Unit outline
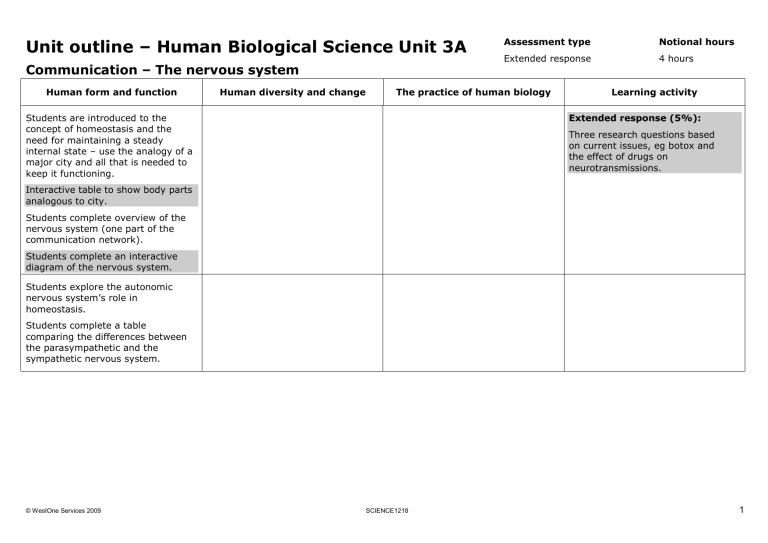
Unit outline – Human Biological Science Unit 3A
Communication – The nervous system
Human form and function Human diversity and change
Assessment type
Extended response
The practice of human biology
Students are introduced to the concept of homeostasis and the need for maintaining a steady internal state – use the analogy of a major city and all that is needed to keep it functioning.
Interactive table to show body parts analogous to city.
Students complete overview of the nervous system (one part of the communication network).
Students complete an interactive diagram of the nervous system.
Students explore the autonomic nervous system’s role in homeostasis.
Students complete a table comparing the differences between the parasympathetic and the sympathetic nervous system.
© WestOne Services 2009 SCIENCE1218
Notional hours
4 hours
Learning activity
Extended response (5%):
Three research questions based on current issues, eg botox and the effect of drugs on neurotransmissions.
1
Unit outline – Human Biological Science Unit 3A
Communication – The endocrine system
Human form and function Human diversity and change
Assessment type
Extended response,
Tests and examinations
The practice of human biology
Notional hours
7 hours
Learning activity
Students will be introduced to the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands.
Interactive diagram (drag and drop) to demonstrate the location of glands in the body.
Students will explore the structure of hormones.
Answer a question on current hormonal replacement practices.
Mode of action of hormones.
Interactive diagram of hormone and receptor site.
Students learn about the relationship between the hypothalamus and pituitary.
Interactive true/false based on text material.
Students will be introduced to the endocrine glands and their respective hormones, target organs and actions.
Using references students will complete a table and answer questions.
Students will explore negative feedback loops involving endocrine activity.
Extended response (5%):
Students will be presented with a short passage describing the
‘hormonal life’ of a family and will then do an analysis on what hormonal activity will be occurring in each family member, students will draw feedback loops and suggest strategies to rectify the hormonal situations. The second part of the assessment relates to a graph showing the menstrual and ovarian cycles with a set of interpretation questions.
© WestOne Services 2009 SCIENCE1218
2
Human form and function
Interactive activities and documents using examples of feedback diagrams. Students explore and then compare an air conditioner’s thermostat to feedback mechanisms in the body.
Negative feedback mechanisms for example, metabolic rate, body temperature, blood glucose and fluid regulation.
Cyclic control of ovarian and menstrual cycles is illustrated using a diagram of a wheel – the various stages of each cycle need to be placed within the diagram by students.
A comparison of nerve and hormonal modes of action is presented in a table that students need to complete
(drag and drop correct information.)
Students revise topic with reflection questions.
© WestOne Services 2009
Human diversity and change The practice of human biology
SCIENCE1218
Learning activity
3
Unit outline – Human Biological Science Unit 3A
Homeostasis
Human form and function Human diversity and change
Assessment type
Investigation
The practice of human biology
Cellular activities
Students revise cell membrane structure relating it to its role in the transport of substances.
Students use search engine to find animation displaying movement of substances through a membrane.
Complete reflection questions for the concept above.
Students investigate the role of cell membrane structure and function in active transport and as a receptor.
Practical activity – ‘Making membranes’. Using simple materials, students will make membranes, record observations and answer questions.
Students explore how DNA controls the production of cellular materials.
General DNA revision activity from website.
Analogy activity – students compare
DNA to a DVD using a table.
Notional hours
9 hours
Learning activity
Students conduct a laboratory experiment to investigate the properties of a cell membrane.
Students identify a problem to formulate hypothesis, then plan and conduct a safe and ethical investigation incorporating two different methods to collect data.
This is a long-term investigation based on one aspect of the student’s own homeostatic mechanisms.
Investigation:
1. Practical exercise – ‘Making membranes’ (3%).
2. Long-term investigation (10%).
This will involve students planning and conducting an investigation using their own body temperature over an extended period of time.
Students will present their findings as a scientific report.
© WestOne Services 2009 SCIENCE1218
4
Human form and function
Homeostasis by feedback systems
Students work through interactive presentations to understand components of a stimulus–response feedback model, then explore each of the homeostatic mechanisms listed:
Body temperature (Drag and drop activity, linking of terms, feedback model exploration.)
Body fluid composition
(Questions from text and completion of feedback model.)
Blood glucose (Definition linking activity, feedback model completion.)
Gas concentrations (Diagram label linking activity, summary completion and feedback model completion.)
Blood pressure (Summarise information from references then complete table and feedback models.)
© WestOne Services 2009
Human diversity and change The practice of human biology
SCIENCE1218
Learning activity
5
Unit outline – Human Biological Science Unit 3A
Disruption to homeostasis
Human form and function Human diversity and change
Assessment type
Extended response,
Tests and examinations
The practice of human biology
Notional hours
8 hours
Learning activity
Students will investigate the main causes of homeostatic dysfunction and the methods of controlling and treating conditions: hormonal, behavioural, disease.
1. Hormonal
Reflective activity – endocrine glands (interactive).
True/false quiz – diabetes type 1 and 2.
Diagnosis of thyroid conditions activity.
Matching symptoms of menopause with body system dysfunction.
Summary of hormonal causes of disruption to homeostasis – interactive tables for students to complete.
Website search – treatments for hormonal conditions.
2. Behavioural
Note taking activity using web and other references – exploring eating disorders, drug use and physical activity.
Graph interpretation and questions – obesity in Australia.
Extended response (5%):
Students will research and present information on how diabetes affects teenagers. Also, they will consider a young, infertile couple’s dilemma when faced with how to start a family.
© WestOne Services 2009 SCIENCE1218
6
Human form and function
3. Disease
Watch videos about a range of diseases, eg cancer, heart attack, stroke and emphysema – and take notes.
Control of homeostatic dysfunction and hormone replacement therapies to assist treatment of:
hypo/hyperthyroidism
diabetes
menopause
reproductive dysfunction.
Summary/definitions of reproductive technologies.
Table summarising the risks, benefits and ethical concerns surrounding four reproductive technologies.
© WestOne Services 2009
Human diversity and change The practice of human biology
SCIENCE1218
Learning activity
7
Unit outline – Human Biological Science Unit 3A
Gene expression
Human form and function Human diversity and change
Assessment type
Investigation
The practice of human biology
Modes of inheritance and variation – polygenic inheritance (no dihybrid crosses).
Revision activity (drag and drop)
‘Genetic terminology’
‘Classifying characteristics’ activity
– students use text to help classify a range of human features as monogenic or polygenic
(interactive).
Polygenic gene combination activity
– students predict and record gene combinations from hypothetical parents in interactive table.
Research activity – symptoms and causes of polygenic conditions.
Multi-allelic inheritance
After reading through explanation of multi-allelic inheritance, students complete the following:
Application of knowledge questions.
Problems activity and ‘Hospital CSI’ exercise.
Website interactive – review of concept.
The effect of the environment on gene expression. Introduction to epigenetics: Students use websites and text for information then engage in questions to test knowledge.
Notional hours
7 hours
Learning activity
Investigation:
Lab exercise (3%)
Polygenic inheritance – using the scenario of a family with a history of cardiovascular disease, students interpret data and provide explanations for possible outcomes.
© WestOne Services 2009 SCIENCE1218
8
Unit outline – Human Biological Science Unit 3A
Variation and gene pools
Human form and function Human diversity and change
Assessment type
Extended response
The practice of human biology
Gene pools are affected by evolutionary mechanisms including natural selection and chance occurrences.
Interactive revision activity to review evolution.
Changes in allele frequencies due to:
mutation
Classification activity for chromosome and gene mutations.
natural selection
incidence of genetic disease in various populations, eg Tay-
Sachs disease
Students use the human example of sickle-cell disease to explore natural selection. They will use a website and interactive map to interpret reasons for the disease remaining in the population.
random genetic drift including founder effect
Research activity on founder effect.
migration
barriers to gene flow, eg geographical and cultural.
Interactive activity on factors favouring gene pool stability.
Notional hours
8 hours
Learning activity
Extended response (5%):
Students will apply their knowledge to a hypothetical gene pool scenario, calculating allele frequencies and answering questions. They will then report on a genetic condition.
© WestOne Services 2009 SCIENCE1218
9
Unit outline – Human Biological Science Unit 3A
Speciation and evidence for evolution
Human form and function Human diversity and change
Assessment type
Investigation,
Tests and examinations
The practice of human biology
Notional hours
9 hours
Learning activity
Speciation
Define and then complete questions.
Watch animation to review concept.
Evidence for theory of evolution by natural selection:
comparative studies of anatomy and homologous structures
Students match limbs of vertebrates interactively.
vestigial organs
Students use a website to assist in answering questions on vestigial organs.
embryology
Students watch a short video from website then answer questions using diagram comparing embryos.
DNA, protein sequences
Using an interactive table comparing humans to other primates, students will learn how these studies provide evidence for evolution. They will graphy the data to visualise the differences.
fossil record.
Definitions and types:
Using references students will complete an interaction on choosing the conditions that best promote fossilisation.
Investigation:
Lab exercise (4%)
Students ‘model’ half-life using a simulation then interpret results.
Then they apply their knowledge to examples of fossil remains to date them.
© WestOne Services 2009 SCIENCE1218
10
Human form and function Human diversity and change
Linking activity – students will link the definition with type of fossil.
Dating
Students will explore the different types of dating:
relative dating:
Complete an interaction on correlation of rock strata.
Writing activity on index fossils and graph interpretation.
Geological time scale interactive activity.
absolute dating:
Linking activity of dating types with the materials that can be dated.
carbon 14:
Students complete ‘Radioisotope decay’ interaction.
Graphing half-life activity.
Problems associated with the fossil record.
Students research and summarise problems.
Interactive activity to review natural selection concepts.
The practice of human biology
© WestOne Services 2009 SCIENCE1218
Learning activity
11