Genetics: Single & Double Trait Crosses Worksheet
advertisement

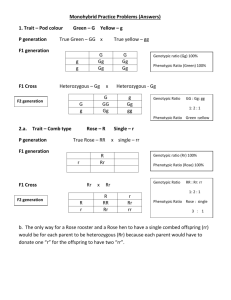
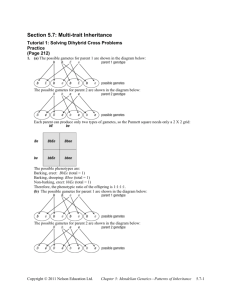
Single Trait Crosses A single trait cross involves the crossing of two individuals while observing the inheritance of a single trait. 1. A homozygous tall pea plant is crossed with a dwarf pea plant. Determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. Step 1: Write the letters that represent the traits. T = tall t = dwarf Step 2: Write the genotypes of the individuals being crossed with an x in between them. TT x tt Step 3: Write all the gametes that each parent could produce with a circle around each. Possible Gametes: T t Step 4: Create a Punnett square by putting the gametes for one parent across the top and the gametes for the other parent down the side. Determine the genotypes of the offspring by filling in the table. T Tt t Step 5: Report the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. Genotype: Tt Phenotype: tall 2. A heterozygous purple flowered pea plant is crossed with a white pea plant. Determine the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the offspring. P = purple p = white Pp x pp Possible Gametes: P p p Punnett Square P P p Pp Pp Genotypic Ratio: 1Pp : 1 pp Phenotypic Ratio: 1 purple : 1 white 3. A homozygous smooth pea plant is crossed with a wrinkled pea plant. Determine the genotypic and phenotypic ratios for the F1 and F2 generations. S = smooth s = wrinkled SS x ss F1 Possible Gametes: S s s S Ss Genotypes: 100% Ss Phenotypes: 100% smooth Monohybrid Cross: mating of two individuals both heterozygous for a particular trait. F2 generation = F1 x F1 Ss x Ss F2 Possible Gametes: S s S s S s S SS Ss s Ss ss Genotype: 1SS : 2Ss : 1 ss Phenotype: 3 smooth : 1 wrinkled * Remember the genotypic ratio 1:2:1 because you will always get this ratio when both parents are heterozygous for the same trait. Test Cross: The mating of an individual of unknown genotype with an individual that is homozygous recessive for a certain trait. Test crosses are performed to determine the unknown genotype. 4. A test cross is performed with a hornless bull (the hornless trait in cows is dominant). Nine of the offspring produced are hornless and 3 offspring have horns. What is the genotype of the hornless bull? Explain how you determined the genotype. The bull’s genotype must be heterozygous Hh because he has produced offspring with the recessive trait. He could only produce offspring with the recessive trait if he also had the recessive allele. Double Trait Crosses A double trait cross involves the crossing of two individuals while observing the inheritance of two separate traits. 1. In mice, a grey coat colour is dominant to a white coat and long tails are dominant over short tails. What fraction of F1 mice would you predict to have grey coats and short tails when a white heterozygous long tailed male is crossed with a homozygous grey, short tailed female? G = grey g = white T = long tail t = short tail Possible Gametes Gt gT GgTt ggTt x GGtt gT gt Gt gt Ggtt Therefore, 50% of the F1 mice will have grey coats and short tails. Dihybrid Cross: the mating of two individuals both heterozygous for two particular traits 2. In humans, brown hair is dominant over blond hair and brown eyes is dominant over blue eyes. If you crossed a heterozygous brown eyed, brown haired male with a heterozygous brown eyed, brown haired female, what would be the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of their offspring? B = brown hair b = blonde hair E = brown eyes e = blue eyes Possible Gametes (Same for both) BE Be bE be BE BBEE BBEe BbEE BbEe Be BBEe BBee BbEe Bbee BbEe x BbEe BE Be bE be bE BbEE BbEe bbEE bbEe Be BBEe BBee BbEe bbee Genotypic Ratio: 4 BbEe: 2 BbEE: 2 Bbee: 2 BBEe: 2bbEc: 1BBEE: 1BBee: 1bbEE: 1bbee Phenotypic Ratio: 9 brown hair, brown eyes: 3 brown hair, blue eyes: 3 blonde hair, brown eyes: 1 blonde hair, blue eyes * Remember the phenotypic ratio 9:3:3:1 because you will always see this phenotypic ratio when both parents are heterozygous for both traits) Single Trait Crosses A single trait cross involves the crossing of two individuals while observing the inheritance of a single trait. 1. A homozygous tall pea plant is crossed with a dwarf pea plant. Determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. Step 1: Write the letters that represent the traits. Step 2: Write the genotypes of the individuals being crossed with an x in between them. Step 3: Write all the gametes that each parent could produce with a circle around each. Possible Gametes: Step 4: Create a Punnett square by putting the gametes for one parent across the top and the gametes for the other parent down the side. Determine the genotypes of the offspring by filling in the table. Step 5: Report the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. Genotype: Phenotype: 2. A heterozygous purple flowered pea plant is crossed with a white pea plant. Determine the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the offspring. Parent Genotypes: Possible Gametes: Punnett Square Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: 3. A homozygous smooth pea plant is crossed with a wrinkled pea plant. Determine the genotypic and phenotypic ratios for the F1 and F2 generations. Monohybrid Cross: mating of two individuals both heterozygous for a particular trait. F2 generation = F1 x F1 Parent Genotypes: F2 Possible Gametes: Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: * Remember the genotypic ratio 1:2:1 because you will always get this ratio when both parents are heterozygous for the same trait. Test Cross: The mating of an individual of unknown genotype with an individual that is homozygous recessive for a certain trait. Test crosses are performed to determine the unknown genotype. 4. A test cross is performed with a hornless bull (the hornless trait in cows is dominant). Nine of the offspring produced are hornless and 3 offspring have horns. What is the genotype of the hornless bull? Explain how you determined the genotype. Double Trait Crosses A double trait cross involves the crossing of two individuals while observing the inheritance of two separate traits. 1. In mice, a grey coat colour is dominant to a white coat and long tails are dominant over short tails. What fraction of F1 mice would you predict to have grey coats and short tails when a white heterozygous long tailed male is crossed with a homozygous grey, short tailed female? G = grey g = white T = long tail t = short tail Parent Genotypes: Possible Gametes: Dihybrid Cross: the mating of two individuals both heterozygous for two particular traits 2. In humans, brown hair is dominant over blond hair and brown eyes is dominant over blue eyes. If you crossed a heterozygous brown eyed, brown haired male with a heterozygous brown eyed, brown haired female, what would be the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of their offspring? B = brown hair b = blonde hair E = brown eyes e = blue eyes Parent Genotypes: Possible Gametes: Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: * Remember the phenotypic ratio 9:3:3:1 because you will always see this phenotypic ratio when both parents are heterozygous for both traits)