Ecosystems and the Biosphere
advertisement

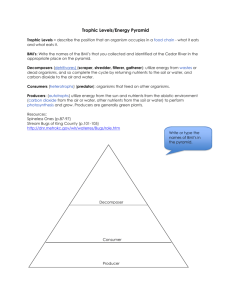
Ecosystems and the Biosphere Energy transfer All organisms need energy to carry out essential functions – growth, movement, maintenance, repair, and reproduction In ecosystems, energy flows from sun to autotrophs to organisms that eat autotrophs to organisms that feed on other organisms. Amount of energy ecosystem receives and the amount. transferred from organism to organism have an effect on the ecosystem’s structure. Energy Flow Whenever one organism eats another, molecules are metabolized and energy is transferred. Energy flows through an ecosystem from producer to consumer Trophic level indicates the organism’s level of nourishment, or position in the sequence of energy transfer illustration o First level – all producers o Second level – herbivores o Third level – predators of herbivoresFood chain – single pathway of feeding relationship that results in energy transfer (pic to right http://www.sugar.ca/english/images/tradealliances/food_chain.jpg) Grass (primary producer) to mouse to snake to hawk Feeding relationships in ecosystems are usually too complex to be represented by a single food chain. Many consumers eat more than one type of food and many organisms may feed on the same organisms. food webs are models of complex feeding networks within ecosystems; series of food chains interwoven (blue pic to left) http://www.absc.usgs.gov/research/seabird_foragefish/marinehabitat/images/Food_Web3.gif) Energy Pyramid – distribution of energy and matter in an ecosystem (pic to right http://www.mesa.edu.au/friends/seashores/images/energy_pyramid.gif) Shows the distribution of energy in a food chain Energy flows upwards from producers to consumers Energy is lost as head between each tier of the pyramid; average of 10% of energy is passesd from one level to the next level Other types of pyramids Biomass pyramid shows the total mass or organisms at each tropic level o Less biomass at higher tropic levels than lower levels Pyramid of numbers shows the actual number of organisms present in each trophic level (pic to right http://www.earthforce.org/files/1284_image2_Energy_Pyramid_for_Galvbay.jpg) Organisms that belong to the lowest trophic level are more abundant th an organisms in the highest level Example – in Africa you will see about 1000 zebras, gazelles, or other herbivores for every lion or leopard and there are a lot more grasses, trees and shrubs than there are herbivores