Earth and Space Science
advertisement

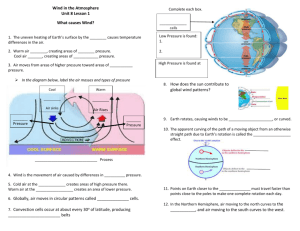
Earth and Space Science Mr. Hurm Chapter 28 Assessment: Air Pressure -please DO NOT WRITE on this exam packet. Instead, use scrap paper- AIR PRESSURE, WINDS, and WIND BELTS – MULTIPLE CHOICE SECTION (2 points each) -Note: choose the best possible answer1. A meteorologist wants to study monsoons. Where should he or she go to collect the best data? A. North Pole B. England C. India D. Australia 2. The average air pressure at sea level for the whole world is: A. 1050.0 millibars B. 960.5 millibars C. 1000.0 millibars D. 1013.2 millibars 3. Which of the following instruments measures air pressure? A. Thermometer B. Barometer C. Anemometer D. Hygrometer 4. Which of the following statements about air pressure is FALSE? A. Air pressure is the weight of the atmosphere per a unit of area B. Air pressure never changes C. The air pressure at sea level is 1 kg per cm2 D. Air pressure is exerted equally in all directions 5. In the Northern Hemisphere, the winds associated with a high pressure system blow: A. Inward and clockwise B. Inward and counterclockwise C. Outward and clockwise D. Outward and counterclockwise 6. In the Northern Hemisphere, the winds associated with a low pressure system blow: A. Inward and clockwise B. Inward and counterclockwise C. Outward and clockwise D. Outward and counterclockwise 7. Local winds always blow from: A. Land to sea B. High latitudes to low latitudes C. High pressure to low pressure D. High elevations to low elevations 8. The force that generates wind is: A. Coriolis effect B. Gravity C. Friction D. Pressure gradient force 9. The Coriolis effect is caused by: A. Low pressure B. High pressure C. The rotation of the Earth D. Gravity 10. Where is it likely to be the windiest due to a lack of friction? A. A forest B. A large city C. At sea D. In the mountains AIR PRESSURE, WINDS, and WIND BELTS – FILL IN THE BLANK SECTION (2 points each) -Note: Fill in the blank with the best possible answer11. When pressure rises, _______________ and _______________ weather is usually on its way. (warmer and more humid / cooler and drier) 12. When pressure falls _______________ and _______________ weather is usually on its way. (warmer and more humid / cooler and drier) 13. Due to the Coriolis effect, wind is turned to the _______________ relative of its direction of motion in the Northern Hemisphere. (right / left) 14. Due to the Coriolis effect, wind is turned to the _______________ relative of its direction of motion in the Southern Hemisphere. (right / left) 15. A barometric pressure of 1002 mb indicates a _______________ pressure. (strong high/weak high/strong low/weak low) 16. A barometric pressure of 1052 mb indicates a _______________ pressure. (strong high / weak high / strong low / weak low) 17. A barometric pressure of 1017 mb indicates a _______________ pressure. (strong high / weak high / strong low / weak low) 18. A barometric pressure of 968 mb indicates a _______________ pressure. (strong high / weak high / strong low / weak low) LOCAL WINDS – MATCHING SECTION (2 points each) -Note: match each local wind with its descriptionSea Breeze Land Breeze Mountain Breeze Valley Breeze Monsoon Chinook Santa Ana Texas Norther Nor’easter Desert Winds Katabatic Winds 19. Powerful East Coast snowstorms are usually foreshadowed by these winds. 20. A daytime breeze that blows from the sea towards the land. 21. Winds that change according to the season. 22. Very cold down sloping winds that usually comes from a large snow covered plateau. 23. Hot, dry winds that are infamous for creating forest fires in Southern California. 24. A bitterly cold wind associated with a cold front comes from Canada and can change the temperature very rapidly. 25. A nighttime breeze that blows from the land toward the sea. 26. A breeze that blows up the mountain from the valley. 27. A warm, dry wind that descends from the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains. 28. A breeze that blows down the mountain towards the valley. 29. Haboobs, dust devils, and whirlwinds are examples of these winds. PRESSURE BELTS AND WINDS – DRAWING SECTION (22 points) 30. Complete the pressure belts and winds map on your answer sheet. WHAT MAKES WIND BLOW? – SHORT ESSAY (20 points) 31. In paragraph form, answer the question, “what makes wind blow?” I am looking for 4 specific steps. If you think drawing a picture along with your essay will help you explain your answer, feel free to do so. CORIOLIS EFFECT 32. A rocket is fired due south from point A, and it reaches the equator one hour later. On the map, draw the rocket’s apparent path relative to Earth’s surface. 33. A second rocket is fired due north from point B and it reaches the equator in three hours. Draw its apparent path. 34. The center of a high pressure area occurs at point C. Draw an arrow indicating the apparent path of a wind moving out from the center of the high and to the north. Do the same for winds moving east, south, and west from point C. 35. The center of a low pressure area occurs at point D. Extend the arrows surrounding this point to indicate the apparent paths of four winds moving toward the low from the north, south, east, and west.