An advice and exercise program has some benefits over natural
advertisement

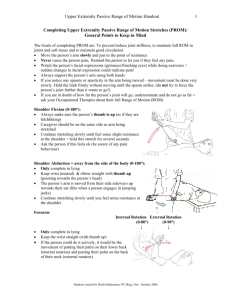
An advice and exercise program has some benefits over natural recovery after distal radius fracture: a randomised trial (Sandra Kay, Margaret McMahoon and Kathy Stiller, 2008) Purpose of study: the aim of this study was to see if physiotherapy interventions following distal radius fracture managed with pins or cast results in improved range of motion, strength, pain and activity. Method: RTC conducted, Randomised into an experimental group and control group. The experimental group received an advised exercise programme from a PT. The control group received nothing. Outcome measures were measured at 3 weeks, 6 weeks and 12 weeks. Therapist- rated outcome measures were collected by an experienced hand therapist who was blinded to group allocation. Patricipants: sample size of 24 for each group. Recruitment criteria: Removal of pins and or a cast following a DRF Excluded: - if unwilling to participate or unable to participate bilateral wrist fractures or concurrent fractures to the affected UL unable to understand English written or spoken had a previous wrist fracture on the same arm and loss of ROM and function had a ipsilateral limb injury pre-exisiting inflammatory joint condition or was managed with I.fixation or R.fixation Intervention: Standerdised advice on fracture protection swelling control and skin care, everyday activitys and exercise programme. Exercise programme was progressive and consisted of AROM shoulder, elbow, wrist and hand. Soft tissue stretches isometric stabilising wrist exercises and from week3, gentle forearm/wrist/hand strengthening exercises including grip. They were given a booklet of the exercises to take and use at home. They were also fitted with an elastic sleeve for swelling purposes and comfort. Control group had no intervention. Outcome Measures: Wrist extension Other ROM ex, and forearm, flexion, radial deviation and ulna, pronation, supination, opposition of the thumb, pain and activity limitations. ROM measured using a GONI. Thumb Opposistion measured using the thumb motion scale, and grip jamar dynamometer. Patient-rated wrist evaluation Questionnare. Quick dash Q UL Questionnare Results 56 patients randomly allocated into each group, one therapist from march 2004-October 2007 Common complications were finger stiffness and swelling in 15 participants and shoulder and neck pain and stiffness apparent in 9 people. Conclusion: This study found that a physiotherapist directed programme of advice and exercises resulted in significant benefits in activity, pain and satisfaction over natural recovery alone for patients following fractures involving the distal radius managed with pins and or cast. This study says that they recommend that patients routinely should be referred to a PT for instructions in advice and exercise programme to allow early detection of complications.