measure of the amount of matter the object contains Volume

Vocabulary
Mass – measure of the amount of matter the object contains
Volume – measure of the space occupied by the object
Extrinsic/extensive property – property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample
Intrinsic/intensive property – property that depends on the type of matter in a sample, not the amount of matter
Substance – matter that has a uniform and definite composition
Physical property – a quality or condition of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing the substance’s composition
Solid – form of matter that has a definite shape and volume
Liquid – form of matter that has indefinite shape, flows, yet has a fixed volume
Gas – form of matter that takes both the shape and volume of its container
Vapor – the gaseous sate of a substance that is generally a liquid or a solid at room temperature
Physical change – some properties of a material change, but the composition of the material does not
Mixture – physical blend of two or more components
Heterogeneous mixture – a mixture in which the composition is not uniform throughout
Homogeneous mixture – a mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout
Solution phase - any part of a sample with uniform composition
Filtration – the process that separates a solid from a liquid in a heterogeneous mixture
Distillation – a liquid is boiled to produce a vapor that is then condensed into a liquid
Element – simplest form of matter that has a unique set of properties
Compound – a substance that contains two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed proportion
Chemical change – a change that produces matter with a different composition than the original matter
Chemical symbol – one or two-letter representation of an element
Periodic table – an arrangement of elements in which the elements are separated into groups based on a set of repeating properties
Period – a horizontal row of elements in the periodic table
Group – a vertical column of elements in the periodic table
Chemical property – the ability of a substance to undergo a specific chemical change
Chemical reaction – a change in which one or more reactants change into one or more products
Reactant – a substance present at the start of a reaction
Product – a substance produced in the reaction
Precipitate – a solid that forms and settles out of a liquid mixture
Law of conservation of mass – in any physical change or chemical reaction, mass is
conserved; mass is neither created nor destroyed
Identifying a Substance
•
Pure substances are made up of only one element ie. An aluminum can
•
Every sample of a given substance has identical intensive properties because every sample has the same composition
•
Hardness, color, conductivity, and malleability are examples of physical properties
States of Matter
•
Solids o The shape does not depend on the shape of its container o Particles packed tightly together, often in an orderly arrangement o Almost incompressible o Expand only slightly when heated o Definite shape and volume
•
Liquids o Particles in close contact with one another but arrangement is not rigid or orderly because the particles can flow from one location to another o Takes the shape of the container o Volume doesn’t change o Shape changes o Almost incompressible o Expand slightly when heated
•
Gases o Takes shape of container o Can expand to fill any volume o Takes both volume and shape of container o Particles much further apart o Gasses are easily compressed
Physical Changes
•
Melting is a physical change because the composition doesn’t change
•
Boil, melt, freeze, split, grind, cut, crush and condense are all words used to describe physical changes
•
However those words split up into two different categories
•
Irreversible o Grind o Cut o Crush o Split
•
Reversible o Boil o Melt o Freeze o Condense
Classifying Mixtures
•
Heterogeneous or homogeneous
•
Heterogeneous o Contents not evenly distributed o No uniform composition o ie: chicken noodle soup o two or more phases
•
Heterogeneous mixture o Substances evenly distributed o Doesn’t look like a mixture o Aka a solution o Many are liquids o Some are gases o Single phase o ie: coffee
Separating Mixtures
•
Methods o Filtration o Distillation
Distinguishing Elements and Compounds
•
Compounds can be broken down elements cannot
Breaking Down Compounds
•
Need a chemical change
•
Heating is one processes
•
There is no process that could break down carbon because it is an element
•
Electricity can cause water to break down
Distinguishing Substances and Mixtures
Chemical Changes
•
Burn, rot, rust, decompose, ferment, explode, corrode – chemical change
•
Composition of matter always changes
•
Aka a chemical reaction
Conservation of Mass
•
Mass of the products is always equal to the mass of the reactants
•
Mass always holds constant in a chemical reaction
•
Mass is neither created nor destroyed
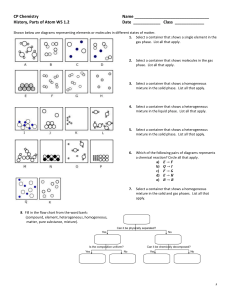
Questions
1.
Which of the following is an example of an intrinsic property a.
A large marker b.
A 5lb weight c.
A hollow chocolate bunny d.
A leather basketball
2.
Which of the following is an example of an extrinsic property a.
A leather basketball b.
A cotton sock c.
A 5lb weight d.
An orange scented marker
3.
Which of the following is NOT a physical change a.
The freezing of ice cubes b.
Condensing a gas into a smaller container c.
Cooking pasta d.
Burning a steak on the grill
4.
Which of the following is irreversible
a.
Melting an ice cube b.
Filing a nail c.
Freezing a banana d.
Boiling soda
5.
Which of the following is heterogeneous a.
Coffee b.
Oil and vinegar c.
Oil d.
Vinegar
6.
Describe the difference between a chemical change and a physical change.
Give an example of each.
7.
How is the arrangement of particles different in a solid and a gas?
8.
When MgS
MgS O
!
O
!
explodes the products are Mg, S, and
originally and 20g of Mg after and 21g of O
!
O
!
I have?
9.
Explain the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic property.
10.
Describe how to break down a compound.
. If I have 50g of
. How many grams of S do