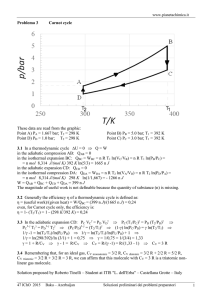
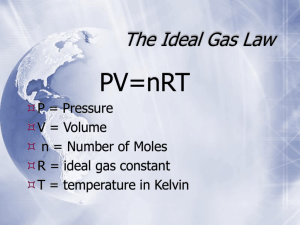
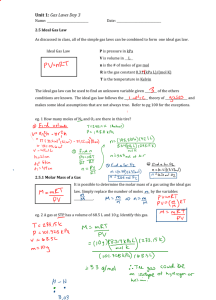
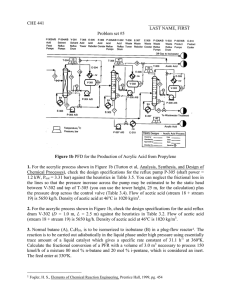
132 lol
advertisement

Constants R = 8.314 J/mol.K = 8.314 kPa.l/mol.K = 0.0821 atm.L/mol.K STP = standard temperature and pressure = 273.2 K and 101.3 kPa SATP = standard ambient temp. and press. = 298 K and 100.0 kPa For monatomic gasses : Cv= 3/2R ; Cp=5/2R cp - cv = R Equations for finding ΔU, ΔH, q and w • ΔU = q + w (special case ΔU = qv); ΔH = ΔU + ΔPV (special case ΔH =qp) For isothermal processes • w = -nRTln(V2/V1) = -nRTln(P1/P2) (reversible); w = -PextΔV (irreversible) For adiabatic processes T1V1γ-1 = T2V2γ-1 ; P1V1γ = P2V2γ where γ = cp/cv (reversible) Thermodynamics Δq=CΔT or Δq=CΔTm - per mole C=heat capacity – per gram C= specific heat ΔU=q+w U is the total internal energy of the system W=-Pext ΔV =nRT/Pext H=U+PV ΔHrxn = ∑ 𝐻𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑡𝑠 − ∑ 𝐻𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 ΔU=qv constant V ΔH=qp Constant P ΔH=ΔU+PΔV (at constant P) = qp=(nCpΔT) Solutions Partial pressures: Pressure of mixture = sum of partial pressures of each compound -- X=mole fraction, all X’s add up to 1. – P*=partial pressure Pa=XaPa* Ptotal=XaPa*+XbPb* = (Pb*-Pa*)Xb+Pa* 𝑃2 ΔHvap 𝑃1 R ln ( ) = − ( )( 1 T2 − 1 𝑇1 ) Somehow useful shit U = ncvΔT = w ; cp - cv = R ΔH = ΔU + ΔPV = ΔU + (P2V2 – P1V1); ΔH = ncpΔT Equations for finding ΔS ΔS =∫ qrev/T; ΔSvap = ΔHvap/Tb;Svap = 88 J/mol.K (Trouton’s rule) Entropy, Enthalpy and Free Energy Changes for Individual Substances ΔS = ncpln(T2/T1); ΔS = ncvln(T2/T1); ΔS = nRln(V2/V1) and ΔS = nRln(P1/P2) constant T ΔStot = ΔSsys + ΔSsur; ΔG = nRTln(P2/P1) Changes Occurring During Reactions ΔXreaction = Σ(s.c.)ΔXf(products) – Σ(s.c.)ΔXf(reactants) where X =H or G ΔSreaction = Σ(s.c.)S(products) – Σ(s.c.)S(reactants) ΔGosys = ΔHosys − ΤΔSosys ΔGsys = ΔGosys + RTlnQ ΔGosys = -RTlnK (at equilibrium) ln(K2/K1) = -(ΔHo/R)[1/T2 – 1/T1] (van’t Hoff equation) Equilibrium Review An+BnCn+Dn K=[C] n[D] n/[A] n[B] n Kp=Kc (RT) ∆ngas Isothermal = constant T Adiabatic = q=o (no heat enters or leaves the system) Isobaric = thermodynamic process with constant pressure Isochoric = constant volume