Advertising Objectives - UoM
advertisement

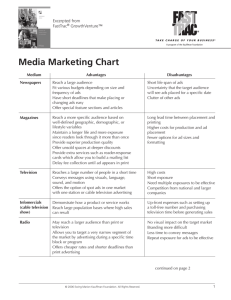
Advertising Objectives Informative advertising Persuasive advertising Reminder advertising Reinforcement advertising Teaser ads Developing Effective Communication Step 1: Identifying the Target Audience Affects decisions related to what, how, when, and where message will be said, as well as who will say it Step 2: Determining Communication Objectives Six buyer readiness stages Goal 3: Learn the steps in developing effective marketing communications Buyer-Readiness Stages Awareness Knowledge Liking Preference Conviction Purchase Goal 3: Learn the steps in developing effective marketing communications Developing Effective Communication Step 3: Designing a Message Message contains appeals or themes designed to produce desired results Rational appeals Emotional appeals Love, pride, joy, humour, fear, guilt, shame Moral appeals Cognitive strategies Affective strategies Goal 3: Learn the steps in developing effective marketing communications Cognitive • Generic • Preemptive • Unique selling proposition • Hyperbole • Comparative Affective • Resonance • Emotional Personal Values • • • • • • • • Comfortable life Equality Excitement Freedom Fun, exciting life Happiness Inner peace Mature love • • • • • • • • Pleasure Salvation Security Self-fulfilment Self-respect Sense of belonging Social acceptance Wisdom Advertising Appeals • • • • • • • Fear Humour Sex Music Rationality Emotions Scarcity Behavioural Response Model • Severity • Vulnerability • Negative behaviour Intrinsic reward Extrinsic reward • Change behaviours Response costs Self-efficacy Response efficiency Developing Effective Communication Message Structure: Key decisions are required with respect to three message structure issues: Whether or not to draw a conclusion One-sided vs. two-sided argument Order of argument presentation Message Format: Design, layout, copy, color, shape, movement, words, sounds, voice, body language, dress, etc. Goal 3: Learn the steps in developing effective marketing communications Structure of an Advertisement • • • • • • Headline Sub-headline Promise of a benefit Amplification Proof of claim Action to take Verbal and Visual Elements • Balance • Visual processing Easier to recall Stored as pictures and words Concrete vs. abstract • Radio visual imagery • Visual esperanto • B-to-B advertisements Executional Frameworks • • • • • • • • Animation Slice of life Dramatisation Testimonial Authoritative Demonstration Fantasy Informative Developing Effective Communication Step 4: Choosing Media Personal communication channels Includes face-to-face, phone, mail, and Internet chat communications Word-of-mouth influence is often critical Buzz marketing cultivates opinion leaders Non-personal communication channels Includes media, atmosphere, and events Goal 3: Learn the steps in developing effective marketing communications Choosing Among Major Media Types Target audience and media habits Product characteristics Message characteristics Cost Media Selection • • • • Reach Frequency Impact Exposure Major Media Types Newspapers Television Direct mail Radio Magazines Outdoor Yellow pages Newsletters Brochures Telephone Internet Television Advantages Reaches broad spectrum of consumers Low cost per exposure Ability to demonstrate product use Ability to portray image and brand personality Disadvantages Brief Clutter High cost of production High cost of placement Lack of attention by viewers Print Ads Advantages Detailed product information Ability to communicate user imagery Flexibility Ability to segment Disadvantages Passive medium Clutter Unable to demonstrate product use Print Ad Evaluation Criteria Is the message clear at a glance? Is the benefit in the headline? Des the illustration support the headline? Does the first line of the copy support or explain the headline and illustration? Is the ad easy to read and follow? Is the product easily identified? Is the brand or sponsor clearly identified? Developing Effective Communication Step 5: Selecting the Message Source Highly credible sources are more persuasive A poor spokesperson can tarnish a brand Step 6: Collecting Feedback Recognition, recall, and behavioural measures are assessed May suggest changes in product/promotion Goal 3: Learn the steps in developing effective marketing communications Principles Effective Advertising • • • • • • Visual consistency Campaign duration Repeated tag lines Consistent positioning Simplicity Identifiable selling point Beating Ad Clutter • • • • • • Presence of competitive ads Repetition Variability theory Multiple media Ads that gain attention Ads that relate to the target audience