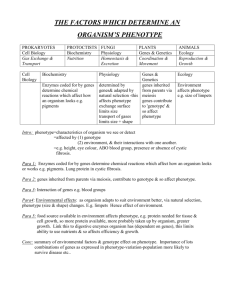
1471-2105-9-463
advertisement
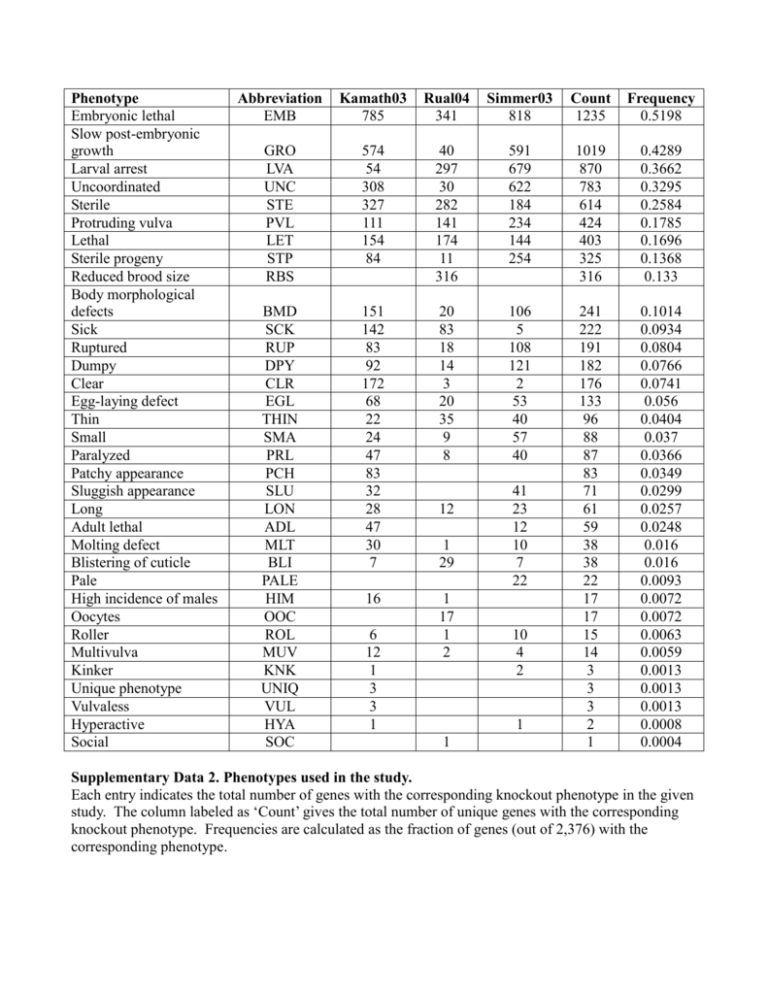
Phenotype Embryonic lethal Slow post-embryonic growth Larval arrest Uncoordinated Sterile Protruding vulva Lethal Sterile progeny Reduced brood size Body morphological defects Sick Ruptured Dumpy Clear Egg-laying defect Thin Small Paralyzed Patchy appearance Sluggish appearance Long Adult lethal Molting defect Blistering of cuticle Pale High incidence of males Oocytes Roller Multivulva Kinker Unique phenotype Vulvaless Hyperactive Social Abbreviation EMB Kamath03 785 Rual04 341 Simmer03 818 Count 1235 Frequency 0.5198 GRO LVA UNC STE PVL LET STP RBS 574 54 308 327 111 154 84 40 297 30 282 141 174 11 316 591 679 622 184 234 144 254 1019 870 783 614 424 403 325 316 0.4289 0.3662 0.3295 0.2584 0.1785 0.1696 0.1368 0.133 BMD SCK RUP DPY CLR EGL THIN SMA PRL PCH SLU LON ADL MLT BLI PALE HIM OOC ROL MUV KNK UNIQ VUL HYA SOC 151 142 83 92 172 68 22 24 47 83 32 28 47 30 7 20 83 18 14 3 20 35 9 8 106 5 108 121 2 53 40 57 40 16 1 17 1 2 241 222 191 182 176 133 96 88 87 83 71 61 59 38 38 22 17 17 15 14 3 3 3 2 1 0.1014 0.0934 0.0804 0.0766 0.0741 0.056 0.0404 0.037 0.0366 0.0349 0.0299 0.0257 0.0248 0.016 0.016 0.0093 0.0072 0.0072 0.0063 0.0059 0.0013 0.0013 0.0013 0.0008 0.0004 6 12 1 3 3 1 12 1 29 41 23 12 10 7 22 10 4 2 1 1 Supplementary Data 2. Phenotypes used in the study. Each entry indicates the total number of genes with the corresponding knockout phenotype in the given study. The column labeled as ‘Count’ gives the total number of unique genes with the corresponding knockout phenotype. Frequencies are calculated as the fraction of genes (out of 2,376) with the corresponding phenotype.