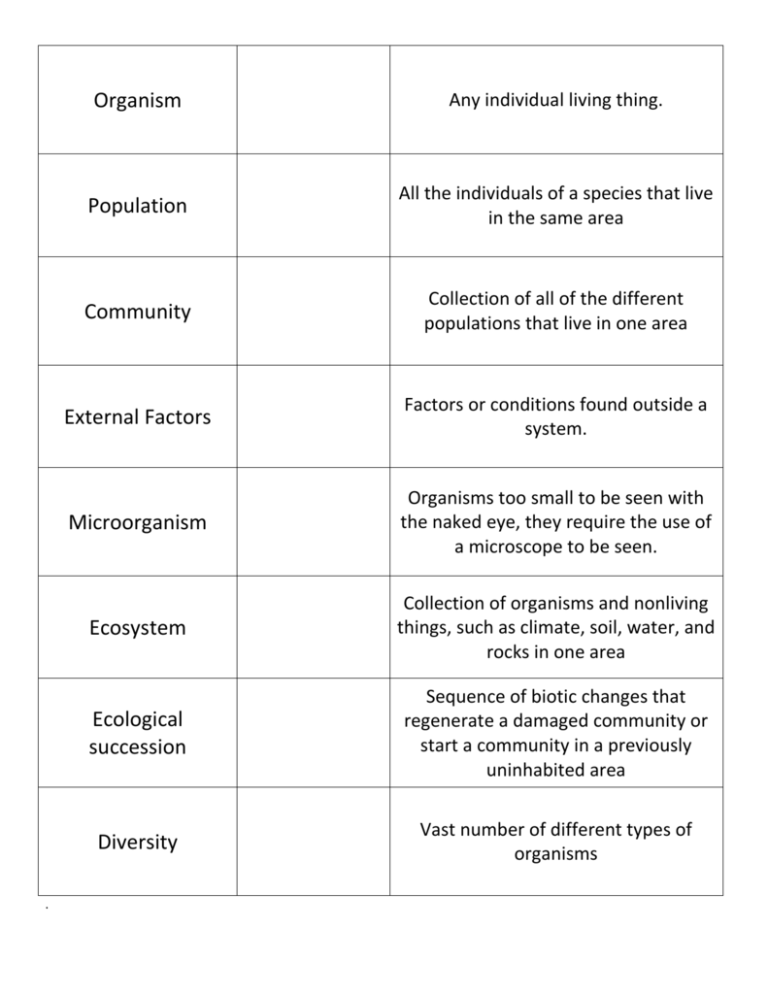
. Organism Any individual living thing. Population All the individuals of a species that live in the same area Community Collection of all of the different populations that live in one area External Factors Factors or conditions found outside a system. Microorganism Organisms too small to be seen with the naked eye, they require the use of a microscope to be seen. Ecosystem Collection of organisms and nonliving things, such as climate, soil, water, and rocks in one area Ecological succession Sequence of biotic changes that regenerate a damaged community or start a community in a previously uninhabited area Diversity Vast number of different types of organisms Symbiosis Relationships Ecological relationship between members of at least two different species that live in direct contact with one another. Predation Process by which one organism hunts and kills another organism for food. Parasitism Ecological relationship in which one organism benefits by harming another organism Commensalism Ecological relationship in which one species receives a benefit but the other species is not affected one way or another Mutualism Ecological relationship between two species in which each species gets a benefit from the interaction Competition Ecological relationship in which two organisms attempt to obtain the same resource. Variation Differences in physical traits of an individual from the group to which it belongs Adaptation Inherited trait that is selected for over time because it allows organisms to better survive in their environment Matter Anything that has a mass and takes space Energy Ability to do work; is associated with motion. Ex:kinetic, potential, thermal, chemical, electrical and nuclear Trophic level Level of nourishment in a food chain Food Chain Model that links organisms by their feeding relationships Food Web Model that shows the complex network of feeding relationships within an ecosystem Ecological Pyramid/Energy Pyramid Diagram that compares energy used by producers, primary consumers and other trophic levels Long-term survival Live for a long time Resources A source of supply Carbon Cycle Carbon continuously flows from the environment to living organisms and back again. Nitrogen cycle Nitrogen continuously flows from the environment to living organisms and back again. Environmental Change Change in the environment (ex: caused by variation in temperature, pollution, water…)