Safety in the Lab

Grade 9 Applied Science – Unit 1 Lesson 2
Safety in the Lab
Safety is paramount in a science lab. Safety includes safe chemical storage, safe chemical use, proper use of equipment, safety equipment and partner work.
Scavenger Hunt
?
Sketch a map of the science lab noting the location of desks, lab benches and other furniture
?
On your map, locate each of the following safety equipment. Use the number to note the location of the equipment on your map.
1. Fire extinguisher
2. Fire blanket
3. Fire alarm
4. Safety goggles
5. Aprons
6. Eyewash station
7. Exits
8. Telephone
9. Disposal container for broken glass
10. Disposal container for chemicals
11. Fume hood
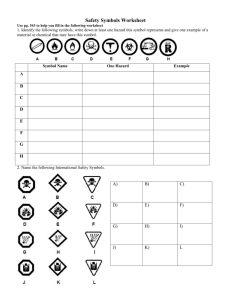
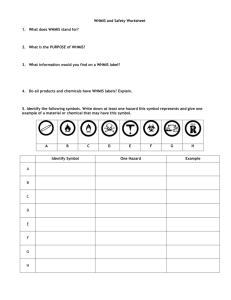
WHMIS and Hazardous Household Product symbols
?
Examine the following symbols
?
Identify the meaning of each symbol
?
Complete the following table identifying the safety concern and precautions
Table 1. WHMIS Symbols
Symbol Meaning Concern Pr e cautions
Table 2. Household Hazardous Products symbols
Symbol Meaning
Questions
1. Why is it important to use a standard set of safety symbols when labeling substances?
2. Briefly describe what you would do if your skin on your arm came in contact with a corrosive chemical.
3. Is it always safe to pour waste chemicals down the sink with lots of water?
Provide two reasons with your answer.
4. Why do hairdressers wear rubber gloves when colouring or chemically straightening hair?
Grade 9 Applied Science – Unit 1 Lesson 2
Kitchen Chemistry Lab #2
Your kitchen can be considered a chemical laboratory. There are many different chemicals is solid and liquid state. To make food, they are mixed together and sometimes heated. During this process, changes in matter can occur.
NOTE: Some household chemicals can form dangerous products when mixed.
Materials
?
Three plates
?
Masking tape
?
Marking pen
?
Table salt (Sodium chloride)
?
Powdered stratch
?
Baking soda (Sodium bicarbonate)
?
Vinegar (Acetic acid)
?
Iodine solution
?
Water
?
Three micro-droppers
SAFETY – Wear safety goggles when using iodine solution
Procedure
1. Using the masking tape and marking pen, label the plates as follows: A –
Salt; B – Starch and C – Baking Soda
2. On Plate A, make three small piles of salt of one teaspoon each. The piles should not touch.
3. Repeat Step #2 for Plate B using starch and Plate C using baking soda
4. Fill a micro-dropper with vinegar. Place 3-5 drops of vinegar on one of the piles on each of the three plates. Record your observations.
5. Fill a second micro-dropper with iodine solution. Repeat Step #4 placing
3-5 drops on a different pile on each of the three plates. Record observations.
6. Fill a third micro-dropper with water. Repeat Step #4 placing 3-5 drops on a different pile on each of the three plates. Record observations.
Questions
1. Which substance caused a change in the table salt? Did a new substance form during any test?
2. Which substance caused a change in the starch? Did a new substance form during any test?
3. For the baking soda, did a new substance form during any test? Provide a reason for your observations.
Grade 9 Applied Science – Unit 1 Lesson 2
Safety in the Lab – Answer Sheet
Safety is paramount in a science lab. Safety includes safe chemical storage, safe chemical use, proper use of equipment, safety equipment and partner work.
Scavenger Hunt
?
Sketch a map of the science lab noting the location of desks, lab benches and other furniture
?
On your map, locate each of the following safety equipment. Use the number to note the location of the equipment on your map.
12. Fire extinguisher
13. Fire blanket
14. Fire alarm
15. Safety goggles
16. Aprons
17. Eyewash station
18. Exits
19. Telephone
20. Disposal container for broken glass
21. Disposal container for chemicals
22. Fume hood
WHMIS and Hazardous Household Product symbols
?
Examine the following symbols
?
Identify the meaning of each symbol
?
Complete the following table identifying the safety concern and precautions
Table 1. WHMIS Symbols
Symbol Meaning Concern Pr e cautions
Compressed
Gas
Could explode due to pressure OR if dropped or heated
Explosion may release contents
Ensure container is secured
Store in designated areas
Do not drop
Flammable or
Combustible
May ignite spontaneously
May release flammable products if allowed to degrade or exposed to water
Avoid heating
Avoid sparks and flames
Ensure electrical sources are safe
Store in designated areas
Oxidizing materials
Toxic Materials
– Immediate and Severe
Hazard
Toxic Materials
– Long Term
Concealed
Biohazardous
Infectious
Materials
Can cause burns to skin and eyes
Increased fire and explosion hazard
May cause combustibles to explode or react violently
May be fatal if ingested or inhaled
May be absorbed through the skin
Small volumes have a toxic effect
May cause permanent injury or death
May cause birth defects or sterility
May cause cancer
May be sensitizers causing allergies
May cause anaphylactic shock
Includes viruses, yeasts, molds, bacteria, and parasites that affect humans
Includes fluids that contain toxic substances
Store oxidizers in containers that will not rust or oxidize
Avoid breathing dust and vapours
Avoid contact with skin or eyes
Work in well ventilated areas
Avoid direct contact
Wear appropriate personal protection
Use hand, body, face and eye protection
Special training required to handle these materials
Avoid forming aerosols
Avoid breathing vapours
Avoid contamination of people and work area
Corrosive
Materials
Dangerously
Reactive
Materials
Includes cellular components
May irritate eyes and skin on exposure
May cause severe burns to tissue upon longer exposure
May damage lungs if inhaled
May cause blindness if contact with eyes
May cause serious environmental damage as a result of fumes
May react with water
May be chemically unstable
May explode if exposed to heat or shock
May release toxic or flammable vapours
May vigorously polymerize
May burn unexpectedly
Avoid all direct body contact
Handle with care, avoiding vibrations, shocks, and sudden temperature changes
Store in appropriate containers
Ensure storage containers are sealed
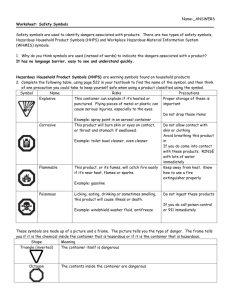
Table 2. Household Hazardous Products symbols
Symbol Meaning
Flammable
Toxic
Corrosive
Explosive