Market Research
advertisement

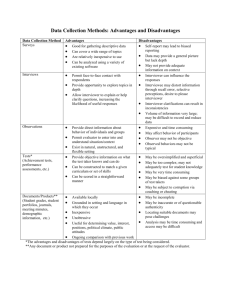
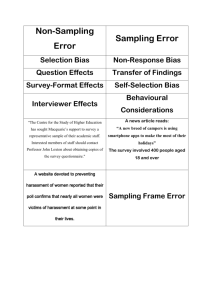
GENE452 Lecture #4 Marketing and Market Research Definition of business: “organised effort to produce goods or services in order to sell them to customers in order to make profit” This Presupposes: People exist who will buy it. • Market Research asks “Who are these people?” and “What do they want/need to buy?” • The activity of Marketing helps them make the decision to buy YOUR product or service. The Better Mousetrap "Though a man live deep within the woods, if he builds a better mouse trap, the world will beat a path to his door." Ralph Waldo Emerson American poet (1803 – 1882) Definition of Marketing “The process of planning and executing the Product concept, the Pricing, Promotion of and the Place of distribution of goods and services to satisfy customer needs.” • In your business plan, you must demonstrate to the reader, that you have grasped the "marketing concept" • This is the idea that the whole firm is directed toward satisfying present and potential customers, while making a profit. • Marketing is not about “selling them what you've got.” (product/technology focus) • Marketing is about “selling them what they want” (customer focus) Marketing Terms Market: “a group of individuals, that have needs for a product and have the ability, willingness and authority to buy them.” Target Market: ”The specific group for whom the firm develops and maintains a marketing mix suitable for the specific needs and preferences of that group.” Market Segmentation: “The act of dividing a market into addressable segments.” Market Segmentation – By Type The Consumer market (B2C) • Thousands maybe millions of potential buyers. • Geographically scattered • Tends to be low margin / high volume • Not necessarily sophisticated or knowledgeable. May contain strata (i.e. “pro-sumers”, DIY) Industrial markets (B2B) • Not necessarily a large number of buyers. • Possibly a specialist, knowledgeable buyer • Probably, clearly defined buying criteria Market Segmentation – By Demographics - age - gender - ethnicity - education - income - family status Market Segmentation – By Geography • • • • • rural or urban Alberta or Quebec North American, European, Asian northern or southern temperate or extreme Market Segmentation – By Psychography • • • • • • • personality - introvert or extrovert motivation - NAch, NAff, NPow selfish or altruistic religious or humanistic lifestyle - traditional or alternative lifestyle – healthy or hedonistic politics - liberal or conservative Market Segmentation – By Behaviour • Frequency/volume of purchases • Benefits desired in product (i.e. full featured vs easy-touse) • Where/when a product or service is used • Social settings Psycho-behavioural - The Technology Adoption Life Cycle1 Market size Early Market Mainstream Market The Chasm Time 2.5% Innovators 13.5% 34% 34% 16% Early Early Late Laggards Adopters Majority Majority Market Segmentation – By Industry By Industry (vertical) • SIC and NAICS codes • Describes role of entire value chain, or significant portion • i.e. steel industry, could include mining, smelting, rolling, slitting, fabricating, distributing By Industry (horizontal) • functional role in value chain • i.e. distributors, system integrators, discreet vs process manufacturers • size of firm • down a level, could include company position or org chart level – i.e. middle managers, line executives, CXOs Market Segmentation – Implications • Marketing budgets are finite. • Where do you focus detailed research? Geoffery Moore – Crossing the Chasm, Marketing and Selling Technology Products to Mainstream Customers (1999) 1 • • • • • • How do you reach potential customers? When? Where? Who are your competitors? What is the value? (How to “pitch”) Can segmentation lead to competitive advantage? Market research “The process of systematically organising, gathering, and analysing data concerning a particular marketing problem” • • • • • • • Helps to confirm and validate and your idea. Confirms if people perceive a real value in your technology Helps refine your value proposition into a more attractive proposal Used to help you refine your technology features by customer ranking Helps to understand the buying decision Helps to understand the real competitive advantage Helps to formulate a more detailed market strategy Two Flavours of Market Research Secondary Market Research Definition: “Use of sources that already exist, collected by someone else, collected for another or general problem.” e.g.: books, magazines, trade journals, census data, government data, industry statistics., etc. • • • • • Secondary market research answers the question: “Is there evidence that a market exists for this kind of product?” Do Secondary Market Research First It is quick. It is cheap. The general problem may already have been solved. Primary Market Research “Data collected or research conducted, by or for you.” • • • Designed to answer your specific questions. Solve your particular problem. Should answer questions: – – Is there market for our product? At our price? Secondary Market Research Secondary Market Research provides general market information Uses existing reference sources that have been collected by someone else, usually for another or general problem or to provide overall statistical information Research will answer questions such as: • • • • • • How many people are current buying this product or a similar product? What is the total dollars spent per annum by users? How do competitor products stack up and how d they sell their features? How is this product currently sold? How large is the current market and is it growing? Current industry trends and regulations. Design of this market research is equally important as there is so much data available, that you have to chose from hundreds of sources and find that which is most relevant. You then have to justify why you have selected this data to other partners and decide what this information shows you. Things that are you might to learn (provided you select the right sources) • • • • • • Current view of the problem Alternative solutions Current price points Potential market size Current distribution strategies. The real market opportunity Sources of this data include: • Web sites, industry association, published market reports, magazines, trade journals, census data, government data, industry statistics., etc. Primary Market Research Primary Market Research provides specific customer feedback Obtained on your value proposition, designed to answer your specific questions, such as: • Will customers pay $X for this product or service? • • • • What percentage of potential customers are likely to buy it? What are the most important features of this product? Who do potential customers view as competitors? Where will customers purchase the product? Design of this market research is very important as it is very expensive to undertake and may provide some very important feedback on key issues affecting the likelihood of success. Things that are you likely to learn (if you listen hard enough) • • • • • Real problem new technology addresses for the customer Whether or not customers are likely to pay for this solution Why they will buy it from a new venture (like yours) or wait until there are other players in the market. The rate of expansion of the business (S curve) May find a real customer Market research techniques 1 Primary Market Research Techniques: • • • • • Mail / e-mail / website questionnaire man-in street surveys telephone survey in-depth interview focus groups Two kinds of data: Quantitative vs. Qualitative Quantitative: • Statistically analysable • Generally requires large sample size • limited depth Qualitative: • Subjective, softer, more nuanced • Can generate hypotheses or ideas to be subsequently tested thru quantitative research • May involve smaller sample size Market research techniques 2 Two ways to collect data: Observation vs. Communication Observation • • • Only applicable if the product/service already exists. No interviewer bias. Answers "what", but not "why“ Communication • Researcher and respondent interact (directly or indirectly). • Risk of interviewer bias. • Opportunity to sell. • Opportunity to “chain” questions and dig deeper, discover unexpected patterns Principal Market Research Techniques - Advantages and Disadvantages - 1 Mail Survey Advantages • Relatively low cost • Wide geographic coverage • No interviewer bias • Respondent has time to think Disadvantages • Poor response rate and doesn't ensure qualified response • Little flexibility and Inability to probe • Poor turnaround time Tips: • S.A.E. • Phone follow up • 2 pages max • offer incentives Internet Survey (email or website): Advantages • Quick • Very low cost • Good for B2B research • Can tailor to push (email) or pull (website) Disadvantages • Skewed demographic sample • Questionable quality of mailing lists • Little ability to probe (but better than mail – can use adaptive questions) • Spam filters Tips: • Phone follow up • Keep screen changes to a minimum • offer incentives Principal Market Research Techniques - Advantages and Disadvantages – 2 Telephone Surveys Advantages • Ensures qualified respondent • Relatively wide geographical Coverage • Ability to probe • Good turnaround time (quick) and good response rate Disadvantages • Medium cost • No time to think • Voice mail / Receptionist • Labour intensive and can't be too personal Tips: • Develop script for consistency and test it out • Let people know how long it will take upfront (be honest) Man in Street Surveys Advantages • Quick way to get sizeable sample and good response rate • Can see respondent, gives some flexibility/ability to probe • Easy demographic identification Disadvantages • Limited geographic scope • Doesn't ensure qualified response • Respondents have no time to think • Very labour intensive/high cost and possible Interviewer bias Tips: • Use 2 or 3 different locations to avoid geographical bias Principal Market Research Techniques - Advantages and Disadvantages - 3 In-Depth one-on-one Interview Key is to ensure respondent is well informed, knowledgeable, representative. Appropriate for industrial market • Best for sophisticated product • Best for qualitative data Advantages • Ensure qualified respondent • • Ability to probe • Good response rate • Good qualitative data Disadvantages • Interviewer bias • Poor turnaround time • High cost • Limited geographic scope • Focus group • In depth but unstructured interview with medium size sample of the target market • Assemble 6 - 10 interested parties: experts / target market / suppliers • Use conference or "round table" setting • Use moderator / facilitator to introduce and "shepherd" discussion • Create an "open-end discussion" atmosphere • Take notes, video tape, or record participants‘ comments • Focus group works like a channelled "brain storming" session Advantages • Great qualitative data • New, unexpected data • Can avoid interviewer bias (if done properly) Disadvantages • Time consuming • Labour intensive • Can be expensive • Technique/art required Tips: • This will impress the Prof. Grocery Gateway • - How big will its revenue be in five years? Current revenue $100,000 25 customers Average grocery order $60 Charge $6 delivery charge Webvan (US) has market capitalization of $6 billion, forecasting annual revenues of $1 billion Why do Venture Capitalists require it? • Easy to obtain • AND very expensive to fix if wrong “Missionary sale”: dreaded words Market risk is - worse than: • • • Financing Risk Management Risk Technical Risk Market Research requirement … expensive to fix: • Astra Zeneca’s new statin – Crestor must displace some of Pfizer’s Lipitor market share • Analysts expect AZ to spend over $500 million in promotion, pre-launch through first year in US • What if promotion does not work? $500 million down the drain. Poor market research is very expensive Why not let potential VCs do it themselves? • They will either be familiar with your market and (a) think it’s a good opportunity (if YOU know the market too, you look good) • OR be familiar with your market and (b) think it’s a bad one (you need to convince them they are wrong) • OR be unfamiliar with your market and therefore less likely to be interested (lack of time) Don’t give them that excuse to say no. Be prepared. Sources of Market Research Sales of secondary research on the web . www.mindbranch.com . www.marketresearch.com . www.ecnext.com Specialized journals, like those published by Windhover, also searchable online (www.windhover.com -- do have teasers) Specialize in healthcare business intelligence Market Research Do I HAVE to do it? YES • Why waste your own time developing a product with no possible market? • Knowing the market BEFORE you develop will affect sales • Knowing the market will probably land you funding. Market Research Not only can it tell you comparable sales growth and approximate market size.. It can help you understand pricing and comparable profit margins It can also lead you to likely funders in your industry…… Market Research • So which is it? Specific or Optimistic? It sounds as if: • 1) better be specific as possible • 2) but also look at the largest potential YES – be specific so (1) you know what to tell funders, honestly, and (2) focus – but imagine the larger market, and plan strategically Market Research: competition Company NewcoBos Sandico YOUR CO Founded 1999 1998 2004 No. Employees 20 35 5 Revenues $12 million $150 million N/A Product name Ok seller Best seller Super Drug Product price $1,000/year $700/year $500/year Benefit A NO YES YES Benefit B NO NO YES Benefit C NO NO YES Location Boston San Diego Baltimore Funders ATV, Sutter Domain Bio Ventures