Earth Science Unit Review Sheet
advertisement

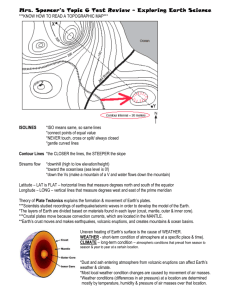
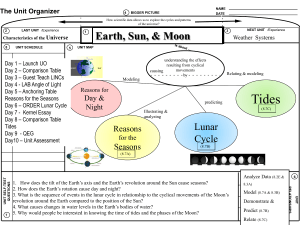
Earth Science Unit Review Summary The Earth/Sun/Moon System The Earth rotates (spins) on its axis in a counterclockwise direction. A single rotation takes one day (24 hours). This is the reason that we have a period of daylight and a period of darkness in NY every “day.” The direction of rotation is what makes the sun rise in the east and set in the west every day. The Earth revolves around the Sun. A single revolution takes one year (364¼ days – we make up the quarter by inserting an extra day in February every four years and call that a “leap year”). We have seasons on Earth because the axis of the Earth is tilted toward Polaris (the North Star) while it revolves around the Sun. The tilt causes seasons by changing the amount of sunlight and the intensity of that sunlight at the same time. When it is summer in NY, the axis is tilted toward the sun so the days are longer and sunlight is more direct/intense. When it is winter in NY, the axis is tilted away from the sun so the days are shorter and sunlight is more indirect/weaker. Seasons are caused by the Tilt of the Earth’s Axis! The moon rotates and revolves around the Earth. It takes the moon about a month (28 days) to rotate and revolve around the Earth. Since we see the moon from the reference of point of Earth, we see a slightly different amount of the lit side of the moon every night. We call the lit portions of the moon that we see Phases of the Moon. The tides are created by the gravitational pull of the moon on the Earth’s oceans. There are two types of tides: spring tides with a big difference between high and low tides (these happen when the Earth/Sun/Moon are all oriented in a straight line) and neap tides where the difference between high and low tides is slight (these happen when the Earth/Sun/Moon are at right angles. Mapping Latitude and Longitude: Latitude and longitude is used to show an exact location on Earth. Latitude is measured in degrees north and south of the Equator and the lines run from left to right across the Earth. Longitude is measured in degrees east and west of the Prime Meridian and the lines run up and down across the Earth. You always write a location as the latitude followed by the longitude (just like latitude comes before longitude in the dictionary). The location of Newburgh is: 41.5197° N, 74.0214° W Earth Science Unit Review Summary Topographic Maps are isoline maps, meaning that the lines on the map all touch points that are equal, in this case, in elevation. There are lines with marked elevations above sea level and unmarked lines. To tell if the land is rising or falling, look at two marked lines and determine if the elevation between two points are going up or going down. Lines that are close together indicate that there is a steep slope and lines that are farther apart indicate a gentler slope. Plate Tectonics The face of the Earth is constantly changing very slowly. The Theory of Plate Tectonics tells us that the lithosphere of the Earth (made up of the crust and the solid mantle) is made up of large plates, which move because of the convection currents in the plastic/liquid part of the mantle. The boundaries where lithospheric plates meet have interesting features as follows: Plate boundary Interesting Features Example Transform (where plates Earthquakes, tsunamis and fault lines when the plates San Adreas Fault, CA slide past each other) move Convergent (where plates move toward each other) Continental-Continental Mountain building occurs when the plates cause Himilayan Mountains, enough force for the rock to bend and fold Nepal, India Continental-Oceanic and Volcanoes form when the oceanic plate subducts and Mt. St. Helens, WA Oceanic-Oceanic melts Divergent (where plates move away from each other) Continental Rift Valleys Iceland, Eastern Africa Oceanic Mid ocean ridges making up a small seam of volcanoes Mid-Atlantic ridge Rocks and Minerals Rocks are made up of minerals. Minerals are naturally occurring crystalline solids. Minerals can be identified using a number of physical characteristics like: hardness, streak, crystal form, and cleavage. Hardness is measured by the relative hardness with established minerals that are on the Moh’s Hardness scale. Something that is harder will scratch something that’s softer. Diamonds are the hardest known minerals and will scratch all others, including other diamonds. Streak is the color of the powder left when the mineral is dragged along an unglazed tile. Different minerals have different characteristic streaks that may or may not be the same color as the mineral itself. There are 3 kinds of rock: igneous (formed by solidification of magma or lava), sedimentary (formed by the cementation of sediment), and metamorphic (formed when any existing rock is exposed to heat or pressure). Rocks are separated into the categories by the way that they are formed. Rocks can all change form as shown in the rock cycle diagam. Weather Air masses (big “chunks” of air) bring the characteristics of their source areas where they go. Air masses that form somewhere cold (Polar) bring cold air, those that form somewhere warm (Tropical) bring warm air. Air masses that form over water (marine) bring moist, humid air and those that form over land (continental) bring dry air. When air masses move, those with different temperatures form fronts (boundaries between different air masses). You name the front by the temperature of the pushing air mass cold front if cold air is moving in and warm front if warm air is moving in. The symbols for each front are shown below. The direction of the triangles or the semicircles point the direction of the movement of the front. Earth Science Unit Review Summary