Homologous & Analogous
advertisement

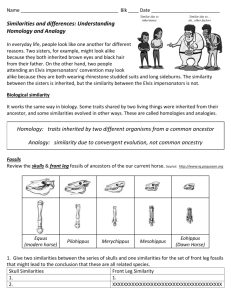
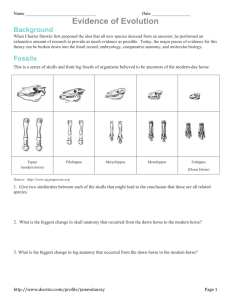
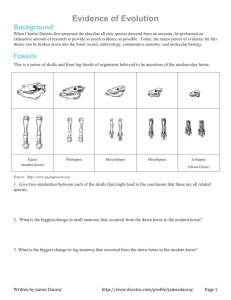
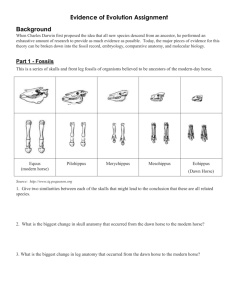
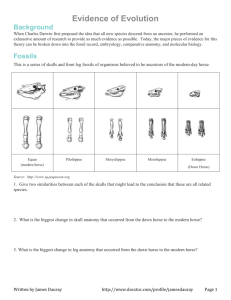
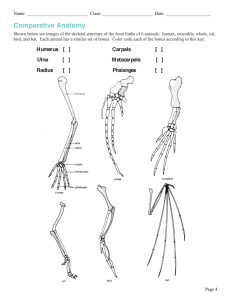
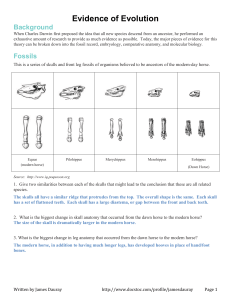
Name _____________________________________ Blk ____ Date __________________________ Similarities and differences: Understanding Homology and Analogy In everyday life, people look like one another for different reasons. Two sisters, for example, might look alike because they both inherited brown eyes and black hair from their father. On the other hand, two people attending an Elvis impersonators' convention may look alike because they are both wearing rhinestone studded suits and long sideburns. The similarity between the sisters is inherited, but the similarity between the Elvis impersonators is not. Biological similarity It works the same way in biology. Some traits shared by two living things were inherited from their ancestor, and some similarities evolved in other ways. These are called homologies and analogies. Homology: traits inherited by two different organisms from a common ancestor Analogy: similarity due to convergent evolution, not common ancestry Fossils Review the skulls & front leg fossils of ancestors of the our current horse. Source: Equus (modern horse) Pilohippus Merychippus Mesohippus http://www.iq.poquoson.org Eohippus (Dawn Horse) 1. Give two similarities between the series of skulls and one similarities for the set of front leg fossils that might lead to the conclusion that these are all related species. Skull Similarities Front Leg Similarity 1. 1. 2. XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX 2. What is the biggest change in the skull and leg of the horse’s anatomy that occurred from the dawn horse to the modern horse? __________________________________________________________________________________ Embryology Source: http://www.starlarvae.org Organisms that are closely related may also have physical similarities before they are even born! Take a look at the six different embryos: 3. Hypothesize which embryo above forms each of the following organisms and what clues did you for deciding: Species Human Chicken Rabbit Tortoise Salamander Fish Embryo Clues These are older, more developed embryos from the same organisms, in the same order. 4. Revisit your choices and determine which embryo forms each of the following organisms and tell any clues that helped you. Species Human Chicken Rabbit Tortoise Salamander Fish Embryo Clues These are embryos at their most advanced stage, shortly before birth. 5. Describe how the embryos changed for each of these organisms from their earliest to latest stages. Species Human Chicken Rabbit Tortoise Salamander Fish Anatomical Changes From Early to Late Stages Comparative Anatomy – Homologous Shown are images of the skeletal structure of the front limbs of 6 animals: human, crocodile, whale, cat, bird, and bat. Each animal has a similar set of bones. 6. Color code each of the bones according to this key: HUMERS RED CARPALS YELLOW ULNA BLUE METCARPALS ORANGE RADIUS GREEN PHALANGES PURPLE 7. For each animal, indicate what type of movement each limb is responsible for. Also, compare the skeletal structure of each limb to the human arm. Relate the differences you see in form to the differences in function. Animal Primary Functions Human Using tools, picking up and holding objects Whale Comparison to Human Arm Comparison to Human Arm in Form in Function XXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXX Whale has a much shorter The whale fin needs to be and thicker humerus, longer to help in movement radius, and ulna. Much through water. Thumbs are longer metacarpals. Thumb not necessary as the fins are has been shortened to a not used for grasping. stub. Cat Bat Bird Crocodile Comparative Anatomy – Analogous Shown are images of the structure of the different wings of: moth, pterodactyl, bird, and bat. Each animal has a similar use for their wings. Compare the anatomy of each of the wings. 8. What is the function of each of these structures? ______________________________________ 9. How are they different in structure? Give specific differences. __________________________________________________________________________________ Vestigial Structures - Compare the overall body structure of the cave fish and the minnow. 10. What is the biggest, most obvious difference between the body structures of these two fish? __________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Assume the two fish came from the same original ancestor. Why might the cave fish have evolved without eyesight? __________________________________________________________________________________ 12. What kind of sensory adaptation would you hypothesize the cave fish has to allow it to navigate in a cave, including catching and eating food? __________________________________________________________________________________ 13. Listed vestigial structures found in humans. Hypothesize what its function may have been. Structure Possible function? Wisdom teeth Appendix Muscles that moves the ear Muscles that stand up body hair Little toe Tailbone You have now studied three different types of relationships between organisms: Homologous structures show individual variations on a common anatomical theme. These are seen in organisms that are closely related. Typically same Structure, different Function. 14. Give an example of a homologous structure from this activity: __________________________ Analogous structures have very different anatomies but similar purposes. These are seen in organisms that are not necessarily closely related, but live in similar environments and have similar adaptations. Typically same Function, different Structure. 15. Give an example of an analogous structure from this activity: ___________________________ Vestigial structures are anatomical remnants that were important in the organism’s ancestors, but are no longer used in the same way. 16. Give an example of a vestigial structure from this activity: ______________________________