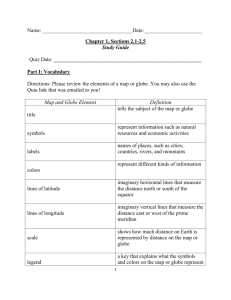
World Geography Introduction • is the study of everything on Earth
advertisement

World Geography Introduction • ________________________________ is the study of everything on Earth, from rocks and rainfall to people and places. • ______________________________ study how the natural environment influences people, how people’s activities affect Earth, and how the world is changing. • Geographers look at many different things including ___________________, _______________, ____________________, ____________________, and _________________________. Perspectives from Space • _______________________________ images have provided additional resources for geographers using a spatial perspective in their study of Earth. • Improvements in satellite technology and imagery now allow geographers to analyze climate and vegetation patterns over time. Who uses Geography? • People all over the world use geography every day. We use it when we find our way to ____________________ or _______________________ and go on _________________. • We also use it when we watch the news and read about other countries. Why use geography? • Most jobs ____________________ the understanding of geography. An example is a restaurant owner must find a good location. __________________________ need to know the geography of their districts. They must understand the issues that are important to the people in the area. REGIONS • Regions can be any size. ___________________________, ______________________, and ____________________________________ are examples of large regions. • Smaller regions include ____________________ and _____________________________. • Regions can also be divided into smaller areas called _________________________. • For example, the _________________________ is a sub-region within North America. Types of Regions • There are three types of regions: 1. ________________________ 2. ________________________3. _____________________ Formal Regions • Formal regions can be based on almost any feature or combination of features. • Those features may include _______________________, _______________________, ______________, ______________________________, or _______________________. • Physical features might define a formal region, such as the _________________________ in the western United States. • For example, an industrial area in the northeastern and Midwestern United States is also a formal region. This region was once called the ________________________ because so many old factories there had shut down. Functional Regions • Functional regions are made up of different places that are linked together and function as a unit. • An example of a functional region is a ________________________________. • The flow of people, trains, subways, and buses link those places together. • Many functional regions are organized around a central point. • Surrounding areas are linked to this point. ___________________________________are an example. Perceptual Regions • Human perception is the awareness and understanding of the ___________________________ around us. • Our views are influenced not only by what is in a region but also by what is in us. • Our _____________________ and ____________________ influence how we perceive the world. • Perceptual regions reflect human ____________________ and ________________________. • An example is “_________________________.” Organizing the Globe • A _____________________ is a of Earth. • One of the first things you will notice on the globe is a pattern of ____________________. • These lines circle the globe in ____________________________________ and ____________________________________ directions. • This pattern is called a _________________________________. • The grid is made up of lines of ______________________________ and ____________________________. Latitude • Lines of latitude are drawn in an east-west direction. • Lines of latitude measure the degree of distance __________________ or _________________ of the ____________________________. Longitude • Lines of longitude are drawn in a north-south direction. • As you see these lines of longitude extend from the north pole to the south pole. • Lines of longitude measure the degree of distance _____________________ or _____________ of the ________________________________. Latitude and Longitude • Lines of latitude measure distance north and south of the equator. • The equator is an imaginary line that circles the globe halfway between the Earth’s North Pole and South Pole. Parallels • Lines of latitude are also called _____________________________. • This is because they are always parallel to the equator and each other. Meridians • Lines of longitude are also called _________________________________. • They measure distance east and west of the Prime Meridian. • This is an imaginary line drawn from the North Pole to Greenwich, England to the South Pole. Measures of Longitude • Lines of longitude range from 0 degrees on the Prime Meridian to 180 degrees on the meridian in the mid-Pacific Ocean. • Meridians west of the prime meridian to 180 degrees are labeled with a W. Those east of the prime meridian are labeled with an E. • Unlike lines of latitude, lines of longitude are ______ ________________________ to one another. Hemispheres • The globe’s grid does more than help us locate places. • Geographers also use grid lines to organize the way we look at the world. • For example the equator divides the globe into two halves or ______________________________. • The half lying north of the equator is the Northern Hemisphere and the southern half is the Southern Hemisphere. • The United States is located in the northern hemisphere. Australia is located in the southern hemisphere. • The Prime Meridian and the 180 degree meridian divide the world into the Eastern Hemisphere and Western Hemisphere • The Eastern and Western Hemispheres are officially divided in the ___________________ Ocean at 20 degrees W. • Due to this division along the Prime Meridian and 20 W, all of _____________________________ and _________________________________ are located in the Eastern Hemisphere. Continents • There are seven continents: • __________________________ • __________________________ • __________________________ • __________________________ • __________________________ • __________________________ • __________________________ • Asia, the largest continent, is five times the size of Australia, the smallest. • Landmasses smaller than continents and surrounded by water are called islands. • ______________________________ is the world’s largest island. Oceans • The ____________________________ areas of water are the global oceans. • Geographers divide these oceans into four areas: the Atlantic Ocean, the Arctic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and the Pacific Ocean. • The ________________________ Ocean is the largest ocean and the world’s largest geographic feature. • It is more than 12 times the size of the smallest ocean, the ___________________________. Maps Geographers use maps to study the Earth. ________________ are _____________ representations of all or parts of Earth’s surface. A ___________________________ of maps in one book is called an _______________. Distance Scales A map’s _______________________ helps us determine __________________distances __________________________ points on a map. On _______________________ maps objects are relatively __________________, whereas on ________________________ maps objects are relatively ____________________. Some may show just one or two miles while others illustrate a few hundred feet. Maps showing larger distances, may cover hundreds and thousands of miles. Directional Indicators A ____________________________________ shows which direction on a map are ________________, __________________, __________________, and __________________. Some mapmakers use a north arrow which points toward the North Pole. Most maps show _______________________ with a ______________________________. Compass Rose A compass rose has arrows that point to all four ___________________________________ (also called ________________________________________). Legends A map’s __________________________, or ______________, identifies the symbols on a map and what they ____________________________________. They may show _______________________, __________________________, or ___________________________ to represent many different kinds of features on a map. Inset Map An _______________________________ is another special element. Inset maps are used to focus in on a ___________________________ part of a ____________________________ map. Some inset maps also show areas that are far away from the main areas of the ______________________________ Climate and Precipitation Maps Some mapmakers use maps to show ____________________________________and __________________________________________. _____________________ maps use ____________ to show various climate regions of the world. Precipitation Maps _____________________________maps show average amount precipitation that a region gets each year. _______________________________refers to condensed droplets of water that fall as rain, sleet, hail, or snow. Each map’s ________________________ uses ___________________ to identify those amounts. By using the legends, you can see which areas receive the most precipitation. Population Maps ___________________________maps give you a snapshot of distribution of people in a region. Each color may represent an _________________________________________ of people living within a square mile. Economic Maps ___________________________maps show a region’s important natural resources and the ways in which land is used. Some maps will show where land is used for farming or other economic activities. Elevation Profiles Some maps focus on an area’s land features. For example, you can see that each ________________________ map in this textbook uses ______________________ to show land _______________________________. _____________________________ is the ____________________ of the land ________________________________________. Each _____________________ represents a different ________________________________. An ________________________________________shows a side view of a place or area. _____________________________distances are measured __________________________, while _____________________________ distances are measured_______________________________. Topographic Maps The purpose of some maps is to show just the__________________________, __________________________, ______________________, and _________________ of the land. Contour Map A special kind of topographical map is called a __________________________ map. ________________________________ provide a way of looking at the __________________________ of land in an area. They use ________________________________to connect points of _____________________ elevation above or below sea level. The _________________________ the lines are to each other, the _____________________ the land. Climate Graphs _________________________ graphs show the average temperatures and precipitation in a place.