Wikispace 1 -Raji Rajalingam - drbperiodcsem2
advertisement
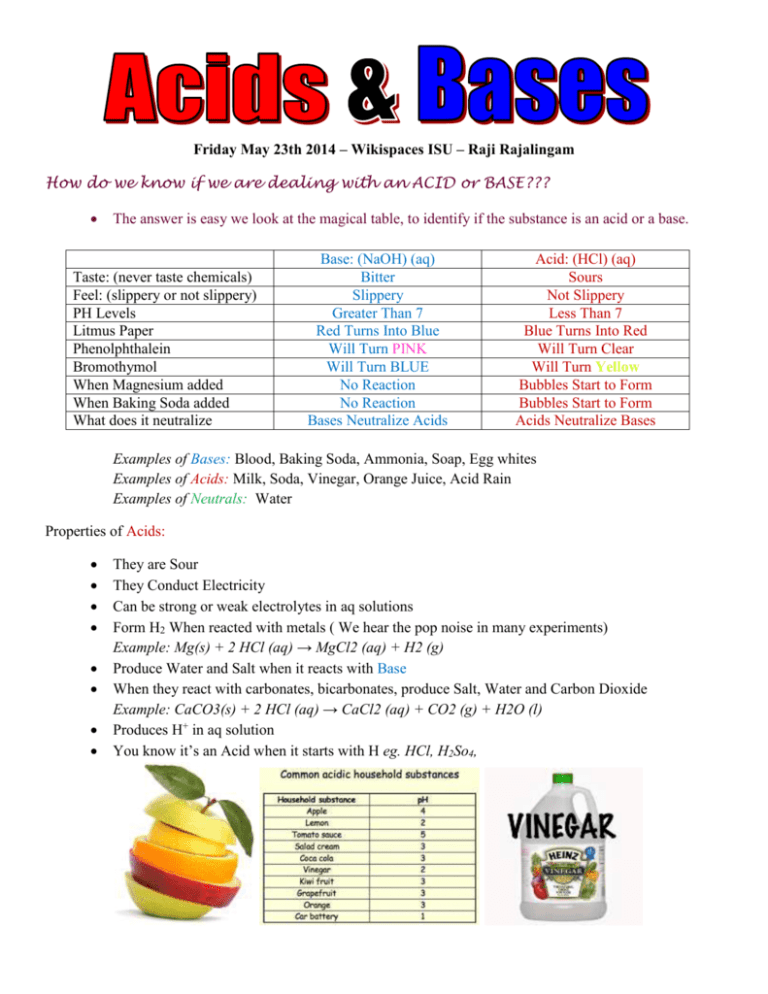
Friday May 23th 2014 – Wikispaces ISU – Raji Rajalingam How do we know if we are dealing with an ACID or BASE??? The answer is easy we look at the magical table, to identify if the substance is an acid or a base. Taste: (never taste chemicals) Feel: (slippery or not slippery) PH Levels Litmus Paper Phenolphthalein Bromothymol When Magnesium added When Baking Soda added What does it neutralize Base: (NaOH) (aq) Bitter Slippery Greater Than 7 Red Turns Into Blue Will Turn PINK Will Turn BLUE No Reaction No Reaction Bases Neutralize Acids Acid: (HCl) (aq) Sours Not Slippery Less Than 7 Blue Turns Into Red Will Turn Clear Will Turn Yellow Bubbles Start to Form Bubbles Start to Form Acids Neutralize Bases Examples of Bases: Blood, Baking Soda, Ammonia, Soap, Egg whites Examples of Acids: Milk, Soda, Vinegar, Orange Juice, Acid Rain Examples of Neutrals: Water Properties of Acids: They are Sour They Conduct Electricity Can be strong or weak electrolytes in aq solutions Form H2 When reacted with metals ( We hear the pop noise in many experiments) Example: Mg(s) + 2 HCl (aq) → MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g) Produce Water and Salt when it reacts with Base When they react with carbonates, bicarbonates, produce Salt, Water and Carbon Dioxide Example: CaCO3(s) + 2 HCl (aq) → CaCl2 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l) Produces H+ in aq solution You know it’s an Acid when it starts with H eg. HCl, H2So4, Properties of Bases: Reacts with Acids to Form Water and Salt Form OH- in aq solution Bases React with Carbon Dioxide to produce carbonate and water Example: Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) In solution can be strong or weak electrolytes Bases have a PH of more than 7 Chalky Taste ACID & BASE THEROIES: 1. Arrhenius Definition- 1887 What did he come up with? o Acids produce H+ In aq solutions o Bases produce OH- In aq solutions What was wrong with his theory? o Only Limited to Aq solutions o States that bases have to have “OH- In aq solutions”, by using this NH3 is not a base, even though in modern times we know it is a base o States that all compounds with Hydrogen are acids, didn’t take in account of water (H20) which is neutral. o Not all hydrogen in acids must be released as ions only those with very polar bonds are ionziable What does the Revised Arrhenius Theory Include? o Collision with water molecules o The nature of hydrogen ions What did we learn in Class Today? Properties of Acids Properties of Bases Identifying If Acid or Base (With Examples) Who Arrhenius was, and What his Theory Was Homework: Finish The Fill in the Blanks for Acid and Bases (H1 and H2) Textbook Questions Pg. 475 #1-12 Read 10.1 and 10.2 (Pg. 164-174) Extra Help Links: http://www.chem4kids.com/files/react_acidbase.html http://www.chemtutor.com/acid.htm http://www.visionlearning.com/en/library/Chemistry/1/Acids-and-Bases/58 More Practice for Acids and Bases: http://misterguch.brinkster.net/namingacidsandbases.pdf http://www.chem4kids.com/extras/quiz_reactacidbase/index.html Still Stuck, Don’t Worry Watch These Helpful Video’s: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xeuyc55LqiY http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MSK1IRaqF24







