M1_pretest_3B.qxd:English Aeronautics WEB
advertisement
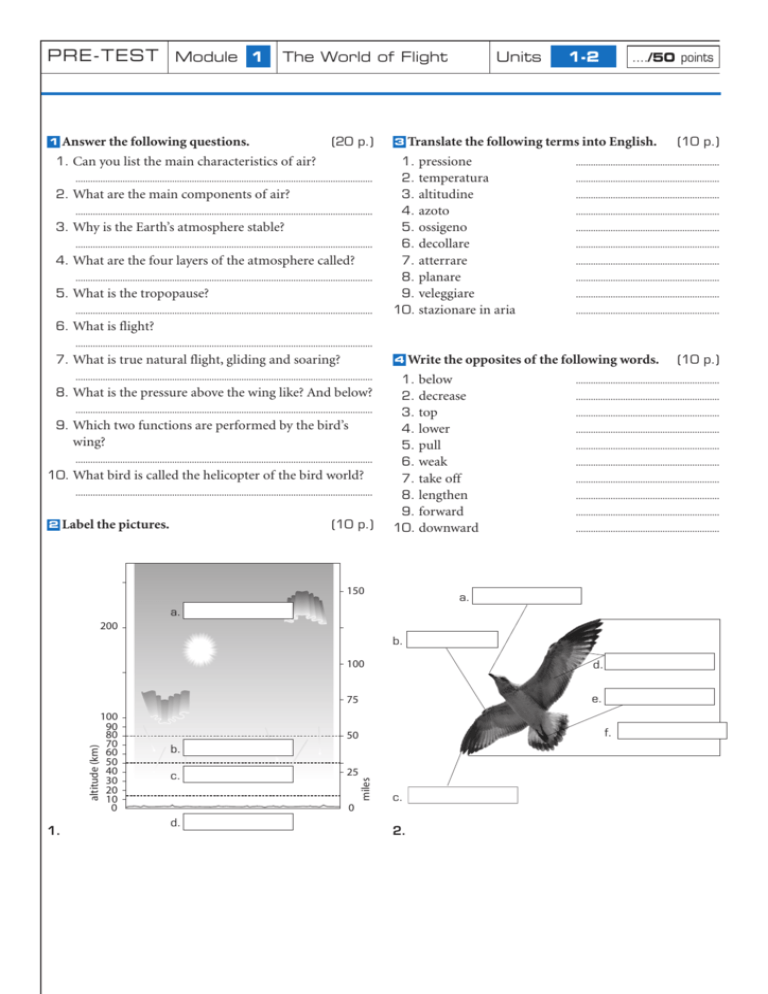
PRE-TEST Module 1 1 The World of Flight Answer the following questions. (20 p.) 1. Can you list the main characteristics of air? ........................................................................................................................ 2. What are the main components of air? ........................................................................................................................ 3. Why is the Earth’s atmosphere stable? ........................................................................................................................ 4. What are the four layers of the atmosphere called? ........................................................................................................................ 5. What is the tropopause? ........................................................................................................................ 3 Units 1-2 ..../50 points Translate the following terms into English. 1. pressione 2. temperatura 3. altitudine 4. azoto 5. ossigeno 6. decollare 7. atterrare 8. planare 9. veleggiare 10. stazionare in aria (10 p.) .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... 6. What is flight? ........................................................................................................................ 7. What is true natural flight, gliding and soaring? 4 ........................................................................................................................ 8. What is the pressure above the wing like? And below? ........................................................................................................................ 9. Which two functions are performed by the bird’s wing? ........................................................................................................................ 10. What bird is called the helicopter of the bird world? ........................................................................................................................ 2 Label the pictures. (10 p.) Write the opposites of the following words. 1. below 2. decrease 3. top 4. lower 5. pull 6. weak 7. take off 8. lengthen 9. forward 10. downward 150 .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... .......................................................... a. a. 200 b. 1. 100 d. 75 e. f. 50 b. c. 25 miles altitude (km) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 c. 0 d. 2. (10 p.) PRE-TEST Module 1 1 The World of Flight Fill in the blanks. (15 p.) 1. In ancient times people told of magic .................................. carpets and .................................. horses. 2. The most famous legend was that of Daedalus and Icarus who .................................. on wings of waxed feathers. 3. On June 5, 1783, the Montgolfier brothers made the first .................................. rise. 4. In 1784, another Frenchman, Jacques Charles, constructed the first .................................. balloon. 5. The first large rigid .................................. was built by Ferdinand von Zeppelin and flew on July 2, 1900. 6. Hydrogen was replaced by .................................. on dirigibles because it is not inflammable. 7. The Wright brothers built a .................................. onto which they mounted an engine. On December 17, 1903, Orville Wright flew the first .................................. . 8. During the Second World War, airplanes became a fundamental weapon in military .................................. control. 9. After the Second World War, civil aviation was improved with the construction of big jet .................................. . 4 Complete the following timeline. Units 3-4 ..../40 points 10. The ‘space age’ is a period in which at first artificial and then .................................. with men aboard were sent into .................................. . 11. In the last years of the 20th century new .................................. and new aircraft were developed. .................................. 2 Compound Nouns. Translate the following phrases (5 p.) into your language. 1. Air speed difference 2. Sea level density 3. Man-powered flight 4. Wing-like membranes 5. Wing top surface 3 ........................................................................ ........................................................................ ........................................................................ ........................................................................ ........................................................................ What are these people famous for? 1. Daedalus and Icarus 2. Jacques Charles 3. Henri Giffard 4. Otto Lilienthal 5. Wiley Post 6. Igor Sikorsky 7. Charles Yeager (7 p.) ........................................................................ ........................................................................ ........................................................................ ........................................................................ ........................................................................ ........................................................................ ........................................................................ (13 p.) Leonardo da Vinci German engineers Neil Armstrong NASA Louis Blériot Ferdinand von Zeppelin 1400 1783 1900 European project Yuri Gagarin 1903 First airplane 1909 1927 1939 1947 1961 1969 1981 First plane Sound barrier Balloon First Atlantic crossing Space Shuttle 1997 2007 PRE-TEST Module 1 1 The World of Flight Answer the following questions. (20 p.) Unit 5 ..../50 points 5. There are no differences between a glider and a sailplane. 1. What is an aircraft? ........................................................................................................................ 2. What are the two main classifications of aircraft? ............................................................................................................................ 6. Unconventional planes can be classified into landplanes, seaplanes and amphibians. ........................................................................................................................ 3. Which force must be overcome to make an aircraft fly? ........................................................................................................................ 4. What do aerostats and aerodynes derive their rising capability from? ............................................................................................................................ 7. S/VTOL need a runway to take off. ............................................................................................................................ 8. An autogiro, like a helicopter, can hover. ............................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ 5. What’s the difference between a balloon and a 4 dirigible? ........................................................................................................................ a Write the names of these aircraft. b 6. How are aerodynes classified? ........................................................................................................................ 7. What do unpowered craft include? ........................................................................................................................ 8. What do powered craft include? ........................................................................................................................ 9. What do unconventional craft include? ........................................................................................................................ c d e f g h i j 10. What’s the difference between an autogiro and a helicopter? ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ 2 Write a definition for each of the following terms. (12 p.) 1. aerostat 2. aerodyne 3. balloon 4. glider 5. amphibian 6. STOL 3 ............................................................................................... ............................................................................................... ............................................................................................... ............................................................................................... ............................................................................................... ............................................................................................... Find the mistake in seven of these eight sentences. (8 p.) 1. A synonym for aerodyne is lighter-than-air craft. ............................................................................................................................ 2. Balloons contain a gas heavier than air. ............................................................................................................................ 3. A dirigible balloon is driven through the air thanks to the propeller. ............................................................................................................................ 4. Unpowered craft are aircraft which utilize an engine. ............................................................................................................................ (10 p.) Module 1 4 Something more about… THE WORLD OF FLIGHT IN-DEPTH ANALYSIS TEXTS A The atmosphere of Earth The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth’s gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night. Dry air contains roughly (by volume) 78.09% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.039% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1%. The atmosphere becomes thinner and thinner with increasing altitude, with no definite boundary between the atmosphere and outer space. An altitude of 120 km (75 mi) is where atmospheric effects become noticeable during atmospheric reentry of spacecraft. The Kármán line, at 100 km (62 mi), also is often regarded as the boundary between atmosphere and outer space. B Birds’ and airplanes’ flight For the most part, birds and airplanes fly for the same reasons. If we look at the shape of a bird’s wings, we will see they are curved the same way airfoils on airplanes are. When a bird glides during level flight, it stays in the air just like airplanes do – its wings provide the lift. However, birds flap their wings up and down to go higher in the sky while airplanes must use a combination of control surfaces and their powerful engines. In the 19th century, before airplanes were around, some inventors tried strapping homemade wings to their arms and jumping off buildings to copy the flapping motion of birds – usually with deadly results. Unlike humans, birds have strong wing muscles that give them the power needed for flight; what’s more their bones are hollow (i.e. empty, not solid). So, after millions of years of evolution, birds and insects continue to fly on their own, but humans still have to depend on machines like airplanes. C The helicopter A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by one or more engine-driven rotors. In contrast with fixed-wing aircraft, this allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forwards, backwards and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft would not be able to take off or land. The capability to efficiently hover for extended periods of time allows a helicopter to accomplish tasks that fixed-wing aircraft and other forms of vertical takeoff and landing aircraft cannot perform. Though most earlier designs used more than one main rotor, it was the single main rotor with antitorque tail rotor configuration of this design that would come to be recognized worldwide as the helicopter. LINKS http://www.espo.nasa.gov/solveII/outreach/middleschool-atmos.htm (Atmosphere) http://www.ucar.edu/learn/1.htm (Earth and atmosphere) http://www.ornithopter.org/how.fly.shtml (Birds and ornithopters) http://www.allstar.fiu.edu (History of Aeronautics Level 3 History of Flight) http://www.spiritus-temporis.com/aircraft/categories-and-classification.html (Aircraft classification) VIDEOS YouTube Atmosphere layers YouTube How birds fly How birds fly + How birds fly (animation) http://videos.howstuffworks.com/nasa/2198-a-history-of-flight-pioneers-video.htm (How men learned to fly) YouTube Wright Brothers’ First Flight YouTube Aircraft