PS#2
advertisement

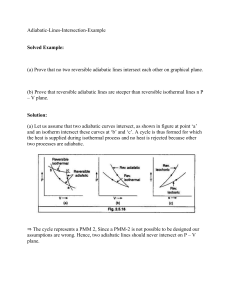
CHEM 341. Fall 2000. Problem Set #2. Work, Heat, Energy 1. One mole of methane is heated from 300 K to 400 K. Calculate U, q, and w at (a) constant pressure and (b) constant volume. Cv,m = 30.86 J/K and is independent of temperature. Assume ideal gas behavior. 2. Calculate the work done when an ideal gas is expanded isothermally from 10 atm, 2.0 L, 293 K to 1 atm if the expansion occurs (a) against Pexternal = 1 atm, and (b) reversibly. Note: 1 atm = 1.01 x 105 Pa; 1 m3 = 103 L. 3. Derive the following equation for the work on reversible expansion of a van der Waals V nb 1 2 1 gas w nRT ln 2 an . V1 nb V2 V1 nRT n2a 1 4. The Redlich-Kwong (RK) equation of state is P . V nb T V V nb Show that the work on an RK gas for a reversible, isothermal expansion is V nb na V2 nb V1 w nRT ln 2 ln V1 nb b T V1 nb V2 Hint: dx 1 x xa bx a ln a bx C 5. A mole of liquid water is vaporized at 100C and 1.013 bar. The heat of vaporization is 40.69 kJ/ mol. What are the values of wrev, q, U, and H? 6. One mole of perfect gas at 25C and 100 bar is allowed to expand reversibly and isothermally to 5 bar. Calculate w, q, U, and H, all in Joules. Note: 1 bar = 105 Pa. 7. Initially, 5 mol of nitrogen are at a temperature of 25C and 10 atm. The gas is ideal; Cv,m = 20.8 J K mol and is independent of temperature. Suppose that the pressure is dropped to 1 atm, reversibly and adiabatically. Calculate the final temperature, U, and H. Expansion, Compression (Adiabatic, Isothermal, Reversible, Irreversible) 8. One mole of a non-linear, polyatomic ideal gas is expanded from 500 K, 5 atm to a final pressure of 1 atm. Calculate the work for an expansion that is (a) isothermal, reversible; (b) adiabatic, reversible. [Hint: For a non-linear polyatomic ideal gas, Cv,m =3R; ignore vibrational contributions to the heat capacity.] 9. During the operation of an internal combustion engine, the fuel-air mixture is compressed until the volume is reduced by a factor of 9 (the compression ratio). Assuming 1 CHEM 341. Fall 2000. Problem Set #2. = 1.4 (the value for nitrogen and oxygen), estimate the final temperature if it starts at 25C and the compression is reversible and adiabatic. 10. A tank contains 20 L of compressed monatomic ideal gas at 10 bar and 25C. Calculate the maximum work (in Joules) that can be obtained when the gas expands to 1 bar pressure (a) isothermally, and (b) adiabatically. [Hint: Consider Cv,m, Cp,m, and for an adiabatic expansion of a monatomic ideal gas.] 11. An ideal gas expanded reversibly and adiabatically to twice its volume. Its initial 3R temperature was 25C, Cv,m = . Calculate Um and Hm. 2 12. In each of the following cases, an ideal gas expands against a constant external pressure. For each case, decide if the expansion is allowed by the first law, and if so, if the expansion can be carried out reversibly. No explanation is needed. (a) isothermal and adiabatic (b) isothermal but not adiabatic (c) neither isothermal nor adiabatic PLEASE NOTE The work you hand in should be neat and well organized, and it should show the strategy and steps you used in solving the problems, as well as the bottom-line answers (or solutions). In grading the problems, both your work-up and your final answers/solutions will be examined and evaluated. The work handed in for grading must carry a pledge that the work is entirely yours and was done without any collaboration with other persons (except for the course instructor and TA's). You are encouraged to work with others in doing the exercises and problems found in the textbook, but all work handed in for grading should be done independently. 2