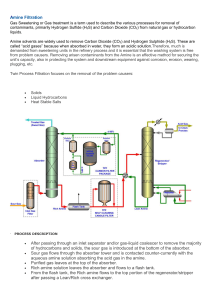
oxime & semicarbazone procedures
advertisement

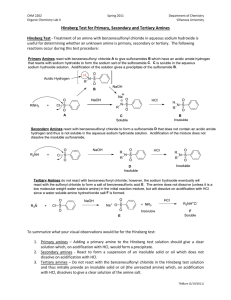
Oxime Derivative Preparation Disolve 0.5 gm. hydroxylamine hydrochloride in 5 mL. of water and 3 mL. of 3M NaOH. Add 0.5 gm./mL of your unknown to the above solution. Warm the mixture in a boiling water bath for 10 minutes. Cool in an ice bath and collect the crystals using vacuum filtration. Dry overnight and determine the compound’s melting range. Semicarbazone Derivative Preparation Disolve 0.5 gm. semicarbazide hydrochloride and 0.8 gm. of Na(OAc) in 5 mL. of water. Add 0.5 gm. of your compound, stopper and shake the solution vigorously. Warm the mixture in a boiling water bath for 10 minutes. Remove the beaker from the heat source and allow the solution to cool to cool to room temperature in the beaker. Collect the crystals using vacuum filtration. Benzenesulfonamide Derivative Preparation Mix 10 mL. 2 M KOH with 0.2 mL/gm of compound and 0.7 mL benzenesulfonyl chloride. Stopper and shake the solution vigorously, with cooling if necessary, for a period of five minutes. Test the solution to be sure it is basic – if not, add 2 M KOH until basic. Collect the crystals using vacuum filtration. If an oil forms, test its solubility with 1.5% HCl. (The sulfonamide if a secondary amine is insoluble, whereas an amine is at least partially soluble. If this solubility test indicates an amine, it may be either tertiary, or one of certain secondary amines that react with benzenesulfonyl chloride only very slowly.) A solid sulfonamide of a secondary amine is insoluble in both water and 1.5% HCl. Acidify the solution from the original reaction mixture to pH 4 ( test with Congo Red paper ); the formation of a precipitate or oil indicates a primary amine.