Exam Review KEY
advertisement
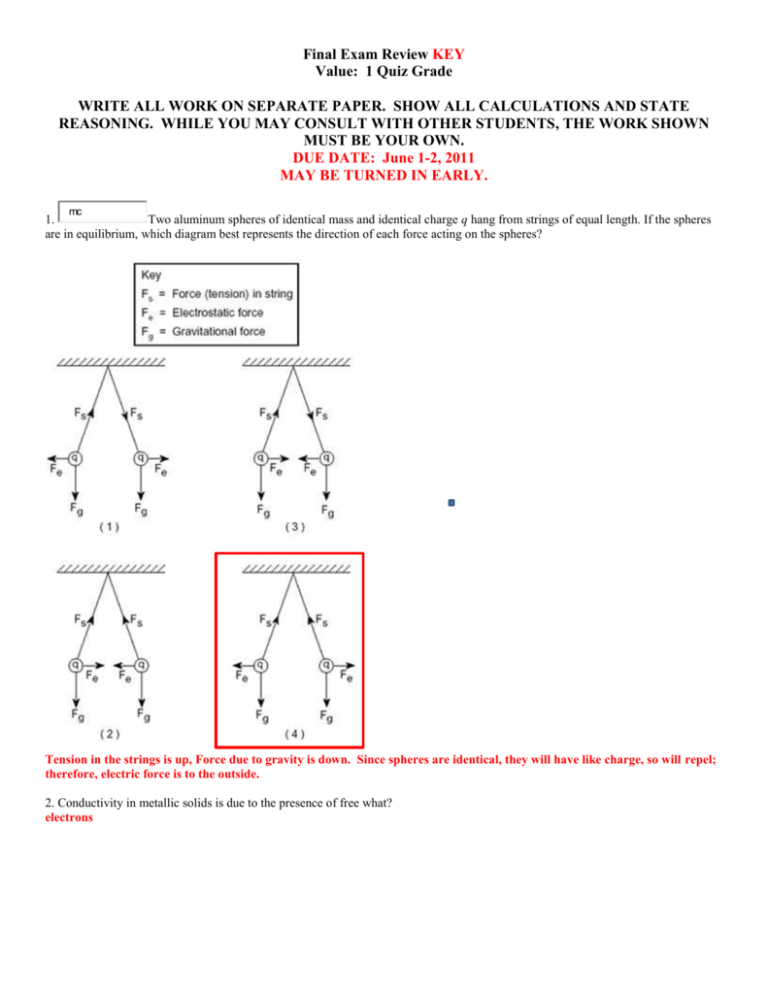
Final Exam Review KEY Value: 1 Quiz Grade WRITE ALL WORK ON SEPARATE PAPER. SHOW ALL CALCULATIONS AND STATE REASONING. WHILE YOU MAY CONSULT WITH OTHER STUDENTS, THE WORK SHOWN MUST BE YOUR OWN. DUE DATE: June 1-2, 2011 MAY BE TURNED IN EARLY. mc 1. Two aluminum spheres of identical mass and identical charge q hang from strings of equal length. If the spheres are in equilibrium, which diagram best represents the direction of each force acting on the spheres? Tension in the strings is up, Force due to gravity is down. Since spheres are identical, they will have like charge, so will repel; therefore, electric force is to the outside. 2. Conductivity in metallic solids is due to the presence of free what? electrons mc 3. The graph below shows the relationship between the work done on a charged body in an electric field and the net charge on the body. What does the slope of this graph represent? (Look at the equations for electricity and figure this question out.) According to the Work-Energy Theorem, potential energy is equal to the work done to put the object in its present state. So the y-axis represents energy. The x-axis is charge (q). Looking at the reference sheet, U E = q V. A plot of energy versus charge would result in a straight line with a slope of V, voltage. mc 4. The diagram below shows two identical metal spheres, A and B, on insulated stands. Each sphere possesses a net charge of -3 10-6 coulomb. If the spheres are brought into contact with each other and then separated, what will be the charge on sphere A? -3 10-6 coulomb; charges would equalize, but in this case, since they are equal to begin with, they stay the same mc 5. The diagram below shows two small metal spheres, A and B. Each sphere possesses a net charge of 4.0 10-6 coulomb. The spheres are separated by a distance of 1.0 meter. Which combination of charged spheres and separation distance produces an electrostatic force of the same magnitude as the electrostatic force between spheres A and B? F = 0.144 N (1) (2) (3) (4) 6. mc F = 0.225 N F = 0.338 N F = 0.113 N F = 0.144 N Correct A positive test charge is placed between an electron, e, and a proton, p, as shown in the diagram below. When the test charge is released, it will move toward which point? Point D. It will move away from the proton and toward the electron 7. A soft drink from Australia is labeled "Low Joule Cola." The label says "100 mL yields 1.9 kJ." The can contains 375 mL. Sally drinks the cola and then wants to offset this input of food energy by climbing stairs. How high would Sally have to climb if she has a mass of 63.0 kg? Energy content of soda: 375 mL x (1900 J/100 mL) = 7125 J = Work to be done By climbing, Sally has to do work against gravity, W = F g d d = W/Fg = 7125 J / (63 kg * 9.81 m/s2) = 11.5 m 8. A compact car, mass 740 kg, is moving at 1.00 102 km/h toward the east. (a) Find the magnitude and direction of its momentum. p = m v = 740 kg x 100 km/h x 1000 m/km x 1 h/3600 s = 20556 kg m/s (b) A second car, mass 2300 kg, has the same momentum. What is its velocity in km/h (state direction)? v = p / m = 20556 kg m/s / 2300 kg = 8.94 m/s x 1 km/1000 m x 3600 s/h = 32.2 km/h 9. A 7.5 kg bowling ball is rolling down the alley with a velocity of 2.8 m/s. For each impulse, a and b, as shown in Figure 9-3, find the resulting speed and direction of motion of the bowling ball. Impulse a: J = 5 Ns Impulse b: J = -5 Ns Figure 9-3 a) J = Δp 5 Ns = p2 – p1 5 Ns = m(v2 – v1) 5 = 7.5 (v2 – 2.8) v2 = 3.47 m/s b) J = Δp - 5 Ns = p2 – p1 -5 Ns = m(v2 – v1) -5 = 7.5 (v2 – 2.8) v2 = 2.13 m/s 10. In a Star Trek episode, a space station orbiting Tanuga IV blows up. The crew of the Enterprise immediately hears and sees the explosion. They realize that there is no chance for rescue. If you had been hired as an advisor, what two physics errors would you have found and corrected? 1. One would not hear and see an explosion at the same time. Just like lightning and thunder, one would see the light and later hear the sound. 2. One would not hear an explosion in space because there is no medium (ie air) to carry the mechanical sound waves. 11. Your brother's mass is 32.9 kg, and he has a 1.3 kg skateboard. What is the combined momentum of your brother and his skateboard if they are going 9.75 m/s? p = m v = (32.9 + 1.3) kg x 9.75 m/s = 333.45 kg m/s 12. A hockey player makes a slap shot, exerting a constant force of 34.7 N on the hockey puck for 0.18 s. What is the magnitude of the impulse given to the puck? J = F Δt = 34.7N x 0.18 s = 6.25 Ns 13. A 2568 kg van runs into the back of a 829 kg compact car at rest. They move off together at 8.5 m/s. Assuming the friction with the road is negligible, find the initial speed of the van. p1 = p2 mAvA1 + mBvB1 = (mA + mB)v2 2568 kg x vA1 + 0 = (2568 + 829)kg x 8.5 m/s vA1 = 11.2 m/s 14. Ball A, rolling west at 2.7 m/s, has a mass of 1.0 kg. Ball B has a mass of 2.0 kg and is stationary. After colliding with ball B, ball A moves south at 2.0 m/s. (a) Sketch the system, showing the velocities and momenta before and after the collision. Before After B B A A (b) Calculate the momentum and velocity of ball B after the collision. Momentum: 3.36 kg m/s Velocity: 1.68 m/s @ 143.5o p1 = p2 mAvA1 + mBvB1 = mA vA2 + mBvB2 1.0 kg x 2.7 m/s W + 0 =1.0 kg x 2.0 m/s S + 2.0 kg x v B2 x y pA1 -2.7 0 pB1 0 0 pA2 0 -2.0 pB2 -2.7 2.0 Using Pythagorean Theorem: (- 2.7)2 + 2.02 = Resultant2 = 11.29 Resultant momentum magnitude = 3.36 kg m/s = mB vB2 vB2 = 3.36 kg m/s / 2 kg = 1.68 m/s ANSWER = tan-1(2.0/2.7) = 36.5o; angle is in Quadrant II, so direction is 180o – 36.5o = 143.5o 15. A 140.0 resistor, a 65.0 resistor, and a 40.0 resistor are connected in parallel and placed across a 12.0 V battery. (a) What is the equivalent resistance of the parallel circuit? 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 = + + 𝑹𝒑 𝑹𝟏 𝑹𝟐 𝑹𝟑 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 = + + = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟒𝟕𝟓 𝑹𝒑 𝟏𝟒𝟎 𝟔𝟓 𝟒𝟎 𝑹𝒑 = 𝟐𝟏. 𝟎𝟒 𝒐𝒉𝒎𝒔 (b) What is the current delivered by the battery? I = V/R = 12 V / 21.04 ohms = 0.57 A (c) What is the current through each branch of the circuit? Through 140.0 resistor: I = V/R = 12 V / 140 ohms = 0.086 A Through 65.0 resistor: I = V/R = 12 V / 65 ohms = 0.185 A Through 40.0 resistor: I = V/R = 12 V / 40 ohms = 0.300 A 16. A 10 resistor, a 15 resistor, and a 5 resistor are connected in series across a 80 V battery. Calculate the voltage drops across each resistor. I = V/R = 80 V / (10+15+5) ohms = 2.67 A = current in circuit (same everywhere in series circuit) 10 resistor: V = IR = 2.67A x 10 ohm = 26.7 V 15 resistor: V = IR = 2.67A x 15 ohm = 40 V 5 resistor: V = IR = 2.67A x 5 ohm = 13.3 V Now calculate the sum of these voltage drops, and check to see if it equals the voltage of the battery. 26.7 + 40 + 13.3 = 80 V 17. Three 17 resistors are connected in parallel and placed across a 36 V battery. (a) What is the equivalent resistance of the parallel circuit? 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 = + + 𝑹𝒑 𝑹𝟏 𝑹𝟐 𝑹𝟑 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 = + + = 𝟎. 𝟏𝟕𝟔 𝑹𝒑 𝟏𝟕 𝟏𝟕 𝟏𝟕 𝑹𝒑 = 𝟓. 𝟔𝟕 𝒐𝒉𝒎𝒔 (b) What is the current delivered by the battery? I = V/R = 36 V / 5.67 ohms = 6.35 A (c) What is the current through each resistor? Current through each 17 resistor: I = V/R = 36 V / 17 ohms = 2.12 A 18. A 2.5 kg ball strikes a wall with a velocity of 8.5 m/s to the left. The ball bounces off with a velocity of 7.5 m/s to the right. If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.25 s, what is the constant force exerted on the ball by the wall? 𝑭∆𝒕 = ∆𝒑 𝒎 𝒎 ∆𝒑 𝒑𝟐 − 𝒑𝟏 (𝟕. 𝟓 𝒔 ) (𝟐. 𝟓 𝒌𝒈) − (−𝟖. 𝟓 𝒔 )(𝟐. 𝟓 𝒌𝒈) 𝑭= = = = 𝟏𝟔𝟎 𝑵 ∆𝒕 ∆𝒕 𝟎. 𝟐𝟓 𝒔 19. A 5.5 g dart is fired into a block of wood with a mass of 22.6 g. The wood block is initially at rest on a 1.5 m tall post. After the collision, the wood block and dart land 2.5 m from the base of the post. Find the initial speed of the dart. Momentum/horizontal projectile motion problem dart block Determine the time it takes dart+block to fall: y = y0 + v0yt + ½ gt2 -1.5 m = 0 m + 0 + ½ (-9.81 m/s2)t2 t = 0.553 s 1.5 m Determine the initial speed of the block+dart: x = x0 + v0xt + ½ at2 2.5 m = 0 m + v0x(0.553 s) + 0 v0x = 4.52 m/s (block+dart) Now, using conservation of momentum, 2.5 m Determine initial speed of dart: p1 = p2 p2 = (mblock+dart)vblock+dart p1 = mdartvdart = 0.0055 kg (vdart) = (0.0055 + 0.0226)kg (4.52 m/s) vdart = 23.1 m/s 20. A moving object has a kinetic energy of 150 J and a momentum with a magnitude of 30.0 kg m/s. Determine the mass and speed of the object. K = ½ mv2 = 150 J K = ½ (mv)v = ½ pv 150 = ½ (30)v v = 300/30 = 10 m/s m = p/v = 30/10 = 3 kg p = mv = 30 kg m/s 21. Andrew hears the sound of the firing of a distant cannon 4.71 s after seeing the flash. How far is Andrew from the cannon? The speed of sound in air is 343 m/s. v = d/t d = vt = 343 m/s (4.71 s) = 1615 m 22. A rescue plane flies horizontally at a constant speed searching for a disabled boat. When the plane is directly above the boat, the boat’s crew blows a loud horn. By the time the plane’s sound detector perceived the horn’s sound, the plane has traveled a distance equal to 1.5 times its altitude above the ocean. If it takes the sound 3.89 s to reach the plane, determine the altitude of the plane. The speed of sound in air is 343 m/s. ½h h2 + (½h)2 = c2 c = 343 m/s (3.89 s) = 1334.3 m (1 + ¼)h2 = (1334.3 m)2 h c h = 1193 m 23. A bat can detect small objects such as an insect whose size is approximately equal to one wavelength of the sound the bat makes. If bats emit a chirp at a frequency of 54.7 kHz, and the speed of sound in air is 343 m/s, what is the smallest insect a bat can detect? v=f = v / f = 343 m/s / 54700 Hz = 0.00627 m = 0.6 mm (small bugs!) 24. Find the equivalent resistance of the portion of a circuit shown below. 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 = + + 𝑹𝒑 𝑹𝟏 + 𝑹𝟐 𝑹𝟑 𝑹𝟒 + 𝑹𝟓 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 = + + 𝑹𝒑 𝟏 + 𝟐 𝟑 𝟒 + 𝟓 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟕 = + + = = 𝟎. 𝟕𝟖 𝑹𝒑 𝟑 𝟑 𝟗 𝟗 𝑹𝒑 = 𝟏. 𝟐𝟗 𝛀 25. What is the voltage drop across each resistor in the circuit shown below if the battery has a voltage of 30 V? R1=10 ohm, R2=20 ohm, R3=10 ohm, R4=20 ohm, R5=40 ohm. 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 = + = + = 𝟎. 𝟏𝟓 𝑹𝒑𝟏 𝑹𝟏 𝑹𝟐 𝟏𝟎 𝟐𝟎 𝑹𝒑𝟏 = 𝟔. 𝟔𝟕 𝛀 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 = + = + = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟕𝟓 𝑹𝒑𝟐 𝑹𝟒 𝑹𝟓 𝟐𝟎 𝟒𝟎 𝑹𝒑𝟐 = 𝟏𝟑. 𝟑𝟑 𝛀 𝑹𝒆𝒒 = 𝑹𝒑𝟏 + 𝑹𝟑 + 𝑹𝒑𝟐 = 𝟑𝟎 𝛀 𝑽 𝟑𝟎 𝑽 𝑰= = =𝟏𝑨 𝑹𝒆𝒒 𝟑𝟎 𝛀 Voltage drop across R1 = Voltage drop across R2 = Rp1: V = IRp1 = 1 A (6.67 ohm) = 6.67 V Voltage drop across R3 : V = IR3 = 1 A (10 ohm) = 10 V Voltage drop across R4 = Voltage drop across R5 = Rp2: V = IRp2 = 1 A (13.33 ohm) = 13.33 V