Geological and Physical Factors of the Marine
advertisement

Geological and Physical Factors of the Marine Environment
1. The Sea Floor
a. The oceans cover most of the globe (71%) and play a crucial
role in regulating our climate and atmosphere
b. Average depth of the oceans is 4 km (3800 m). Pacific is the
deepest, Arctic is the shallowest.
2. Geography of the Ocean Basins
a. Oceans are divided into 4 large basins: Atlantic, Pacific,
Indian & Arctic
3. Topography of the ocean Floor
a. Continental Margins
i. Continental Shelf
The part connected to the continent
8% of the ocean floor
Most productive portion of the ocean. Has most
life (more Fishing)
Atlantic side of N. America is wide, Pacific side is
narrow
Drops off at approximately100-200 meters
ii. Continental Slope
Steeper gradient to the ocean floor
Edge of the continent
iii. Continental Rise
The boundary between the continental slope and
the ocean floor
b. Ocean Basin
i. Abyssal Plains – flattest part of the Earth
ii. Abyssal Hills – small hills on the abyssal plains
iii. Seamount – underwater volcanoes
iv. Trenches – deepest part of the ocean
v. Guyots – flat topped seamounts
vi. Ridges – mountain ranges within the ocean
vii. Rifts – cracks that are found generally by the ridges
c. Mid Ocean Ridges – formed when material rising from below
the mantle pushes up on the oceanic crust
i. Central Rift Valley – a great gap or depression caused
by the plates pulling apart at the center of the ridge
ii. Hydrothermal Vents – water seeps down through the
rifts, gets heated and forces its way back up thorough the
crust
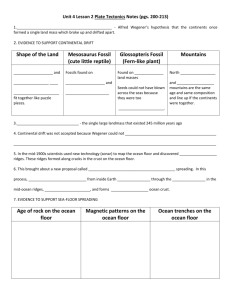
4. Plate Tectonics – the mid-ocean ridge system is a continuous chain
of submarine volcanoes that run through the ocean basins.
Earthquakes and volcanoes are associated with the mid-ocean ridge.
The Earth’s surface is broken up into a number of plates that are
separated by the earthquake belts, which are trenches, ridges and
faults.
a. There are 7 major plates:
i. North American
ii. African
iii. Indian Australian
iv. South American
v. Eurasian
vi. Pacific
vii. Antarctic
b. Plate Boundaries
i. Convergence – 2 plates coming together
→} {←
The site of mountains
ex. Himalayas
ii. Divergence – 2 plates separating
←} {→
The site of sea floor spreading
New sea floor is formed
ex. Mid Atlantic Ridge
iii. Subduction – 1 plate goes under the other
The site of trenches
Where old sea floor is destroyed
ex. Hawaii, Marianas Trench
iv. Transform Fault – 2 plates going in opposite directions
↑} {↓
Site of earthquakes
Fault is a crack in the Earth’s crust
ex. San Andreas Fault