Catastrophic Events - Answers / Microsoft Word

Natural Catastrophic Events on Earth
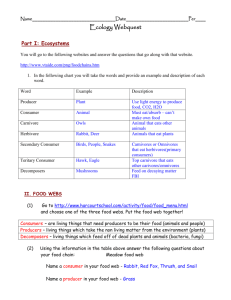
** An incident that causes loss of life or widespread impact on ecosystems. **
1. Earthquake - A sudden tremor, or shaking, of the earth’s surface.
Impact: Can trigger other events such as landslides, rockslides, avalanches, floods, and tsunamis; in urban areas, severe destruction of buildings can occur, resulting in loss of life in the tens of thousands.
Causes:
Release of underground stress along plate boundaries and faults in Earth’s crust
2. Hurricane - An intensely powerful storm originating at sea in warm, tropical waters.
Impact: High, destructive winds of 74-200 mph; widespread coastal flooding and erosion due to heavy rains and storm surges of 15 to 20 feet; one of nature's most destructive forces, it can cause enormous damage to life and property; can also cause mudslides and tornadoes
Causes: An intense buildup of moisture, heat, and energy above tropical waters
3.
Wildfire - Any uncontrolled fire occurring in the wild.
Impact: Can destroy millions of acres of wilderness and forestland, but can also be beneficial to the health of many ecosystems since many plants depend on this for regeneration; can be very destructive to property and human life if it advances into urban areas; because plant life is destroyed, extensive erosion and mudslides can happen during the rainy season
Causes: Naturally caused by lightning strikes but most are caused by human activity
4. Flood - An overflowing of water onto land that is normally dry.
Impact: Widespread destruction of dry-land ecosystems; massive erosion; destruction of manmade structures and loss of life; responsible for the world’s deadliest recorded catastrophic event in China in 1931 (killing an estimated 2,000,000 to 4,000,000 people)
Causes: Excessive precipitation, snow-melt, failure of man-made or natural dams
5. Tsunami A huge ocean wave that can travel up to 600 mph in the ocean and reach heights of
50 to 150 feet near shores.
Impact: widespread flooding and erosion of coastal areas; can completely erode entire coastlines and small islands; in 2004, one caused by an earthquake in the Indian Ocean killed over 200,000 people in Indonesia, Thailand, Sri Lanka, and India.
Causes: Usually caused by ocean-floor earthquakes, volcanoes, or coastal landslides
6. Volcano An opening in the earth's crust through which molten lava, ash, and gases are ejected.
Impact: can completely destroy surrounding ecosystems; can significantly change the Earth’s climate through the ash and gases released into the atmosphere; responsible for the creation of new land; can trigger earthquakes and tsunamis; believed to be responsible for mass extinction of some species
Causes:
The release of pressure from molten rock beneath the earth’s surface
7. Tornado - A violently rotating, narrow column of air, ranging in width from a few yards to over a mile wide.
Impact: Extremely high, destructive winds of 40-300 mph; can cause extreme and sometimes total destruction of habitats, property and structures, but usually in a small area
Causes: Developed from large-scale circulation of a supercell thunderstorm
8. Drought - An extended period of extremely dry weather resulting in water shortages.
Impact: Will directly reduce the growth of producers, significantly impacting the entire food web of an ecosystem; can result in widespread wildfires; will reduce crop yields or result in crop failure, sometimes resulting in widespread famine and disease in human populations
Causes: Caused by an extended period of little or no rainfall
9. Asteroid or Comet Impact - A large object from the solar system striking the earth
Impact: Believed by many scientists that a large one, can destroy most, if not all, life on Earth by partially destroying Earth’s atmosphere and significantly changing the climate
Causes: The orbits of the earth and another object crossing at the same place and time