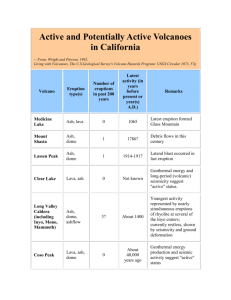
Volcanoes lesson
advertisement

Volcanoes lesson Learning objectives: nature of molten rock = lava. Simple terminology (lava, magma, erupt, pumice, hawaiian, plinian). Features of a hawaiian eruption. Handle basalt samples. Features of plinian eruption. Historical significance of Vesuvius AD79. Handle pumice and identify properties (density) and causes (bubbles). Scale of plinian eruptions. Why explosive? (dissolved gases in ascending magma cf. fizzy drink uncapped). 1 Who's been on a volcano? Who's been to Tenerife / Santorini / Hawaii / Iceland`? None in UK (though can see volc rocks in NW Scotland (55 Ma), Lakes (400 Ma) So have to travel overseas to see volcanoes in action: Hawaii in Pacific and Naples in Italy Q. What is a volcano? How would you describe to someone what a volcano is? A volcano is a place where molten rock comes out of the ground. Erupts. Often you see a hill or mountain, but sometimes not. (All that remains of the biggest volcanoes is a big lake.) Q. What name(s) do we give to molten rock: Lava (when flowing on the surface) Magma (when still under the ground, before it erupts) 2 Hawaii (globe) 3 What is lava like? How sticky/stiff, how hot? Bright red hot - means about 850˚C or above. Note cools to a black rock (basalt). Molten basalt is 1100–1200˚C Video of lava flowing. Behaves like syrup/treacle/porridge/custard Note pleated folds, very characteristic of Hawaiian basalts 4 What are characteristics of hawaiian eruptions? Lava fountaining Lava lake Skin like custard/porridge - cracks glow 5 Lava lake erupting and bubbling. Get a feel for what it's like. 6 Lava tube Skin forms on flowing lava too. Forms a roof that becomes fixed, while red hot molten lava continues to flow underneath. Lava tube. Note not full: lava draining faster than replenished. Roof may collapse here and there, forming 'skylights' that allow us to see down into lava stream below. May drain entirely ... 7 Thurston lava tube in Hawai'i national park. See tide marks. 8 Movie of lava flowing vigorously in Halema'uma'u lava tube 9 Time-lapse movie of night's eruption from MLK vent, Pu'u O'o 10 Basalt magma can erupt in other ways too: firework show of Strombolian 11 Vesuvius in Italy (globe) - top missing - Gaius Plinius, or Pliny the Younger. Witnessed highly explosive eruption of Vesuvius in AD 79 from Misenum. Wrote first known account of a volcanic eruption, age 17. Hence this very explosive style of eruption is today know as a Plinian eruption after him. Y6 volcanoes talk 2010 1 Volcano then higher than it is today. 12 Map and position in Italy. Note how urban it is today. Where is Misenum? 13 Vesuvius today from Boscoreale (E). Mention umbrella pine. 14 Vesuvius today from excavated Roman town of Pompeii. Population in AD79 about 20k. Town completely buried by what was erupted from Vesuvius in AD79. Forgotten until archaeological excavations began in 1748 . 15 No pictorial record of AD79 eruption. For visual impression need to look a modern plinian eruptions. Mt St Helens volcano in Cascade Mountains, western USA (Washington). Globe. How it looked before 18 May 1980. From Johnston ridge 16 MSH after eruption. Ditto. Top missing, like Vesuvius. 17 MSH before, different veiw from Spirit Lake 18 MSH after. Ditto. Lava dome. 19 During. Ash column rose as a mushroom shaped cloud 25 km high (= roughly here to Huntingdon/Bicester), lasted 9 hours, ash fallout covering large parts of central N America. 20 Mushroom cloud of later MSH plinian eruption 22 July 1980. Umbrella pine. 21 What is the main product erupted in a plinian eruption? In ash cloud and what's deposited on the ground. Samples: Pumice. Describe: structure under magnifier; any shiny crystals? .... Q. What's special? Low density. Define. Sometimes floats on water. Krakatau. 1883. Show on globe. Q. Why? Bubbles. Q. Why bubbles? Fizzy drink. Gas dissolved under pressure. Q. What is 'pressure'? Compare fizzy mineral water bottle with natural. Gas forms bubbles and expands on release. 'Explodes' Magma rising from 10–30 km underground beneath MSH was very rich in dissolved gases (H2O, CO2, H2S, SO2) which exploded as it approached the surface (low pressure). Where do volcanoes occur (globe)? Ring of fire (V). Ocean ridges. Ocean islands (H). Why? Melting deep in mantle. 22 Back to Vesuvius. Excavated Roman villa. Can see thickness of beds of AD79 ash in cliff behind. Modern buildings on top. Measurements on the pumice and ash deposits around Vesuvius tell us that the Vesuvius ash column extended up to about 33 km - bigger than MSH, 3.6 km3 magma erupted. 23 Skeleton of Roman victim. Asphyxiated and burned by hot ash and gas 24 Naples hazard map. Potential casualties. 25 Pinatubo 12 June 1991 from Clark Air Base 20 km away (globe). Bigger than MSH. Column 35 km high (roughly here to Bedford/High Wycombe). 5–8 km3 magma erupted as pumice and ash. Circled globe in a few days. Climate effect. Y6 volcanoes talk 2010 2