Administration in Medical Settings Certificate Level 2 PROGRAMME
advertisement

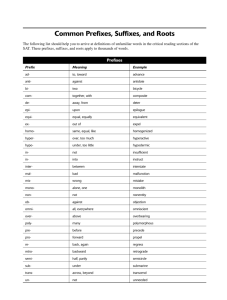
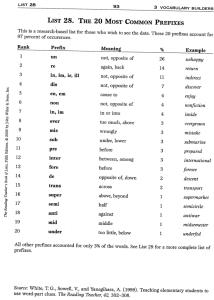
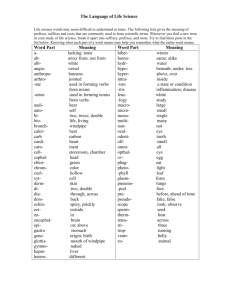
Administration in Medical Settings Certificate Level 2 PROGRAMME Learner Name: …………………………………………………………………… Company: ………………………………………………………………………… Tutor/Mentor: …………………………………………………………………….. Start Date: ………………………………………………………………………… Contents Module 1 Medical vocabulary Module 2 Medical administration skills in the work setting Module 3 Communication skills in a medical setting Module 4 Principles for the administrator in a medical setting Module 1 Medical vocabulary Introduction The aim of this module is to allow the learner to gain an understanding of the terminology that is used within the medical profession. They will learn the structure of medical words and the meanings of these words, which will enable them in their role in administration. The learner will also acquire knowledge of medical terminology in regards to the human body and the abbreviations that are used within the pharmaceutical department. Learning outcomes When the module is completed, the learner will: Know how medical word parts are constructed and what they mean Understand the meaning of medical terms in relation to the human body Understand the meaning of medical terminology relating to medical specialities Know the meaning of pharmaceutical abbreviations. Definitions of medical word parts There are thousands of different words, abbreviations and terms that are used within the medical profession. It would be impossible to learn and remember each and every one of them; however, there are some that you will undoubtedly see on many occasions whilst doing your job. This module will help you to recognise and understand many of the terms, compositions and abbreviations. Most of the medical words that you will be working with are made up of root words and are combined with prefixes and suffixes. A prefix has what is called a droppable ‘o’; this connects the prefix to the root word which begins with a consonant. This means that the ‘o’ is dropped when it is connected to a root word that begins with a vowel. The root word is a term which usually describes a body part or the central part of the word, i.e.: Cardio means heart Derma means skin Mal means bad Poly means many Path means feeling or suffering. Prefixes are letters or words at the beginning of a root word, for instance un or pre; these make up another word: Un-successful Pre-menstrual. Suffixes are letters or words at the end of another word to create a different word, such as: -ology as in pathology Droppable o's are in place in certain words such as osteopathy - oste is the root word, o is the combining vowel and -apathy is the suffix. Medical terms derived from the medical word parts Here you will discover some of the commonly-used medical root words, suffixes and prefixes of words. Common medical root words: A's Abdomin/o: Abdomen Aden/o: Gland Anter/o: Front Audi/o: Hearing Adip/o: Fat Axill/o: Armpit Aden/o: Gland Acous/o: Hearing. Bio: Life Bronch/o: Bronchial tube Bronch/i, bronch/o: Bronchus. Carcin/o: Cancer Cardi/o: Heart Cyt/o: Cell Cyst/o: Urinary bladder. Derm/a, derm/o, dermat/o: Skin Dors/i, dors/o: Back or posterior. Encephal/o: Brain. Gastr/o: Stomach Gynec/o: Female. B's C's D's E's G's H's Hemat/o: Blood Histio: Tissue. Intestin/o: Intestine. Lymph/o: Lymph vessels Lapar/o: Abdomen. Malign: Harmful My/o: Muscle. Neur/o: Nerve. Ocul/o: Eye Or/o: Mouth Ot/o: Ear. Pharmac/o: Drug Paed: Children. Thorac/o: Chest/thorax Trachel/o: Neck or neck-like Toxo: Poison. Ventr/i, ventr/o: Front of body Viscer/o: Viscera (internal organs). I's L's M's N's O's P's T's V's Some examples of suffixes: -AEMIA means condition of blood -OSIS means disease/condition -ECTOMY means excision/removal -ITIS means inflammation -OMA means tumour -PATHY means disease -OLOGY means study/science of -PHERESIS means removal. Some examples of prefixes: A's ab- means away from ad- means near/toward abdomin(o)- of or relating to the abdomen acous(io)- of or relating to hearing adip(o)- of or relating to fat or fatty tissue. B's C's D's E's F's I's P's S's bi- means two/both. capit- means pertaining to the head (as a whole) chem(o)- means chemistry, drug. dys- means difficult/painful de- means away from, cessation. ecto- means outside endo- means inside epi- means upon enter(o)- means of or pertaining to the intestine. fore- means before or ahead hyper- means excessive or above. inter- means between. peri- means around post- means after. sub- means under/below. Medical terminology relating to the human body Definitions of medical terms relating to the human body Here you will learn the systems of the body and the medical conditions that affect that specific condition. The systems of the body are: The digestive system The circulatory and cardiovascular systems The endocrine and urinary systems The excretory system The immune system The lymphatic system The integumentary system The nervous and sensory systems The muscular system The reproductive system The skeletal system. Administration in Medical Settings Certificate Level 2 Student Assessment Workbook Learner Name: …………………………………………………………………… Company: ………………………………………………………………………… Tutor/Mentor: …………………………………………………………………….. Start Date: ………………………………………………………………………… ACTIVITY EXERCISES The purpose of the following exercises is to enable you to identify what you have learned from reading your programme. The exercises will assist you to be ready to complete your final examination. Try to answer each question thoroughly and only include relevant information in the answers. You may find it helpful to jot down your answers first in the ‘notes’ pages throughout your workbook. You can then summarise your information to contain only the main points, before writing your answers. Write your answers neatly in your workbook. If you have any difficulty finding answers to any of the questions, you must always ask for support. If you require additional space to write down your answers add loose pages to the workbook, making sure that they are securely attached and cannot get lost. When you have completed each module, remove the relevant sheets, staple them together and submit them to your tutor by the method agreed. Please remember to insert your name on each sheet of paper. Use the grid below (using a tick) to record the fact that you have submitted work to the tutor and that you have received it back with feedback. Modules Sent to Tutor 1 2 3 4 Received Back © NCC Asset Management and NCC Resources Ltd 2014 Product Code: NCCCW052 The author, publisher and distributor of this book have made every effort to ensure the accuracy, completeness and reliability of the content of this publication. In all instances you should take advice in relation to any local policies or procedures prior to making any decisions or taking any actions relating to the subject matter contained herein. No warranty is given or implied with respect to its content. Consequently in no event will the author, publisher or distributor be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequential damages arising out of the use of the information contained in this book. V1.0214 issue April 2014 Published by NCC Resources Ltd, Alexandra Business Park, Prescot Road, St Helens WA10 3TT Tel. 01744 639746 Fax 01744 639775 email enquiries@ncc.ac.uk Web www.ncc.ac.uk Module 1 - Medical vocabulary Activity 1.1 What is meant by the term root words? Give two examples of them. (1.1.1) Activity 1.2 What is meant by the term prefix? Give two examples of them. (1.1.2) Activity 1.3 What is meant by the word suffix? Give two examples of them. (1.1.2) Activity 1.4 Which of the digestive conditions directly affect the bowel? (1.2.1) Activity 1.5 If left untreated, what can high cholesterol levels result in? (1.2.1) Activity 1.6 What are polycystic ovaries? (1.2.1)