Thinking Skills Across Learning
advertisement
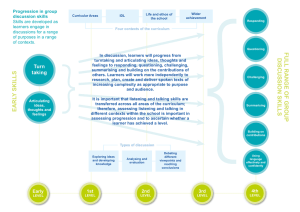
Thinking Skills Across Learning It is important that all learners are given appropriate opportunities to develop their thinking skills. These skills can be developed across a range of contexts including through more practical or applied learning opportunities: Remembering involves such activities as recall, recognition or locating information Understanding might involve activities such as describing, explaining, summarising and translating Applying requires the learner to use or apply their knowledge and understanding in different contexts Analysing requires learners to break down information into component parts and search for relationships Evaluating involves making an informed judgement about something, for example an issue or method. Activities such as comparing, appraising, prioritising, rating or selecting, could involve learners in evaluating Creating happens when learners are required to generate new ideas and products through activities such as designing, creative writing, planning, reconstructing, inventing, formulating, producing and composing Building the Curriculum 4 pg. 11 Practitioners and establishments should reflect on and build on their existing strengths as well as considering new approaches to developing thinking skills. The activity below has been designed to help practitioners begin to reflect on how they are developing thinking skills across the curriculum with their learners. Reflect on ‘where you are’ in developing ‘Thinking Skills’ with your learners. Where do you feel you are with this? - area of strength ? – some positives X – area of development Section 1: Plan for Developing Thinking Value Thinking Thinking skills are explicitly taught in authentic and meaningful contexts Time is planned for developing thinking skills with learners Tasks challenge learners across all the skills The learning area is organised to help facilitate thinking and dialogue Think about Thinking with your learners Allow time to review thinking (individually, paired and teacher led) Allow time to connect the thinking to new contexts, across the curriculum and beyond school Section 2: Develop a Shared Understanding Make Thinking Visible Model thinking through teacher dialogue (use of questioning, word banks/cards, posters etc.) Develop a thinking vocabulary (swatches, question stems etc.) Use thinking wall displays Use thinking diagrams to scaffold thinking (i.e. graphic organisers/ active learning structures) What evidence do you have? What could be your next steps?